Korean Diabetes J.
2010 Jun;34(3):182-190. 10.4093/kdj.2010.34.3.182.
Association between Obesity and Physical Fitness, and Hemoglobin A1c Level and Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Adults
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Sport and Leisure Studies, Yonsei University College of Education, Seoul, Korea. jjeon@yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Department of Family Medicine, Myongji Hospital, Kwandong University School of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- 3Department of Nursing, Yonsei University College of Nursing, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Physical Education, Yonsei University College of Education, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2222374
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2010.34.3.182
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The purpose of the current study was to investigate the association of obesity level, physical fitness level, hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) level and metabolic syndrome (MetS) risk factors among Korean adults.
METHODS
A total of 557 adults (272 males and 285 females) who underwent medical check-up at local hospital were recruited. In addition to regular health check-up, cardiopulmonary fitness, muscular endurance were measured and their association were analyzed.
RESULTS
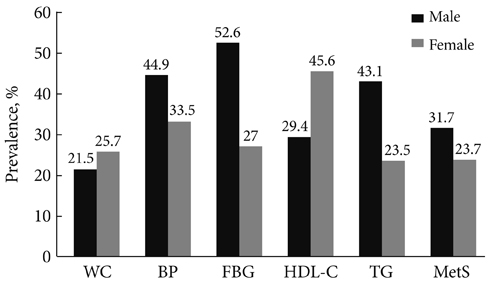
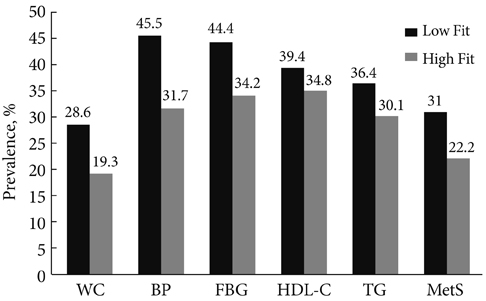
The prevalence of MetS was 31.7% for males and 23.7% for females. Females with the higher muscular endurance had lower waist circumference, triglyceride level, and HbA1c level than those with the lower muscular endurance. Males with the higher level of cardiopulmonary fitness had lower diastolic blood pressure, lower high-sensitivity C-reactive protein level and higher high density lipoprotein cholesterol level than males with the lower level of cardiopulmonary fitness. Females with the higher level of cardiopulmonary fitness had lower body weight, body mass index, systolic blood pressure, and fasting blood glucose level than females with the lower level of cardiopulmonary fitness. Participants with the higher level of adiposity and the lower level of physical fitness were 5.26 times (95% confidence interval [CI], 2.19 to 12.62), 5.71 times (95% CI, 2.23 to 14.60) more likely to have MetS, respectively, in male and female compared to participants who were neither obese nor have the lower level of fitness.
CONCLUSION
This study suggests that maintaining a healthy body weight as well as a certain level of fitness is important for the prevention of MetS.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adiposity
Adult
Blood Glucose
Blood Pressure
Body Mass Index
Body Weight
C-Reactive Protein
Cholesterol
Cholesterol, HDL
Fasting
Female
Hemoglobins
Humans
Hypotension
Lipoproteins
Male
Obesity
Physical Fitness
Prevalence
Risk Factors
Waist Circumference
Blood Glucose
C-Reactive Protein
Cholesterol
Cholesterol, HDL
Hemoglobins
Lipoproteins
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Epidemiology of Physical Activity Participation and Type 2 Diabetes in Korea
Yoonsuk Jekal, Justin Y Jeon
J Korean Diabetes. 2011;12(1):13-20. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2011.12.1.13.
Reference
-
1. Ministry of Health and Welfare, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The Third Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES III), 2005. 2006. Seoul: Ministry of Health and Welfare.2. Arnlov J, Ingelsson E, Sundstrom J, Lind L. Impact of body mass index and the metabolic syndrome on the risk of cardiovascular disease and death in middle-aged men. Circulation. 2010. 121:230–236.3. Aschner P. Metabolic syndrome as a risk factor for diabetes. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2010. 8:407–412.4. Jekal Y, Kim ES, Im JA, Park JH, Lee MK, Lee SH, Suh SH, Chu SH, Kang ES, Lee HC, Jeon JY. Interaction between fatness and fitness on CVD risk factors in Asian youth. Int J Sports Med. 2009. 30:733–740.5. Lee CD, Blair SN, Jackson AS. Cardiorespiratory fitness, body composition, and all-cause and cardiovascular disease mortality in men. Am J Clin Nutr. 1999. 69:373–380.6. Wessel TR, Arant CB, Olson MB, Johnson BD, Reis SE, Sharaf BL, Shaw LJ, Handberg E, Sopko G, Kelsey SF, Pepine CJ, Merz NB. Relationship of physical fitness vs body mass index with coronary artery disease and cardiovascular events in women. JAMA. 2004. 292:1179–1187.7. Carnethon MR, Gulati M, Greenland P. Prevalence and cardiovascular disease correlates of low cardiorespiratory fitness in adolescents and adults. JAMA. 2005. 294:2981–2988.8. Wei M, Kampert JB, Barlow CE, Nichaman MZ, Gibbons LW, Paffenbarger RS Jr, Blair SN. Relationship between low cardiorespiratory fitness and mortality in normal-weight, overweight, and obese men. JAMA. 1999. 282:1547–1553.9. Gordon BA, Benson AC, Bird SR, Fraser SF. Resistance training improves metabolic health in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2009. 83:157–175.10. Lee DC, Koh MY, Kim YS, Gang HJ. Correlation between cardiorespiratory fitness measured by step test and Hba1C, blood pressure and blood lipids in type II diabetic patients. Korean J Sport Sci. 2006. 17:28–36.11. National Cholesterol Education Program/National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute/National Institute of Health. Third report of the Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). 2002. Bethesda: National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute/National Institute of Health.12. Tan CE, Ma S, Wai D, Chew SK, Tai ES. Can we apply the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel definition of the metabolic syndrome to Asians? Diabetes Care. 2004. 27:1182–1186.13. Jekal Y, Lee MK, Kim ES, Park JH, Lee HJ, Han SJ, Kang ES, Lee HC, Kim SH, Jeon JY. Effects of walking and physical activity on glucose regulation among type 2 diabetics. Korean Diabetes J. 2008. 32:60–67.14. Church TS, Cheng YJ, Earnest CP, Barlow CE, Gibbons LW, Priest EL, Blair SN. Exercise capacity and body composition as predictors of mortality among men with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004. 27:83–88.15. Church TS, LaMonte MJ, Barlow CE, Blair SN. Cardiorespiratory fitness and body mass index as predictors of cardiovascular disease mortality among men with diabetes. Arch Intern Med. 2005. 165:2114–2120.16. McAuley PA, Myers JN, Abella JP, Tan SY, Froelicher VF. Exercise capacity and body mass as predictors of mortality among male veterans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2007. 30:1539–1543.17. Jee SH, Sull JW, Park J, Lee SY, Ohrr H, Guallar E, Samet JM. Body-mass index and mortality in Korean men and women. N Engl J Med. 2006. 355:779–787.18. Katzmarzyk PT, Church TS, Janssen I, Ross R, Blair SN. Metabolic syndrome, obesity, and mortality: impact of cardiorespiratory fitness. Diabetes Care. 2005. 28:391–397.19. Sui X, Hooker SP, Lee IM, Church TS, Colabianchi N, Lee CD, Blair SN. A prospective study of cardiorespiratory fitness and risk of type 2 diabetes in women. Diabetes Care. 2008. 31:550–555.20. Adams GM. Exercise physiology laboratory manual. 1990. Boston: WCB/McGraw-Hill.21. Montoye HJ. Physical activity and health: an epidemiologic study of an entire community. 1975. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Halls.22. Chen CN, Chuang LM, Wu YT. Clinical measures of physical fitness predict insulin resistance in people at risk for diabetes. Phys Ther. 2008. 88:1355–1364.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Relative Importance of Fitness and Fatness in Obesity Intervention
- Relationship between Hemoglobin A1c Levels and Metabolic Syndrome using Data Collected during a Medical Check-ups Program
- The Relationship Between Fitness, BMI and Risk Factors of Metabolic Syndrome Among University Students in Korea
- Letter: Association between Exercise and Metabolic Syndrome in Koreans (J Obes Metab Syndr 2018;27:117-24)
- How Does Obesity and Physical Activity Affect Aging?: Focused on Telomere as a Biomarker of Aging