Korean Circ J.
2012 Nov;42(11):772-775. 10.4070/kcj.2012.42.11.772.
Pulmonary Arterial Thrombosis in a Patient With an Atrial Septal Defect and Eisenmenger Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Taipei Veterans General Hospital and National Yang-Ming University, Taipei, Taiwan. huangbsvgh@vghtpe.gov.tw
- KMID: 2224978
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2012.42.11.772
Abstract
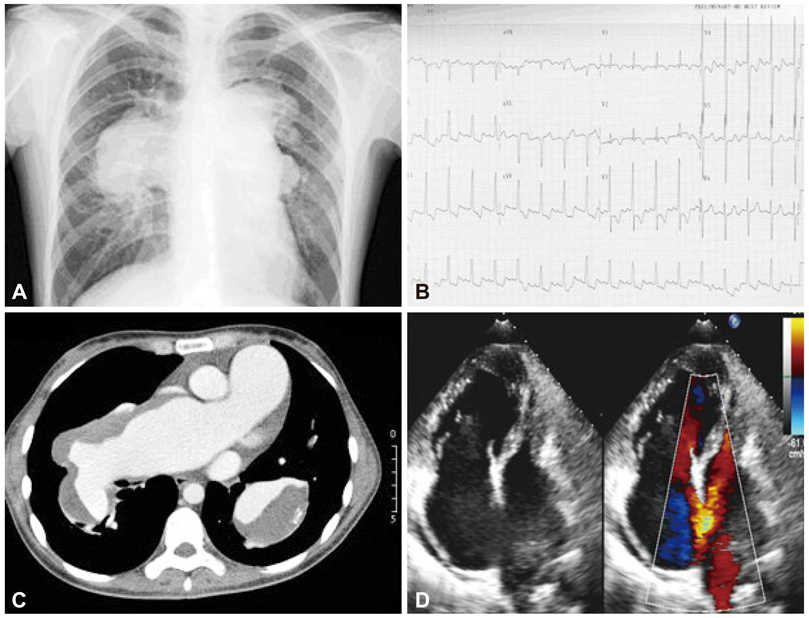
- Pulmonary hypertension is characterized by elevated pulmonary arterial pressure and secondary right ventricular failure. A thromboembolic occlusion of the proximal or distal pulmonary vasculature results in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. We report an uncommon case that presented to our hospital with symptoms of dyspnea on exertion over 2 years. The patient had been treated for profound pulmonary thrombosis and right ventricular failure with adequate anticoagulation and sildenafil. Our echocardiography disclosed a large atrial septal defect with severe pulmonary hypertension and right ventricular failure. A diagnosis of Eisenmenger syndrome with pulmonary artery thrombosis was made. Although Eisenmenger syndrome with pulmonary thrombosis is well described in western societies, a huge pulmonary thrombosis is seldom reported in eastern countries. Profound pulmonary thrombosis may obfuscate the actual diagnosis of pulmonary artery hypertension with underlying congenital heart disease. A physical examination and echocardiography are essential in patients with pulmonary hypertension.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hassell KL. Altered hemostasis in pulmonary hypertension. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1998. 9:107–117.2. Broberg CS, Ujita M, Prasad S, et al. Pulmonary arterial thrombosis in Eeisenmenger syndrome is associated with biventricular dysfunction and decreased pulmonary flow velocity. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007. 50:634–642.3. Silversides CK, Granton JT, Konen E, Hart MA, Webb GD, Therrien J. Pulmonary thrombosis in adults with Eisenmenger syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003. 42:1982–1987.4. Jensen AS, Iversen K, Vejlstrup NG, Sondergaard L. Images in cardiovascular medicine: pulmonary artery thrombosis and hemoptysis in Eisenmenger syndrome. Circulation. 2007. 115:e632–e634.5. Broberg C, Ujita M, Babu-Narayan S, et al. Massive pulmonary artery thrombosis with haemoptysis in adults with Eisenmenger's syndrome: a clinical dilemma. Heart. 2004. 90:e63.6. Piazza G, Goldhaber SZ. Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2011. 364:351–360.7. Moser KM, Fedullo PF, Finkbeiner WE, Golden J. Do patients with primary pulmonary hypertension develop extensive central thrombi? Circulation. 1995. 91:741–745.8. Niwa K, Perloff JK, Kaplan S, Child JS, Miner PD. Eisenmenger syndrome in adults: ventricular septal defect, truncus arteriosus, univentricular heart. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1999. 34:223–232.9. Niwa K, Perloff JK, Bhuta SM, et al. Structural abnormalities of great arterial walls in congenital heart disease: light and electron microscopic analyses. Circulation. 2001. 103:393–400.10. Lopes AA, Caramurú LH, Maeda NY. Endothelial dysfunction associated with chronic intravascular coagulation in secondary pulmonary hypertension. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2002. 8:353–358.11. Fuster V, Steele PM, Edwards WD, Gersh BJ, McGoon MD, Frye RL. Primary pulmonary hypertension: natural history and the importance of thrombosis. Circulation. 1984. 70:580–587.12. Rich S, Kaufmann E, Levy PS. The effect of high doses of calcium channel blockers on survival in primary pulmonary hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1992. 327:76–81.13. Beghetti M, Gallè N. Eisenmenger syndrome a clinical perspective in a new therapeutic era of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009. 53:733–740.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The effect of perioperative inhaled iloprost on congenital heart disease with severe pulmonary arterial hypertension
- Anesthetic Management for Elective Total Hip Replacement Arthoroplasty in a Patient with Eisenmenger's Syndrome
- Anesthetic Considerations Concerning VSD a Patient with Eisenmenger's Syndrome: A case report
- Atrial Septal Defect with Down Syndrome and Postsurgical Pulmonary Hypertension
- Noonan Syndrome with Double-Chambered Right Ventricle and Atrial Septal Defect: 1 Case Report