Korean Circ J.
2012 Nov;42(11):781-783. 10.4070/kcj.2012.42.11.781.
A Silent and Late Embolization of Atrial Septal Defect Occluder Device Into the Right Pulmonary Artery: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Cardiology, Adana Numune Education and Research Hospital, Adana, Turkey. cardiology79@yahoo.com
- 2Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Adana Numune Education and Research Hospital, Adana, Turkey.
- KMID: 2224980
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2012.42.11.781
Abstract
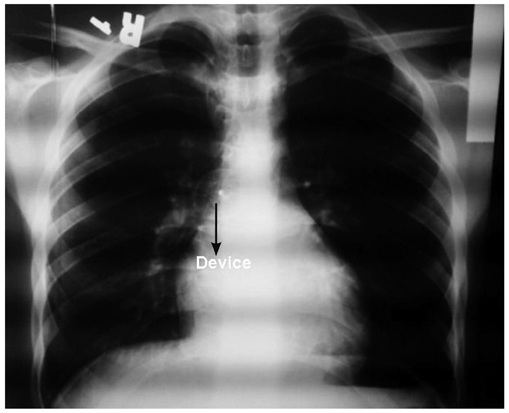
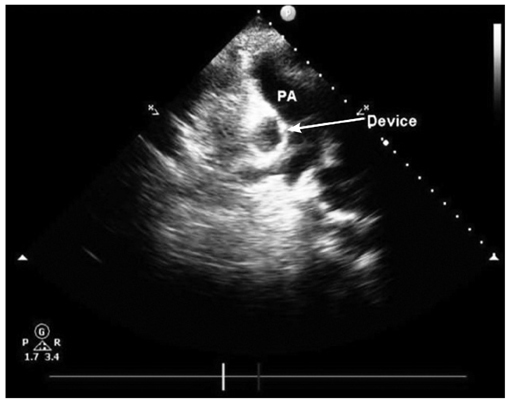
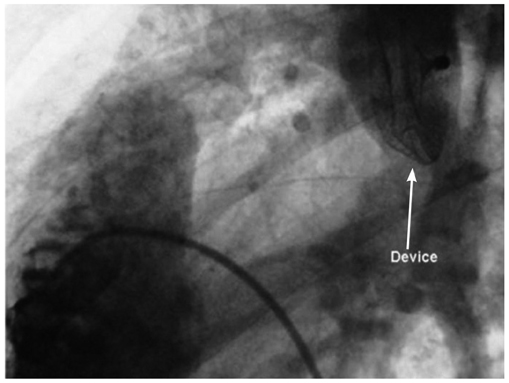
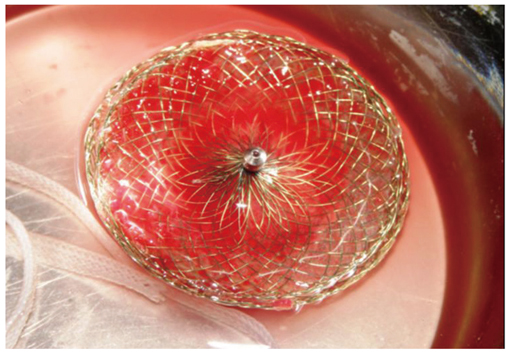
- Percutaneous device closure of atrial septal defect (ASD) is an alternative treatment to surgery. The main advantages of the percutaneous approach include avoidance of surgery, short procedure time and hospital length, in addition to comparable rates of complications. However, percutaneous device closure is associated with infrequent early and late complications including device embolization, air embolism, cardiac tamponade and thrombotic complications. We report a rare complication of silent and late device embolization of the ASD occluder device into the right pulmonary artery, three months after implantation.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Clark EB. Emmanouilides GC, Riemenschneider TA, Allen HD, editors. Epidemiology of congenital cardiovascular malformations. Heart disease infants, children, and adolescent including the fetus and young adult. 1995. 5th ed. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins;60–70.2. Misra M, Sadiq A, Namboodiri N, Karunakaran J. The 'aortic rim' recount: embolization of interatrial septal occluder into the main pulmonary artery bifurcation after atrial septal defect closure. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2007. 6:384–386.3. King TD, Mills NL. Nonoperative closure of atrial septal defects. Surgery. 1974. 75:383–388.4. Berdat PA, Chatterjee T, Pfammatter JP, Windecker S, Meier B, Carrel T. Surgical management of complications after transcatheter closure of an atrial septal defect or patent foramen ovale. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2000. 120:1034–1039.5. Hopkins RA, Bert AA, Buchholz B, Guarino K, Meyers M. Surgical patch closure of atrial septal defects. Ann Thorac Surg. 2004. 77:2144–2149.6. Butera G, Carminati M, Chessa M, et al. Percutaneous versus surgical closure of secundum atrial septal defect: comparison of early results and complications. Am Heart J. 2006. 151:228–234.7. Chessa M, Carminati M, Butera G, et al. Early and late complications associated with transcatheter occlusion of secundum atrial septal defect. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002. 39:1061–1065.8. Sinha A, Nanda NC, Khanna D, et al. Morphological assessment of left ventricular thrombus by live three-dimensional transthoracic echocardiography. Echocardiography. 2004. 21:649–655.9. Chiappini B, Gregorini R, Di Eusanio M, et al. Embolization of an Amplatzer atrial septal closure device to the pulmonary artery. J Card Surg. 2008. 23:164–167.10. Mashman WE, King SB, Jacobs WC, Ballard WL. Two cases of late embolization of Amplatzer septal occluder devices to the pulmonary artery following closure of secundum atrial septal defects. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2005. 65:588–592.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Subacute, Silent Embolization of Amplatzer Atrial Septal Defect Closure Device to the Pulmonary Artery
- The Operative Management of Embolized Septal Occluder at Ascending Aorta
- Surgical Extraction of an Embolized Atrial Septal Defect Occluder Device into Pulmonary Artery after Percutaneous Closure
- Amplatzer septal occluder found in the thoracic descending aorta by transesophageal echocardiography: A case report
- Late Migration of Amplatzer Septal Occluder Device to the Descending Thoracic Aorta