Korean Circ J.
2015 Sep;45(5):364-371. 10.4070/kcj.2015.45.5.364.
Elevation of the Serum Apurinic/Apyrimidinic Endonuclease 1/Redox Factor-1 in Coronary Artery Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Divison of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Chungnam National University Hospital, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. jojeong@cnu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Physiology, Chungnam National University Hospital, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 2223799
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2015.45.5.364
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES
Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1/redox effector factor-1 (APE1/Ref-1) is a multifunctional protein involved in the DNA base excision repair pathway, inflammation, angiogenesis, and survival pathways. We investigated serum APE1/Ref-1 in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD).
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
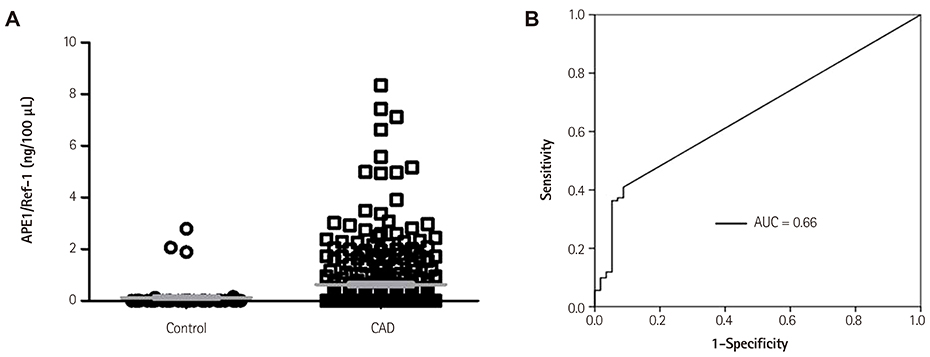
Serum APE1/Ref-1 was measured with a sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay from 360 patients who received coronary angiograms. They were divided into two groups; a control (n=57) and a CAD group (n=303), the latter included angina (n=128) and myocardial infarction (MI, n=175).
RESULTS
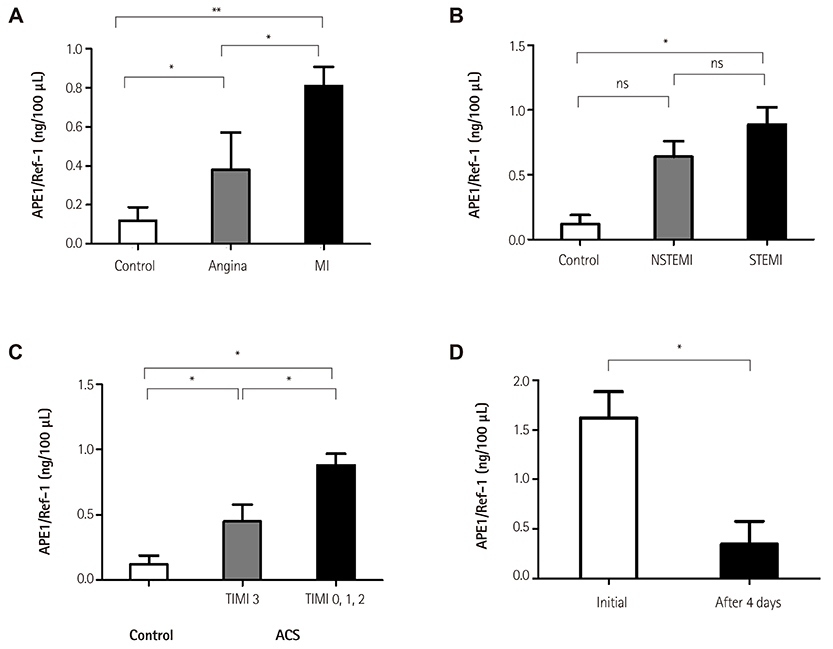
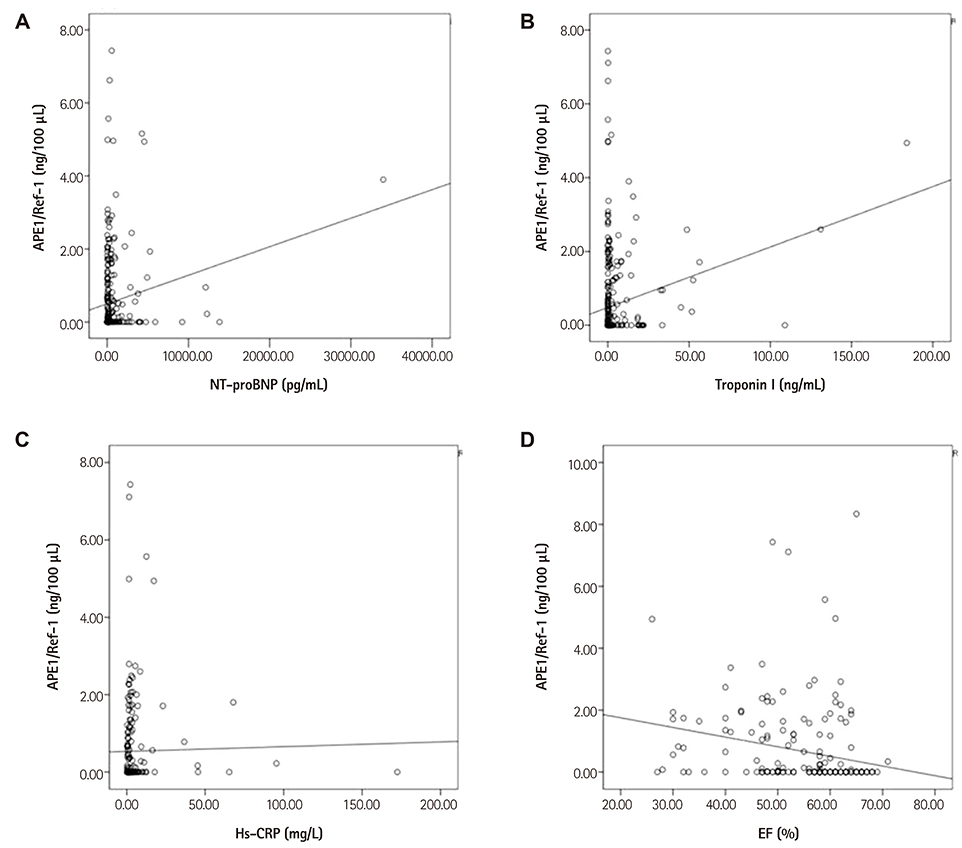
The levels of APE1/Ref-1 were higher in the CAD than the control (0.63+/-0.07 vs. 0.12+/-0.07 ng/100 microL, respectively; p<0.01). They were also higher in MI than angina (0.81+/-0.10 vs. 0.38+/-0.11 ng/100 microL, respectively; p<0.01) and different according to the thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (TIMI) flow (0.88+/-0.09 for TIMI flow 0, 1, 2 vs. 0.45+/-0.13 ng/100 microL for TIMI flow 3, p<0.01) in acute coronary syndrome. In correlation analysis, the levels of APE1/Ref-1 were positively correlated with Troponin I (r=0.222; p<0.0001) and N-terminal pro-B type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP, r=0.217; p<0.0001) but not high sensitivity to C-reactive protein. Also, they revealed a negative correlation with ejection fraction (EF, r=-0.221; p=0.002). However, there were no significant differences among the three groups, were divided by their levels of APE1/Ref-1, for major adverse cardiovascular events (death, recurrent MI, stroke, revascularization) (8.2 vs. 14.0 vs. 12.5%, p=ns).
CONCLUSION
The levels of serum APE1/Ref-1 are elevated in CAD, and are higher in MI than in angina. They are correlated with Troponin I, NT-proBNP, and EF.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Dynamic Regulation of APE1/Ref-1 as a Therapeutic Target Protein
Sunga Choi, Hee Kyoung Joo, Byeong Hwa Jeon
Chonnam Med J. 2016;52(2):75-80. doi: 10.4068/cmj.2016.52.2.75.
Reference
-
1. Kim HC. Clinical utility of novel biomarkers in the prediction of coronary heart disease. Korean Circ J. 2012; 42:223–228.2. Vasan RS. Biomarkers of cardiovascular disease: molecular basis and practical considerations. Circulation. 2006; 113:2335–2362.3. Tell G, Quadrifoglio F, Tiribelli C, Kelley MR. The many functions of APE1/Ref-1: not only a DNA repair enzyme. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2009; 11:601–620.4. Thakur S, Sarkar B, Cholia RP, Gautam N, Dhiman M, Mantha AK. APE1/Ref-1 as an emerging therapeutic target for various human diseases: phytochemical modulation of its functions. Exp Mol Med. 2014; 46:e106.5. Naganuma T, Nakayama T, Sato N, et al. Haplotype-based case-control study on human apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1/redox effector factor-1 gene and essential hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2010; 23:186–191.6. Zhang Y, Wang J, Wang D, Xin X. Alterations in the expression of the apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease-1/redox factor-1 (APE1/Ref-1) in human ovarian cancer and indentification of the therapeutic potential of APE1/Ref-1 inhibitor. Int J Oncol. 2009; 35:1069–1079.7. Botto N, Rizza A, Colombo MG, et al. Evidence for DNA damage in patients with coronary artery disease. Mutat Res. 2001; 493:23–30.8. Mahmoudi M, Mercer J, Bennett M. DNA damage and repair in atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Res. 2006; 71:259–268.9. Martinet W, Knaapen MW, De Meyer GR, Herman AG, Kockx MM. Elevated levels of oxidative DNA damage and DNA repair enzymes in human atherosclerotic plaques. Circulation. 2002; 106:927–932.10. Jeon BH, Gupta G, Park YC, et al. Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 regulates endothelial NO production and vascular tone. Circ Res. 2004; 95:902–910.11. Patterson C. Blood pressure control goes nuclear. Circ Res. 2004; 95:849–851.12. Song SH, Cho EJ, Park MS, et al. Redox regulating protein APE1/Ref-1 expression is increased in abdominal aortic coarctation-induced hypertension rats. J Korean Soc Hypertens. 2012; 18:126–135.13. Park MS, Lee YR, Choi S, et al. Identification of plasma APE1/Ref-1 in lipopolysaccharide-induced endotoxemic rats: implication of serological biomarker for an endotoxemia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013; 435:621–626.14. Choi S, Lee YR, Park MS, et al. Histone deacetylases inhibitor trichostatin A modulates the extracellular release of APE1/Ref-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013; 435:403–407.15. Dai N, Cao XJ, Li MX, et al. Serum APE1 autoantibodies: a novel potential tumor marker and predictor of chemotherapeutic efficacy in non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e58001.16. Shin JH, Choi S, Lee YR, et al. APE1/Ref-1 as a serological biomarker for the detection of bladder cancer. Cancer Res Treat. 2015; 01. 02. DOI: 10.4143/crt.2014.074. [Epub].17. Tell G, Damante G, Caldwell D, Kelley MR. The intracellular localization of APE1/Ref-1: more than a passive phenomenon? Antioxid Redox Signal. 2005; 7:367–384.18. Evans AR, Limp-Foster M, Kelley MR. Going APE over ref-1. Mutat Res. 2000; 461:83–108.19. Pines A, Perrone L, Bivi N, et al. Activation of APE1/Ref-1 is dependent on reactive oxygen species generated after purinergic receptor stimulation by ATP. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005; 33:4379–4394.20. Vasko MR, Guo C, Kelley MR. The multifunctional DNA repair/redox enzyme Ape1/Ref-1 promotes survival of neurons after oxidative stress. DNA Repair (Amst). 2005; 4:367–379.21. Wang D, Luo M, Kelley MR. Human apurinic endonuclease 1 (APE1) expression and prognostic significance in osteosarcoma: enhanced sensitivity of osteosarcoma to DNA damaging agents using silencing RNA APE1 expression inhibition. Mol Cancer Ther. 2004; 3:679–686.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Dynamic Regulation of APE1/Ref-1 as a Therapeutic Target Protein
- Altered Secretory Activity of APE1/Ref-1 D148E Variants Identified in Human Patients With Bladder Cancer
- APE1/Ref-1 as a Serological Biomarker for the Detection of Bladder Cancer
- Studies on rat liver nuclear DNA damaged by chemical carcinogen (3'-Me DAB) and AP DNA endonuclease. I. Purification and some properties of AP DNA endonucleases in rat liver chromatin
- Alteration of Apurinic/Apyrimidinic Endonuclease-1/Redox Factor-1 in Human Non-small Cell Lung Cancer