J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2014 Sep;55(9):1355-1360. 10.3341/jkos.2014.55.9.1355.
The Effect of One Myopic Eye on Visual Field Testing
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Dankook University Medical College, Cheonan, Korea. Changmh@dankook.ac.kr
- KMID: 2217120
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2014.55.9.1355
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To investigate the effect of lens-corrected myopia on Humphrey Matrix and Humphrey Field Analyser (HFA).
METHODS
A total of 59 lens-corrected myopic eyes of 59 normal volunteers underwent Humphrey Field Analyser and Humphrey Matrix (FDP) testing. Spherical equivalent divided into 3 groups: -3 < or = D < 0, -6 < or = D < -3, D < -6. HFA and FDP sensitivity for mean deviation (MD) and pattern standard deviation (PSD), as well as axial length and astigmatism, were compared between these 3 groups.
RESULTS
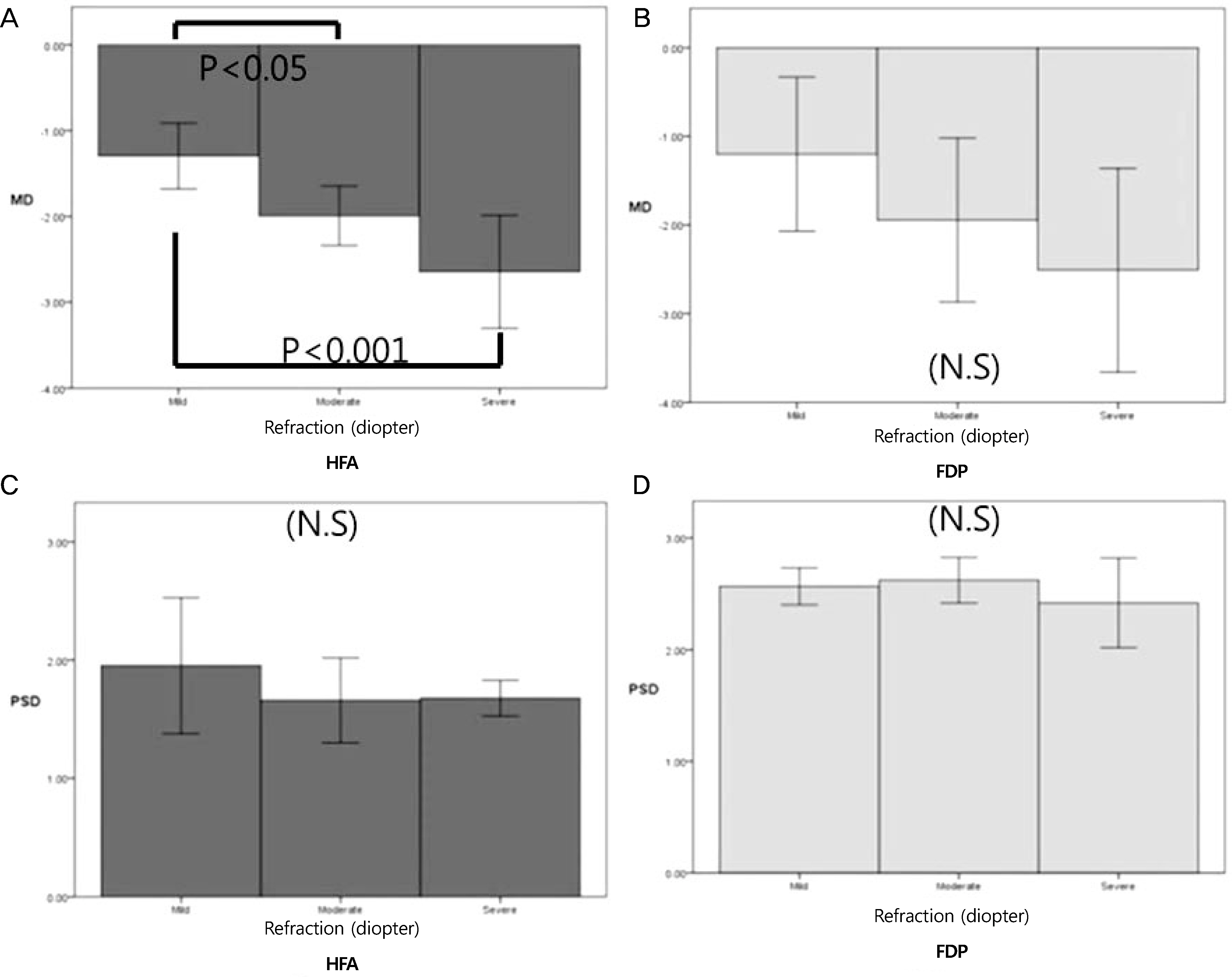
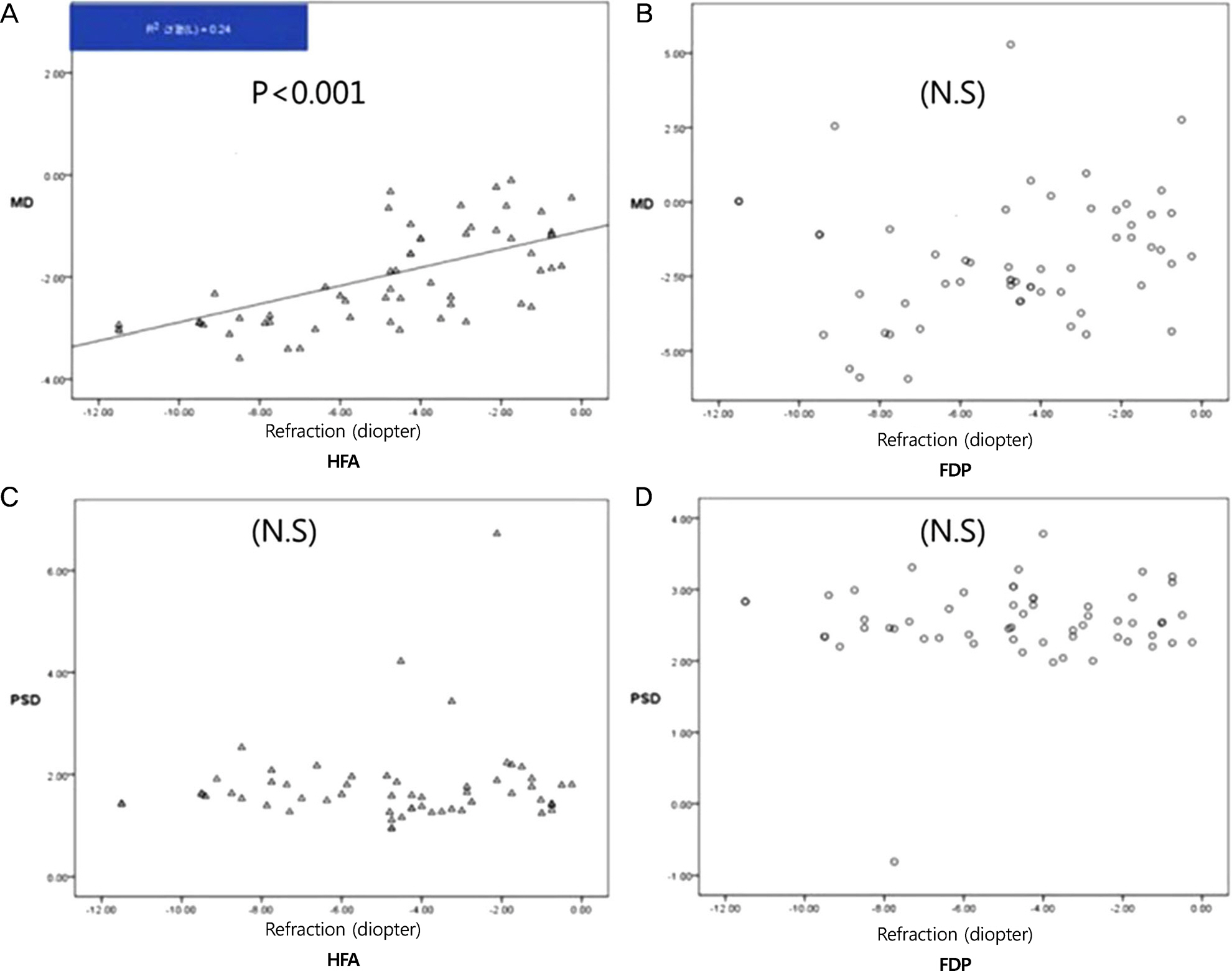
The MD of the fields as determined by the HFA decreased significantly as the refractive errors increased, despite correction. However, there were no significant differences in MD or PSD of FDP, or in the PSD of HFA. There were no significant differences in axial length or astigmatism as calculated by MD and PSD for HFA and FDP.
CONCLUSIONS
The spherical equivalent showed that lens correction alters the MD for HFA but not for FDP.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Jung SK, Lee JH, Kakizaki H, Jee D. Prevalence of myopia and its association with body stature and educational level in 19-year-old male conscripts in seoul, South Korea. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012; 53:5579–83.
Article2. Lee JH, Jee D, Kwon JW, Lee WK. Prevalence and risk factors for myopia in a rural Korean population. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013; 54:5466–71.
Article3. Aung T, Foster PJ, Seah SK, et al. Automated static perimetry: the influence of myopia and its method of correction. Ophthalmology. 2001; 108:290–5.
Article4. Mitchell P, Hourihan F Sand, bach J, Wang JJ. The relationship between glaucoma and myopia: the Blue Mountains Eye Study. Ophthalmology. 1999; 106:2010–5.5. Marcus MW, de Vries MM, Junoy Montolio FG, Jansonius NM. Myopia as a risk factor for open-angle glaucoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology. 2011; 118:1989–94.e2.
Article6. David R, Zangwill LM, Tessler Z, Yassur Y. The correlation between intraocular pressure and refractive status. Arch Ophthalmol. 1985; 103:1812–5.
Article7. Rudnicka AR, Edgar DF. Automated static perimetry in myopes with peripapillary crescents–Part II. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 1996; 16:416–29.
Article8. Kawabata H, Fujimoto N, Adachi-Usami E. [Sensitivity loss of short wavelength sensitive cones in myopic eyes by blue-on-yellow perimetry]. Nihon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 1997; 101:648–55.9. Anand A, De Moraes CG, Teng CC, et al. Short-duration transient visual evoked potential for objective measurement of refractive errors. Doc Ophthalmol. 2011; 123:141–7.
Article10. Kawabata H, Adachi-Usami E. Multifocal electroretinogram in myopia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1997; 38:2844–51.11. Johnson CA, Adams AJ, Casson EJ, Brandt JD. Blue-on-yellow perimetry can predict the development of glaucomatous visual field loss. Arch Ophthalmol. 1993; 111:645–50.
Article12. Kim JH, Kee C. The effect of myopic optical defocus on the humphrey matrix 30-2 test. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2008; 49:119–24.
Article13. Cheon HC, Jeung WJ, Rho SH. The comparison of the matrix perimetry and humphrey standard perimetry in various patients group. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007; 48:678–85.14. Anderson AJ, Johnson CA. Frequency-doubling technology perimetry and optical defocus. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003; 44:4147–52.
Article15. Tay E, Seah SK, Chan SP, et al. Optic disk ovality as an index of tilt and its relationship to myopia and perimetry. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005; 139:247–52.
Article16. Yoshii T, Matsuura T, Yukawa E, Hara Y. Effects of astigmatism on the Humphrey Matrix perimeter. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2009; 19:425–8.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of Myopic Optical Defocus on the Humphrey Matrix 30-2 Test
- OCTOPUS Program G1 in Normlid Subjects
- The Influence of Miotics on Visual Field in Glaucoma
- A Case of High Myopic Astigmatism Corrected with a Toric Intraocular Lens
- Acute Transient Myopic Shift in a Patient With Fever of Unknown Origin: A Case Report