Healthc Inform Res.
2013 Jun;19(2):137-147. 10.4258/hir.2013.19.2.137.
Computational Approach for Protein Structure Prediction
- Affiliations
-
- 1Centre for Bioinformatics, Pondicherry University, Kalapet, Pondicherry, India. amouda@yahoo.com
- KMID: 2229495
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2013.19.2.137
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
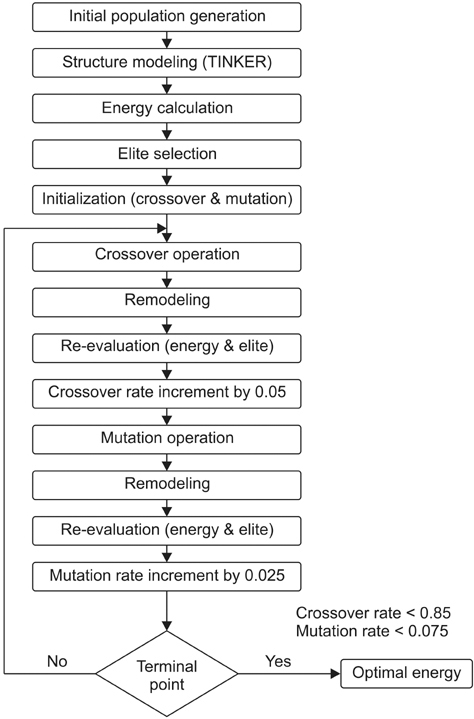
To predict the structure of protein, which dictates the function it performs, a newly designed algorithm is developed which blends the concept of self-organization and the genetic algorithm.
METHODS
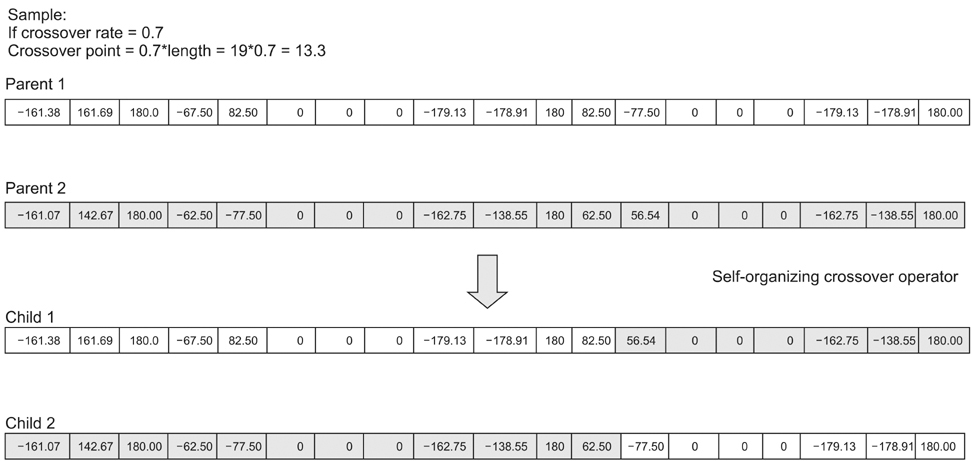
Among many other approaches, genetic algorithm is found to be a promising cooperative computational method to solve protein structure prediction in a reasonable time. To automate the right choice of parameter values the influence of self-organization is adopted to design a new genetic operator to optimize the process of prediction. Torsion angles, the local structural parameters which define the backbone of protein are considered to encode the chromosome that enhances the quality of the confirmation. Newly designed self-configured genetic operators are used to develop self-organizing genetic algorithm to facilitate the accurate structure prediction.
RESULTS
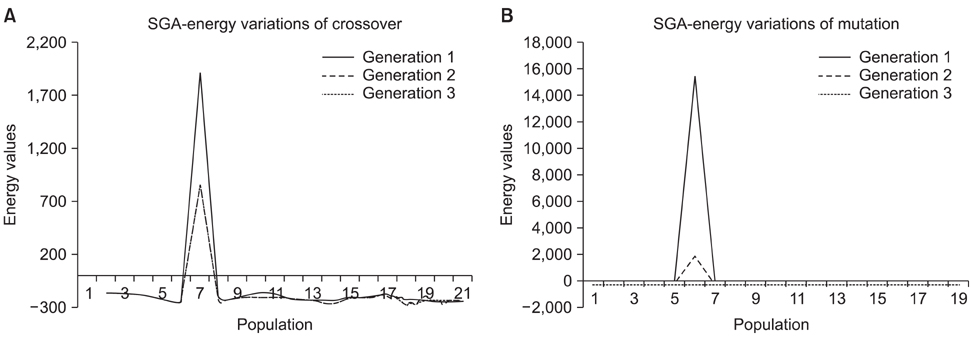
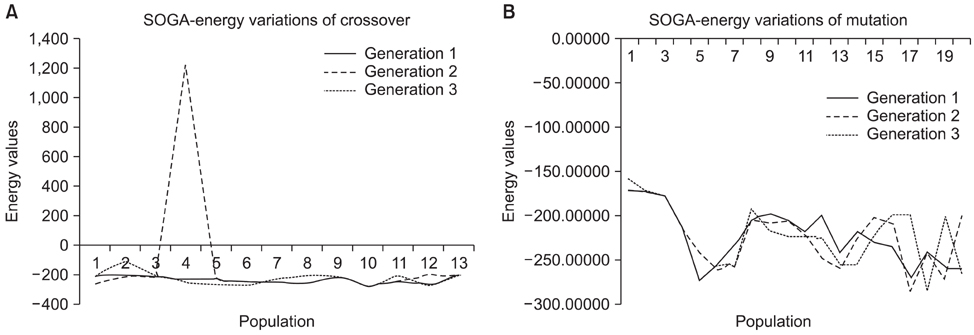
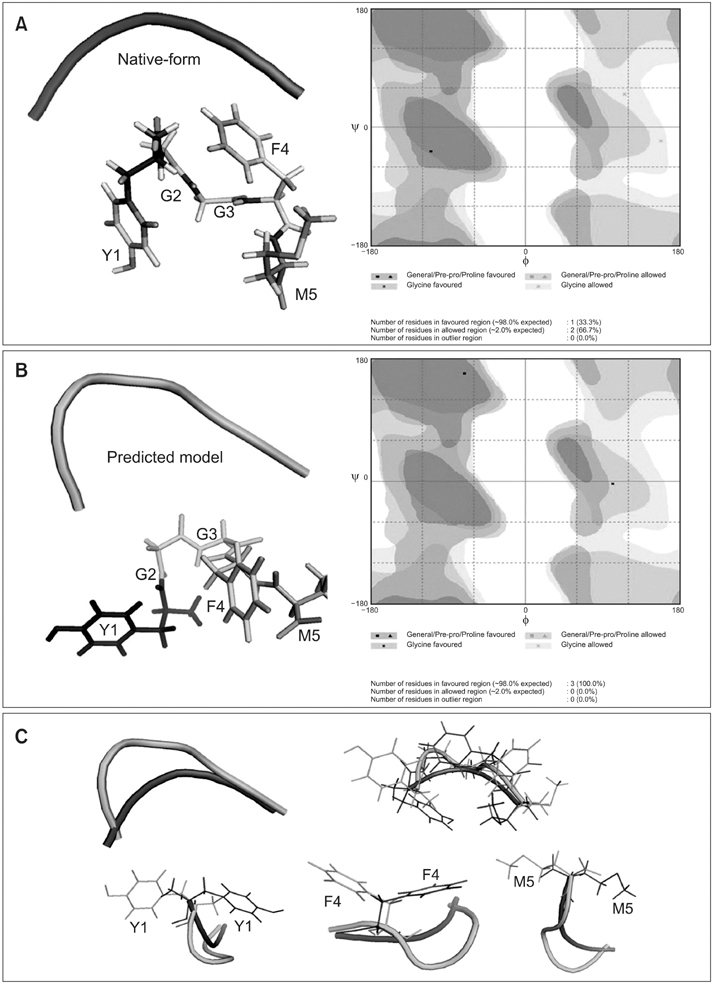
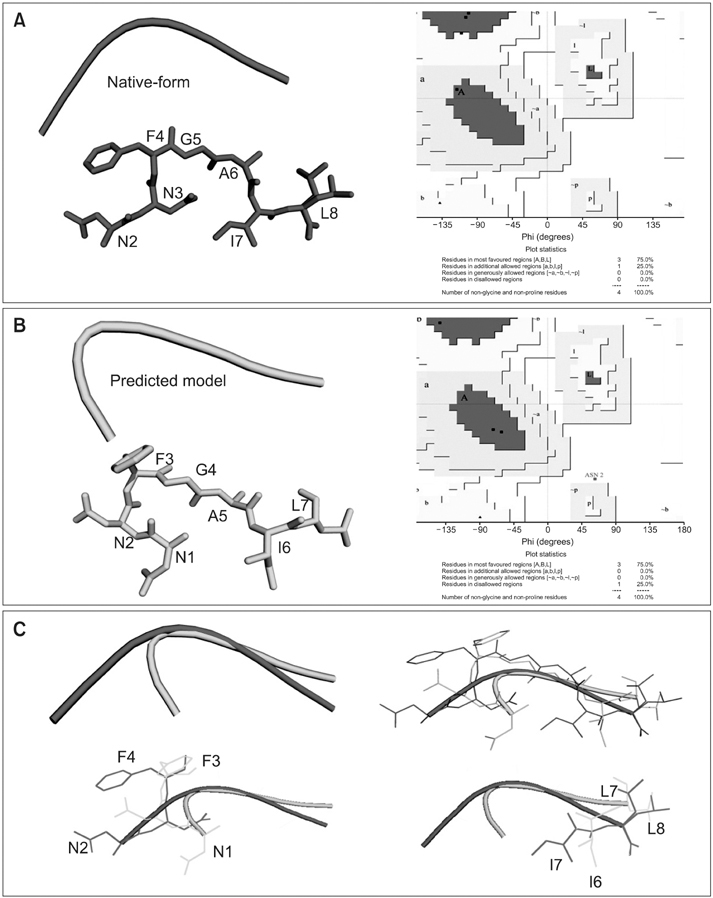
Peptides are used to gauge the validity of the proposed algorithm. As a result, the structure predicted shows clear improvements in the root mean square deviation on overlapping the native indicates the overall performance of the algorithm. In addition, the Ramachandran plot results implies that the conformations of phi-psi angles in the predicted structure are better as compared to native and also free from steric hindrances.
CONCLUSIONS
The proposed algorithm is promising which contributes to the prediction of a native-like structure by eliminating the time constraint and effort demand. In addition, the energy of the predicted structure is minimized to a greater extent, which proves the stability of protein.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pedersen JT, Moult J. Genetic algorithms for protein structure prediction. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1996; 6(2):227–231.
Article2. de Lima TW, Gabriel PH, Delbem AC, Faccioli RA, da Silva IN. Evolutionary algorithm to ab initio protein structure prediction with hydrophobic interactions. In : Proceedings of the IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation; 2007 Sep 25-28; Singapore. p. 612–619.3. Piccolboni A, Mauri G. Application of evolutionary algorithm to protein folding prediction. In : Hao JK, Lutton E, Ronald E, Schoenauer M, Snyers D, editors. Artificial Evolution. Heidelberg, Germany: Springer;1998. p. 123–135.4. Carnevali P, Toth G, Toubassi G, Meshkat SN. Fast protein structure prediction using monte carlo simulations with modal moves. J Am Chem Soc. 2003; 125(47):14244–14245.
Article5. Lee B, Kurochkina N, Kang HS. Protein folding by a biased Monte Carlo procedure in the dihedral angle space. FASEB J. 1996; 10(1):119–125.
Article6. Mandal S, Jana ND. Protein structure prediction using 2D HP lattice model based on integer programming approach. In : Proceedings of 2012 International Congress on Informatics, Environment, Energy and Applications; 2012 Mar 17-18; Singapore. p. 171–175.7. Benitez CM, Lopes HS. Protein structure prediction with the 3D-HP side-chain model using a master-slave parallel genetic algorithm. J Braz Comput Soc. 2010; 16(1):69–78.
Article8. Cui Y, Chen RS, Wong WH. Protein folding simulation with genetic algorithm and supersecondary structure constraints. Proteins. 1998; 31(3):247–257.
Article9. Zhang X, Wang T, Luo H, Yang JY, Deng Y, Tang J, et al. 3D protein structure prediction with genetic tabu search algorithm. BMC Syst Biol. 2010; 4:Suppl 1. S6.
Article10. Hoque MT, Chetty M, Sattar A. Genetic algorithm in ab initio protein structure prediction using low resolution model: a review. In : Sidhu AS, Dillon TS, editors. Biomedical data and applications. Heidelberg, Germany: Springer;2009. p. 317–342.11. Dandekar T, Argos P. Applying experimental data to protein fold prediction with the genetic algorithm. Protein Eng. 1997; 10(8):877–893.
Article12. Contreras-Moreira B, Fitzjohn PW, Offman M, Smith GR, Bates PA. Novel use of a genetic algorithm for protein structure prediction: searching template and sequence alignment space. Proteins. 2003; 53:Suppl 6. 424–429.
Article13. Goldberg DE. Genetic algorithms in search, optimization and machine learning. Reading (MA): Addison-Wesley Publishing Co.;1989.14. Kaiser CE, Merkle LD, Lamont GB, Gates GH Jr, Pachter R. Case studies in protein structure prediction with real-valued genetic algorithms. In : Proceedings of the 8th SIAM Conference on Parallel Processing for Scientific Computing; 1997 Mar 14-17; Minneapolis, MN.15. Day RO, Zydallis JB, Lamont GB, Pachter R. Solving the protein structure prediction problem through a multiobjective genetic algorithm. In : Proceeding of the International Conference on Computational Nanoscience and Nanotechnology; 2002 Apr 21-25; San Juan, Puerto Rico. p. 32–35.16. Deerman KR, Lamont GB, Pachter R. Linkage-learning genetic algorithm application to the protein structure prediction problem. In : Proceedings of the ACM Symposium on Applied Computing; 2001 Mar 11-14; Las Vegas, NV. p. 333–339.17. Schulze-Kremer S, Tiedemann U. Parameterizing genetic algorithms for protein folding simulation. In : Proceedings of the 27th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences; 1994 Jan 4-7; Wailea, HI. p. 345–354.18. Tragante-do-O V, Tinos R. A self-organizing genetic algorithm for protein structure prediction. Learn Nonlinear Model. 2010; 8(3):135–147.
Article19. Fogel GB, Corne DW. Evolutionary computation in bioinformatics. Boston (MA): Morgan Kaufmann Publishers;2003.20. Klepeis JL, Pieja MJ, Floudas CA. Hybrid global optimization algorithms for protein structure prediction: alternating hybrids. Biophys J. 2003; 84(2 Pt 1):869–882.
Article21. Accelrys Software Inc. Discovery Studio modeling environment, release 3.1. San Diego (CA): Accelrys Software Inc.;2012.22. Srinivasan R. Phi, psi distribution of amino-acids from 42 proteins [Internet]. Baltimore (MD): RoseLab, Johns Hopkins University;cited 2013 May 1. Available from: http://roselab.jhu.edu/~raj/Research/Linus/phipsi.html.23. Tuffery P, Etchebest C, Hazout S, Lavery R. A new approach to the rapid determination of protein side chain conformations. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1991; 8(6):1267–1289.
Article24. Thierens D. Adaptive mutation rate control schemes in genetic algorithms. In : Proceedings of the 2002 Congress on Evolutionary Computation; 2002 May 12-17; Honolulu, HI. p. 980–985.25. Bao-Juan H, Jian Z, De-Hong Y. A novel and accelerated genetic algorithm. WSEAS Trans Syst Control. 2008; 3(4):269–278.26. Breukelaar R, Back T. Self-adaptive mutation rates in genetic algorithm for inverse design of cellular automata. In : Proceedings of the 10th Annual Conference on Generic and Evolutionary Computation; 2008 Jul 12-16; Atlanta, GA. p. 1101–1102.27. Jay Ponder Lab. TINKER: software tools for molecular design (TINKER 3.9, June 2001) [Internet]. St. Louis (MO): Washington University;c2013. cited 2013 May 1. Available from: http://dasher.wustl.edu/tinker/.28. Rampage. Cambridge: Department of Biochemistry, University of Cambridge;cited 2013 May 1. Available from: http://mordred.bioc.cam.ac.uk/~rapper/rampage.php.29. Wiltzius JJ, Sievers SA, Sawaya MR, Cascio D, Popov D, Riekel C, et al. Atomic structure of the cross-β spine of islet amyloid polypeptide (amylin). Protein Sci. 2008; 17(9):1467–1474.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Computational approaches for molecular characterization and structure-based functional elucidation of a hypothetical protein from Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- Prediction of Drug–Drug Interactions by Using Profile Fingerprint Vectors and Protein Similarities
- Computational Neuroscience Approach to Psychiatry: A Review on Theory-driven Approaches
- Got target?: computational methods for microRNA target prediction and their extension
- Prediction of Metal Ion Binding Sites in Proteins from Amino Acid Sequences by Using Simplified Amino Acid Alphabets and Random Forest Model