J Cardiovasc Ultrasound.
2012 Dec;20(4):201-204. 10.4250/jcu.2012.20.4.201.
Subacute, Silent Embolization of Amplatzer Atrial Septal Defect Closure Device to the Pulmonary Artery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Severance Cardiovascular Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University Medical Center, Daegu, Korea. pjs@med.yu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2177409
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4250/jcu.2012.20.4.201
Abstract
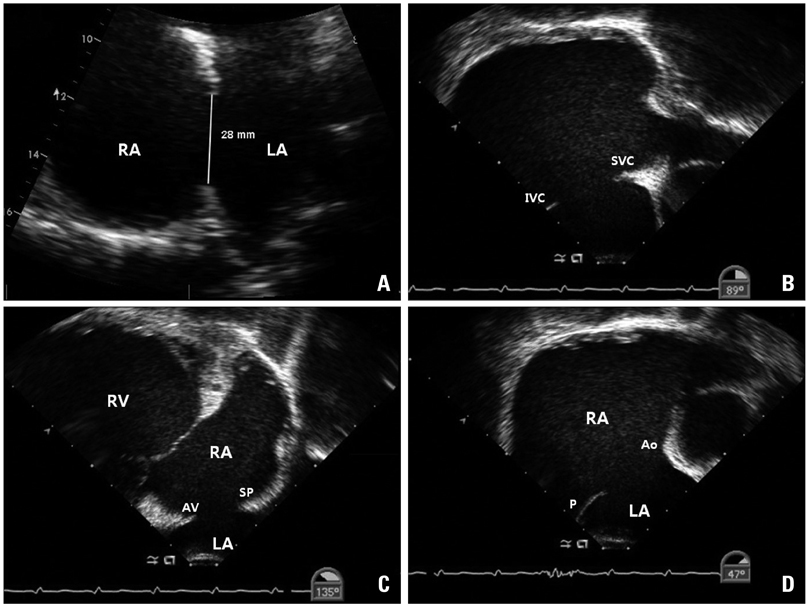
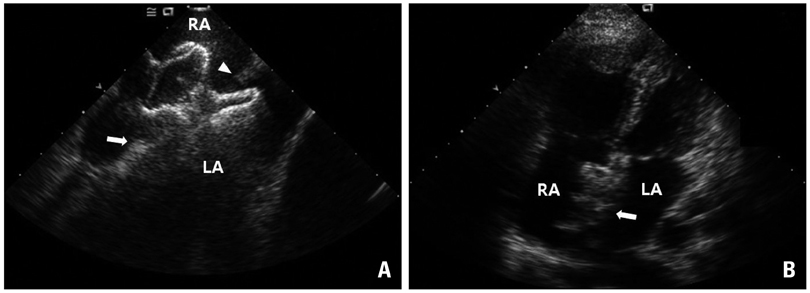
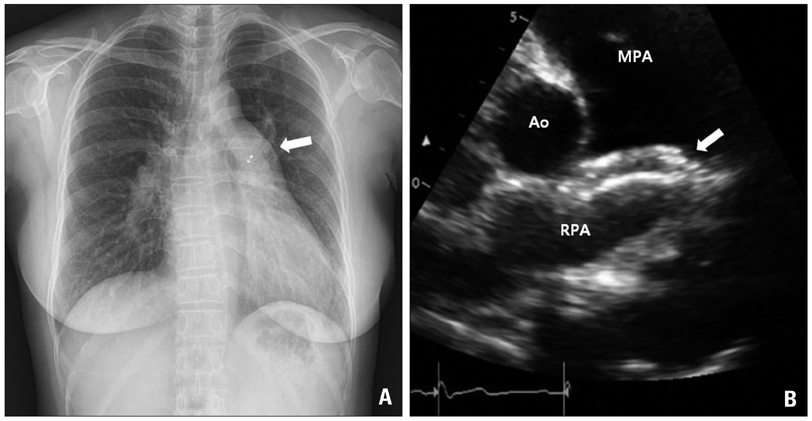
- Embolization of the closure device is a rare but potentially fatal complication of percutaneous atrial septal defect (ASD) closure. We report a case of 45-year-old woman who underwent ASD device closure with 32 mm Amplatzer device, which was embolized to the pulmonary artery without symptom one day after successful device implantation.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jo SS, Han SJ, Jung MJ, Lee SJ, Seol KH, Kim GH, Lee HS, Shin EK, Park IS, Kim SH. Transcatheter closure of atrial septal defect using amplatzer septal occluder. Korean Circ J. 2002. 32:17–24.
Article2. Chessa M, Carminati M, Butera G, Bini RM, Drago M, Rosti L, Giamberti A, Pomè G, Bossone E, Frigiola A. Early and late complications associated with transcatheter occlusion of secundum atrial septal defect. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002. 39:1061–1065.
Article3. King TD, Mills NL. Nonoperative closure of atrial septal defects. Surgery. 1974. 75:383–388.4. Majunke N, Bialkowski J, Wilson N, Szkutnik M, Kusa J, Baranowski A, Heinisch C, Ostermayer S, Wunderlich N, Sievert H. Closure of atrial septal defect with the Amplatzer septal occluder in adults. Am J Cardiol. 2009. 103:550–554.
Article5. Du ZD, Hijazi ZM, Kleinman CS, Silverman NH, Larntz K. Amplatzer Investigators. Comparison between transcatheter and surgical closure of secundum atrial septal defect in children and adults: results of a multicenter nonrandomized trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002. 39:1836–1844.
Article6. Levi DS, Moore JW. Embolization and retrieval of the Amplatzer septal occluder. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2004. 61:543–547.
Article7. Misra M, Sadiq A, Namboodiri N, Karunakaran J. The 'aortic rim' recount: embolization of interatrial septal occluder into the main pulmonary artery bifurcation after atrial septal defect closure. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2007. 6:384–386.
Article8. Braga SL, Sousa AG, Pedra CA, Esteves CA, Pedra SR, Fontes VF. {Clinical efficacy and safety of the percutaneous treatment of secundum atrial septal defect with the Amplatzer occluder}. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2004. 83 Spec No:7–13.9. Lin SM, Tsai SK, Wang JK, Han YY, Jean WH, Yeh YC. Supplementing transesophageal echocardiography with transthoracic echocardiography for monitoring transcatheter closure of atrial septal defects with attenuated anterior rim: a case series. Anesth Analg. 2003. 96:1584–1588.
Article10. Kijima Y, Taniguchi M, Akagi T, Nakagawa K, Kusano K, Ito H, Sano S. Torn atrial septum during transcatheter closure of atrial septal defect visualized by real-time three-dimensional transesophageal echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2010. 23:1222.e5–1222.e8.
Article11. Ko SF, Liang CD, Yip HK, Huang CC, Ng SH, Huang CF, Chen MC. Amplatzer septal occluder closure of atrial septal defect: evaluation of transthoracic echocardiography, cardiac CT, and transesophageal echocardiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009. 193:1522–1529.
Article12. Balbi M, Pongiglione G, Bezante GP. Percutaneous rescue of left ventricular embolized amplatzer septal occluder device. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2008. 72:559–562.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Silent and Late Embolization of Atrial Septal Defect Occluder Device Into the Right Pulmonary Artery: A Case Report
- Amplatzer septal occluder found in the thoracic descending aorta by transesophageal echocardiography: A case report
- Surgical Extraction of an Embolized Atrial Septal Defect Occluder Device into Pulmonary Artery after Percutaneous Closure
- Percutaneous Retrieval of Embolized Amplatzer Septal Occluder after Treatment of Double Atrial Septal Defect: A Case Report
- Transcatheter Closure of Secundum Atrial Septal Defect with the Amplatzer Septal Occluder