Korean Circ J.
2012 Mar;42(3):192-196. 10.4070/kcj.2012.42.3.192.
B-Type Natriuretic Peptide Assay for the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Preterm Infants
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Anyang, Korea. baby4019@hallym.or.kr
- KMID: 2225033
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2012.42.3.192
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES
Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in preterm infants. Measurement of plasma B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) has been reported to be a useful bedside screening tool for the presence of hemodynamically significant PDA (hsPDA) in neonates. This study was conducted to investigate the usefulness of a BNP assay as a biochemical marker for the diagnosis of hsPDA and predictive biomarker of the response to indomethacin in preterm infants.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
Preterm infants born at <37 weeks' gestational age were prospectively enrolled within 24 hours of birth. Plasma BNP levels were measured on days 1, 4, and 7. Significant PDA was diagnosed by large ductal flow with left to right shunt on color Doppler echocardiography, along with clinical features of PDA. Following that, hsPDA was treated with indomethacin.
RESULTS
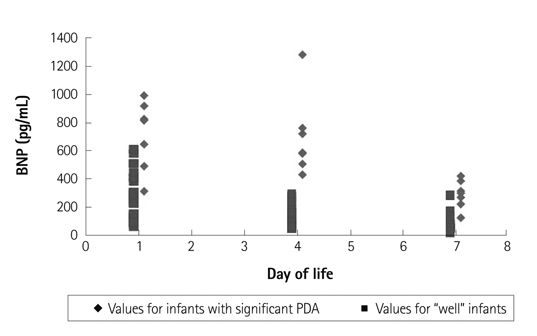
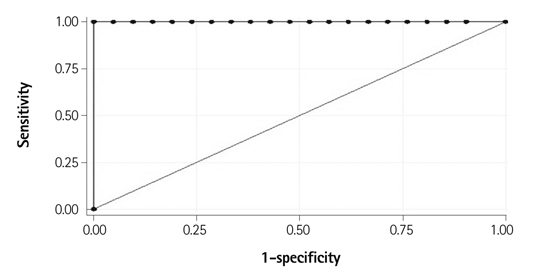
A total of 28 preterm infants were prospectively enrolled in this study. Seven infants with PDA had higher on day 4 plasma BNP values (median 654.68 pg/mL; range 428.29-1280.00) compared to the control group (median 124.52 pg/mL; range 37.21-290.49). The area under the receiver operator characteristic curve for the detection of hsPDA was high: 0.998 (95% confidence interval: 0.995-1.002). The cutoff of BNP concentration for the diagnosis of hsPDA was determined to be 412 pg/mL (sensitivity: 100%; specificity: 95%).
CONCLUSION
B-type natriuretic peptide can be a useful biomarker for the screening and diagnosis of PDA in preterm infants. Serial BNP measurements are valuable for assessing the clinical course and indomethacin responsiveness of PDA.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effectiveness of B-type Natriuretic Peptide in Caring for Preterm Infants
Narae Lee, Mi-hye Bae, Young-Mi Han, Kyung-Hee Park, Shin-Yun Byun
Perinatology. 2018;29(2):78-82. doi: 10.14734/PN.2018.29.02.78.
Reference
-
1. Bancalari E, Claure N, Gonzalez A. Patent ductus arteriosus and respiratory outcome in premature infants. Biol Neonate. 2005. 88:192–201.2. Clyman RI. Ductus arteriosus: current theories of prenatal and postnatal regulation. Semin Perinatol. 1987. 11:64–71.3. Heymann MA, Rudolf AM. Control of the ductus arteriosus. Physiol Rev. 1975. 55:62–78.4. Clyman RI. Mechanisms regulating the ductus arteriosus. Biol Neonate. 2006. 89:330–335.5. Rojas MA, Gonzalez A, Bancalari E, Claure N, Poole C, Silva-Neto G. Changing trends in the epidemiology and pathogenesis of neonatal chronic lung disease. J Pediatr. 1995. 126:605–610.6. Kluckow M, Evans N. Ductal shunting, high pulmonary blood flow, and pulmonary hemorrhage. J Pediatr. 2000. 137:68–72.7. Hammerman C. Patent ductus arteriosus: clinical relevance of prostaglandins and prostaglandin inhibitors in PDA pathophysiology and treatment. Clin Perinatol. 1995. 22:457–479.8. Cotton RB, Stahlman MT, Kovar I, Catterton WZ. Medical management of small preterm infants with symptomatic patent ductus arteriosus. J Pediatr. 1978. 92:467–473.9. Walther FJ, Benders MJ, Leighton JO. Persistent pulmonary hypertension in premature neonates with severe respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatrics. 1992. 90:899–904.10. Flynn PA, da Graca RL, Auld PA, Nesin M, Kleinman CS. The use of a bedside assay for plasma B-type natriuretic peptide as a biomarker in the management of patent ductus arteriosus in premature neonates. J Pediatr. 2005. 147:38–42.11. Holmström H, Hall C, Thaulow E. Plasma levels of natriuretic peptides and hemodynamic assessment of patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants. Acta Paediatr. 2001. 90:184–191.12. Daniels LB, Maisel AS. Natriuretic peptides. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007. 50:2357–2368.13. Cantinotti M, Clerico A, Murzi M, Vittorini S, Emdin M. Clinical relevance of measurement of brain natriuretic peptide and N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide in pediatric cardiology. Clin Chim Acta. 2008. 390:12–22.14. Reynolds EW, Ellington JG, Vranicar M, Bada HS. Brain-type natriuretic peptide in the diagnosis and management of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Pediatrics. 2004. 114:1297–1304. Erratum in: Pediatrics 2005;115:1454.15. Puddy VF, Amirmansour C, Williams AF, Singer DR. Plasma brain natriuretic peptide as a predictor of haemodynamically significant patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants. Clin Sci (Lond). 2002. 103:75–77.16. Attridge JT, Kaufman DA, Lim DS. B-type natriuretic peptide concentrations to guide treatment of patent ductus arteriosus. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2009. 94:F178–F182.17. Evans N. Diagnosis of patent ductus arteriosus in the preterm newborn. Arch Dis Child. 1993. 68(1 Spec No):58–61.18. Skelton R, Evans N, Smythe J. A blinded comparison of clinical and echochardiographic evaluation of the preterm infant for patent ductus arteriosus. J Paediatr Child Health. 1994. 30:406–411.19. Skinner J. Diagnosis of patent ductus arteriosus. Semin Neonatol. 2001. 6:49–61.20. Tammela O, Ojala R, Iivainen T, et al. Short versus prolonged indomethacin therapy for patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants. J Pediatr. 1999. 134:552–557.21. El Hajjar M, Vaksmann G, Rakza T, Kongolo G, Storme L. Severity of the ductal shunt: a comparison of different markers. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2005. 90:F419–F422.22. Young TE, Mangum B. Neofax: a Manual of Drugs Used in Neonatal Care. 2007. 20th ed. Montvale, NJ: Thompson Healthcare.23. Levin ER, Gardner DG, Samson WK. Natriuretic peptides. N Engl J Med. 1998. 339:321–328.24. Da Graca RL, Hassinger DC, Flynn PA, Sison CP, Nesin M, Auld PA. Longitudinal changes of brain-type natriuretic peptide in preterm neonates. Pediatrics. 2006. 117:2183–2189.25. Lee HS, Choi WS, Choi BM, et al. Usefulness of B-type natriuretic peptide assay in predicting symptomatic patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants. J Korean Soc Neonatol. 2004. 11:44–53.26. Choi BM, Lee KH, Eun BL, et al. Utility of rapid B-type natriuretic peptide assay for diagnosis of symptomatic patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants. Pediatrics. 2005. 115:e255–e261.27. Hsu JH, Yang SN, Chen HL, Tseng HI, Dai ZK, Wu JR. B-type natriuretic peptide predicts responses to indomethacin in premature neonates with patent ductus arteriosus. J Pediatr. 2010. 157:79–84.28. Tomaru Ki K, Arai M, Yokoyama T, et al. Transcriptional activation of the BNP gene by lipopolysaccharide is mediated through GATA elements in neonatal rat cardiac myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2002. 34:649–659.29. Ueda S, Nishio K, Akai Y, et al. Prognostic value of increased plasma levels of brain natriuretic peptide in patients with septic shock. Shock. 2006. 26:134–139.30. El-Khuffash A, Molloy EJ. Are B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and N-terminal-pro-BNP useful in neonates? Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2007. 92:F320–F324.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Applications of Plasma B-type Natriuretic Peptide Assays in Preterm Infants with Patent Ductus Arteriosus
- B-type natriuretic peptide may have a role in the management of patent ductus arteriosus
- Strategy of Dagnosis and Treatment for Hemodynamically Significant Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Preterm Infants
- Usefulness of Pasma Atrial Natriuretic Peptide Concentration in the Diagnosis of Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Preterm Infants
- Correlation of B-type natriuretic peptide levels and echocardiographic parameters in preterm infants with patent ductus arteriosus