J Rheum Dis.
2014 Aug;21(4):196-200. 10.4078/jrd.2014.21.4.196.
Delayed and Long-term Remission of Refractory Hemolytic Anemia in a Child with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Treated with Rituximab
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea. jsoh@uuh.ulsan.kr
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea.
- KMID: 2222961
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2014.21.4.196
Abstract
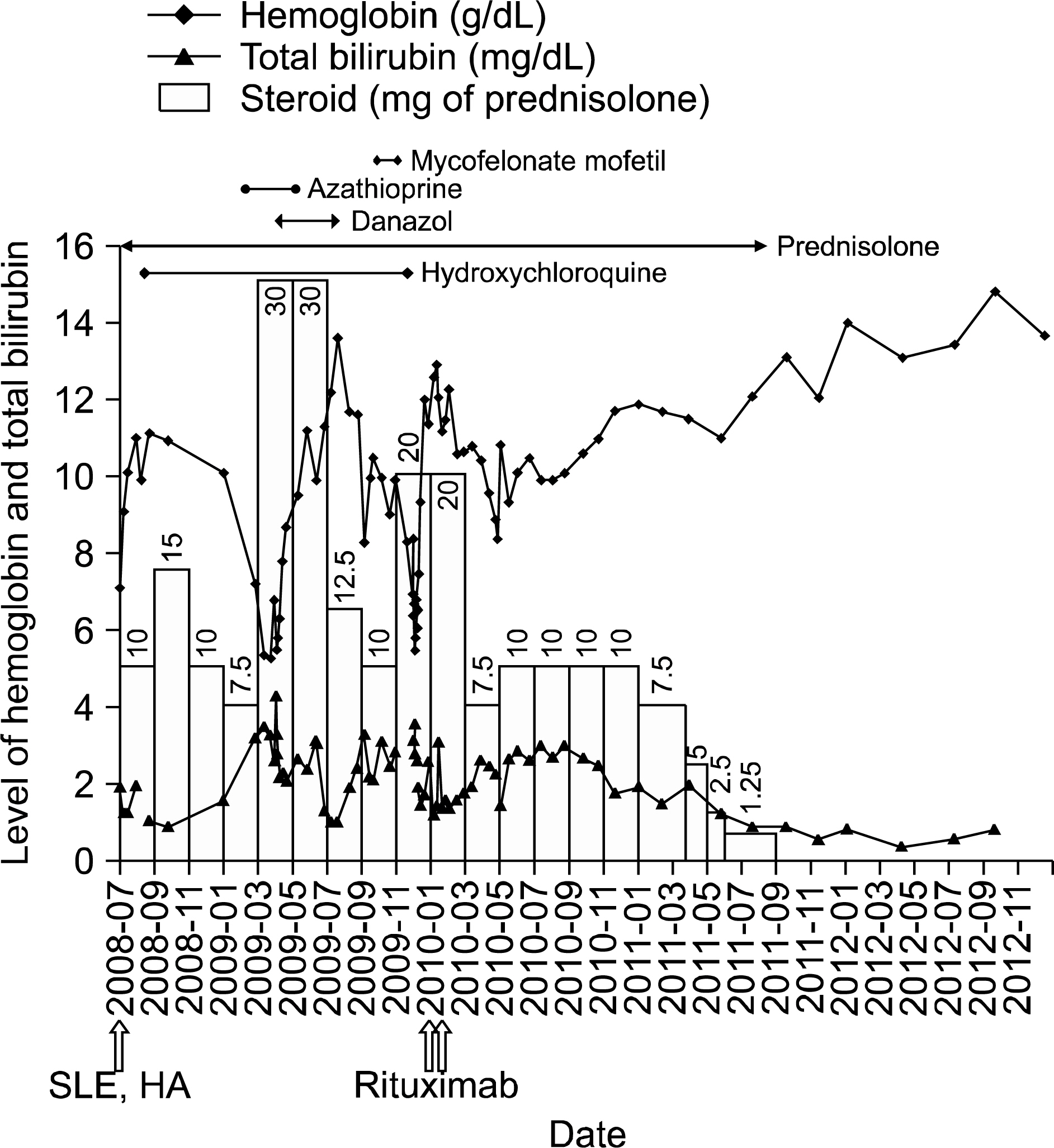
- Autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA) is a relatively common cause of anemia in children and adults with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Although AIHA responds to steroids, in case of refractory or steroid-dependent AIHA, immunosuppressants and intravenous immunoglobulin have been used as second line agents. Rituximab, an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, is emerging in the treatment of SLE refractory to conventional therapy. Herein, we report a case of delayed and sustained remission of refractory hemolytic anemia in a child with SLE, post rituximab treatment. A 12-year-old female child with dizziness was referred to our department and was diagnosed with SLE combined with hemolytic anemia and renal tubular acidosis. Since frequent relapse of hemolytic anemia had occurred during the steroid tapering course, even though she had been treated with additional immunosuppressants (azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil), the patient received 2 doses of rituximab 500 mg at 2 weeks interval at 18 months post diagnosis. After 15 months of rituximab administration, her anemia and renal tubular acidosis were fully recovered, enough to stop all medications. She remained well without recurrence for up to 3 years and 4 months after rituximab treatment.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee SG, Yoo B, Kim KM, Choi HO, Oh JS, Nah SS, et al. Successful Treatment of Neuropsychiatric Syndrome with Rituximab in a Patient with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Dermatomyositis Overlap Syndrome. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2008; 15:170–4.
Article2. Wang SW, Cheng TT. Systemic lupus erythematosus with refractory hemolytic anemia effectively treated with cyclosporin A: a case report. Lupus. 2005; 14:483–5.3. Tokunaga M, Saito K, Nakatsuka K, Nakayamada S, Nakano K, Tsujimura S, et al. Successful treatment of intravenous cyclophosphamide pulse therapy for systemic lupus erythematosus complicated with steroid-resistant hemolytic anemia. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2003; 26:304–9.
Article4. Sarles HE, Levin WC. The role of splenectomy in the management of acquired autoimmune hemolytic anemia complicating systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med. 1959; 26:547–54.
Article5. Hwang KW, Ahn YS, Moon JY, Kim IY, Park YE, Kim GT, et al. Experience of Rituximab Treatment in Two Patients with Severe Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2006; 13:230–5.6. Reff ME, Carner K, Chambers KS, Chinn PC, Leonard JE, Raab R, et al. Depletion of B cells in vivo by a chimeric mouse human monoclonal antibody to CD20. Blood. 1994; 83:435–45.
Article7. Leandro MJ, Cambridge G, Edwards JC, Ehrenstein MR, Isenberg DA. B-cell depletion in the treatment of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a longitudinal analysis of 24 patients. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005; 44:1542–5.
Article8. Looney RJ, Anolik JH, Campbell D, Felgar RE, Young F, Arend LJ, et al. B cell depletion as a novel treatment for systemic lupus erythematosus: a phase I/II dose-esca-lation trial of rituximab. Arthritis Rheum. 2004; 50:2580–9.
Article9. Leandro MJ, Edwards JC, Cambridge G, Ehrenstein MR, Isenberg DA. An open study of B lymphocyte depletion in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2002; 46:2673–7.
Article10. Bussone G, Ribeiro E, Dechartres A, Viallard JF, Bonnotte B, Fain O, et al. Efficacy and safety of rituximab in adults' warm antibody autoimmune haemolytic anemia: retrospective analysis of 27 cases. Am J Hematol. 2009; 84:153–7.
Article11. Dierickx D, Verhoef G, Van Hoof A, Mineur P, Roest A, Triffet A, et al. Rituximab in autoimmune haemolytic anaemia and immune thrombocytopenic purpura: a Belgian retrospective multicentric study. J Intern Med. 2009; 266:484–91.
Article12. Kumar S, Benseler SM, Kirby-Allen M, Silverman ED. B-cell depletion for autoimmune thrombocytopenia and autoimmune hemolytic anemia in pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Pediatrics. 2009; 123:e159–63.
Article13. Oh HJ, Yun MJ, Lee ST, Lee SJ, Oh SY, Sohn I. Evans syndrome following longstanding Hashimoto's thyroiditis and successful treatment with rituximab. Korean J Hematol. 2011; 46:279–82.
Article14. Park CY, Chung CH. A patient with mixed type Evans syndrome: efficacy of rituximab treatment. J Korean Med Sci. 2006; 21:1115–6.
Article15. Lee JH, Lee KS. A Case of Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia Treated with Rituximab in a Child. Korean J Hematol. 2006; 41:321–5.
Article16. Smith KG, Jones RB, Burns SM, Jayne DR. Long-term comparison of rituximab treatment for refractory systemic lupus erythematosus and vasculitis: Remission, relapse, and retreatment. Arthritis Rheum. 2006; 54:2970–82.
Article17. Ng KP, Cambridge G, Leandro MJ, Edwards JC, Ehrenstein M, Isenberg DA. B cell depletion therapy in systemic lupus erythematosus: long-term follow-up and predictors of response. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007; 66:1259–62.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia Associated with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- A Case of Successful Danazol Therapy in Autoimmune Thrombocytopenia Associated with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- A Case of Rituximab Therapy in Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Refractory to Steroid Pulse Therapy
- A 22-month-old Boy with Acute Glomerulonephritis Coexistent with Hemolytic Anemia and Idiopathic Thrombocytopenia
- Cold haemagglutinin disease in systemic lupus erythematosus