J Rheum Dis.
2011 Sep;18(3):212-215. 10.4078/jrd.2011.18.3.212.
A Case of Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in a Patient with Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with Adalimumab
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Ulsan University Hospital, College of Medicine, University of Ulsan, Ulsan, Korea. choisw@uuh.ulsan.kr
- KMID: 2223153
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2011.18.3.212
Abstract
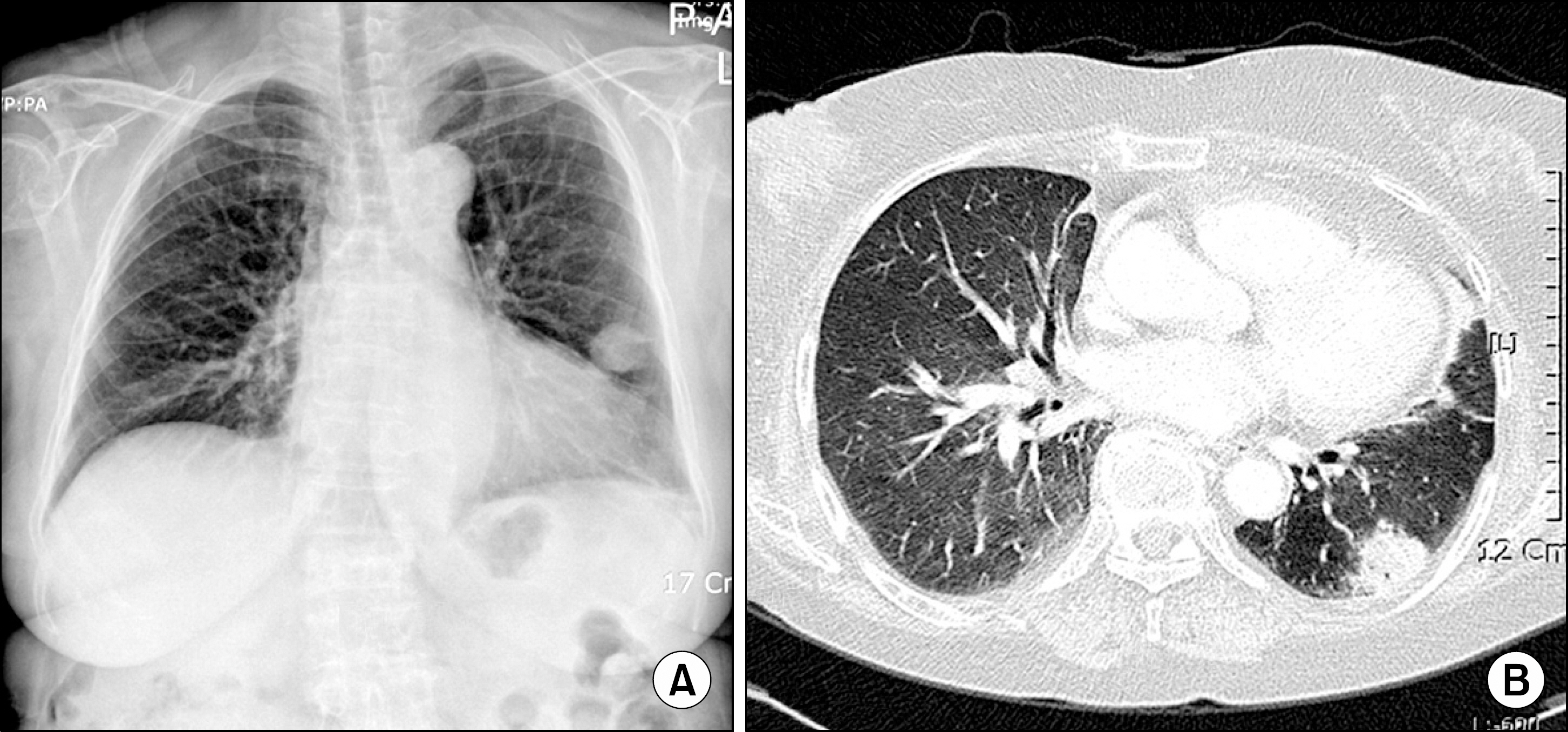
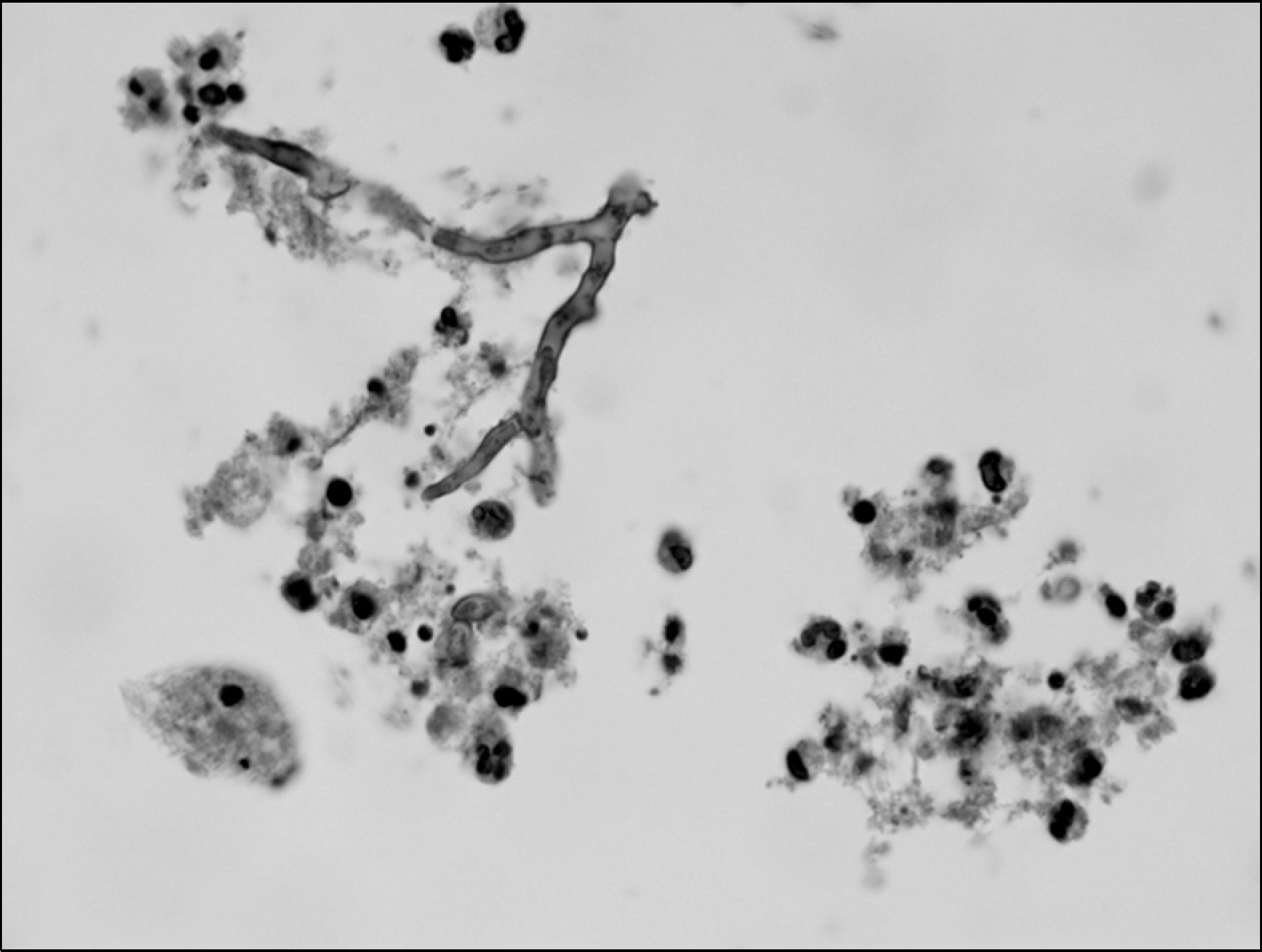
- We describe a fatal case of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis receiving the TNF-alpha inhibitor, adalimumab. The use of TNF-alpha inhibitor has been associated with an increased risk of infections, including tuberculosis and other opportunistic infections. Physicians should have a high index of suspicion for opportunistic infection that can develop during TNF-alpha inhibitor treatment.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Crum NF, Lederman ER, Wallace MR. Infections associated with tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonists. Medicine (Baltimore). 2005; 84:291–302.2. Giles JT, Bathon JM. Serious infections associated with anticytokine therapies in the rheumatic diseases. J Intensive Care Med. 2004; 19:320–34.
Article3. Rychly DJ, DiPiro JT. Infections associated with tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonists. Pharmacotherapy. 2005; 25:1181–92.4. Tsiodras S, Samonis G, Boumpas DT, Kontoyiannis DP. Fungal infections complicating tumor necrosis factor alpha blockade therapy. Mayo Clin Proc. 2008; 83:181–94.5. Bakleh M, Tleyjeh I, Matteson EL, Osmon DR, Berbari EF. Infectious complications of tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonists. Int J Dermatol. 2005; 44:443–8.6. Yi SM, Lim MJ, Kwon SR, Jeong JC, Lee JS, Kwon SH, et al. A case of cryptococcal pneumonia in a rheumatoid arthritis patient after tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonist therapy. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2007; 14:412–6.
Article7. Lee KS, Lee HY, Lee SW, Jung HJ, Song JS. A case of candida bursitis associated with etanercept treatment in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2008; 15:175–9.
Article8. Lee EJ, Song R, Park JN, Lee YA, Son JS, Hong SJ, et al. Chronic necrotizing pulmonary aspergillosis in a patient treated with a tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitor. Int J Rheum Dis. 2010; 13:e16–9.9. Listing J, Strangfeld A, Kary S, Rau R, von Hinueber U, Stoyanova-Scholz M, et al. Infections in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with biologic agents. Arthritis Rheum. 2005; 52:3403–12.
Article10. Burmester GR, Mariette X, Montecucco C, Monteagudo-Sáez I, Malaise M, Tzioufas AG, et al. Adalimumab alone and in combination with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in clinical practice: the Research in Active Rheumatoid Arthritis (ReAct) trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007; 66:732–9.
Article11. Kim HO, Kang KY, Ju JH, Kim HY, Park SH. The incidence of serious infection among rheumatoid arthritis patients exposed to tumor necrosis factor antagonists. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2010; 17:246–53.
Article12. Soubani AO, Chandrasekar PH. The clinical spectrum of pulmonary aspergillosis. Chest. 2002; 121:1988–99.
Article13. Warris A, Bj⊘rneklett A, Gaustad P. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis associated with infliximab therapy. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344:1099–100.
Article14. Winthrop KL. Risk and prevention of tuberculosis and other serious opportunistic infections associated with the inhibition of tumor necrosis factor. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2006; 2:602–10.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Development of Rheumatoid Nodules after Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Treatment with Adalimumab for Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage after Adalimumab Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- New-onset Psoriasis Induced by Adalimumab Administered for Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Adalimumab-induced Lupus Erythematosus Profundus in a Rheumatoid Arthritis Patient
- Adalimumab Induced Acute Exacerbation of Rheumatoid Arthritis Related Interstitial Lung Disease