J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2013 Mar;54(3):437-442. 10.3341/jkos.2013.54.3.437.
Relationship between Cataract Maturation and Pain Scale during Cataract Surgery under Topical Anesthesia
- Affiliations
-
- 1The Institute of Vision Research, Department of Ophthalmology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. tikim@yuhs.ac
- 2Siloam Eye Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2216763
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2013.54.3.437
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To investigate the relationship between maturity of a cataract and the pattern of pain during cataract surgery under topical anesthesia.
METHODS
This study comprised 105 eyes of 75 patients undergoing cataract surgery under topical anesthesia. The pain scale during each procedure was scored from 0 to 10 in numeric pattern and analyzed with the cataract maturation degree. Additionally, pain scores were compared between the first and the second eye in 14 consecutive cataract patients.
RESULTS
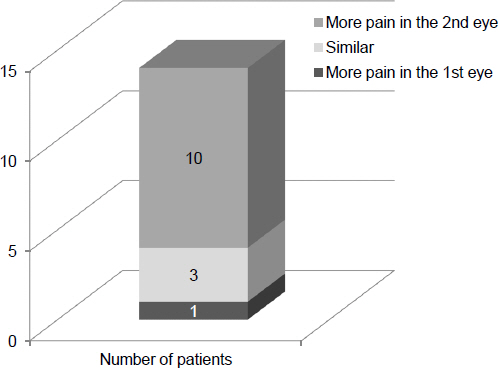
The average pain score during cataract surgery was 0.86 +/- 0.55, and the average maximal pain experience score during surgery was 3.24 +/- 1.51, which was generally tolerable. Phacoemulsification was marked as the most painful step among cataract surgery procedures (1.93 +/- 1.64), followed by the removal of the surgical draping (1.31 +/- 1.53) and the initial instillation of topical anesthetic (1.29 +/- 1.28). Progression and cataract typing was not related to pain either during overall cataract surgery procedures or when separately analyzed during procedures. There was no significant difference between the pain scores reported in consecutive cataract surgeries. However, in subjective comparison of consecutive surgeries, more patients reported greater pain in the second operation.
CONCLUSIONS
The pain score reported during cataract surgery procedures under topical anesthesia was within a generally tolerable range. Cataract progression does not appear to be related to pain during the operation. In consecutive surgeries, pain measured by a numerical scale and subjective pain experience showed different results.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The Comparison of Post-Operative Pain between Topical Anesthesia and Monitored Anesthesia Care in Cataract Surgery
Seon Do Kim, Jin Ho Jeong
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2015;56(5):715-720. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2015.56.5.715.
Reference
-
References
1. Fichman RA. Use of topical anesthesia alone in cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1996; 22:612–4.
Article2. Coelho RP, Weissheimer J, Romão E, Velasco e Cruz AA. Pain induced by phacoemulsification without sedation using topical or peribulbar anesthesia. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005; 31:385–8.
Article3. Crandall AS, Zabriskie NA, Patel BC, et al. A comparison of patient comfort during cataract surgery with topical anesthesia versus topical anesthesia and intracameral lidocaine. Ophthalmology. 1999; 106:60–6.4. Zehetmayer M, Radax U, Skorpik C, et al. Topical versus peribulbar anesthesia in clear corneal cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1996; 22:480–4.
Article5. Manners TD, Burton RL. Randomised trial of topical versus sub-Tenon's local anaesthesia for small-incision cataract surgery. Eye (Lond). 1996; 10:367–70.
Article6. Duker JS, Belmont JB, Benson WE, et al. Inadvertent globe perfo-ration during retrobulbar and peribulbar anesthesia. Patient characteristics, surgical management, and visual outcome. Ophthalmology. 1991; 98:519–26.
Article7. Hay A, Flynn H Jr., Hoffman JI, Rivera AH. Needle penetration of the globe during retrobulbar and peribulbar injections. Ophthalmology. 1991; 98:1017–24.
Article8. Morgan CM, Schatz H, Vine AK, et al. Ocular complications associated with retrobulbar injections. Ophthalmology. 1988; 95:660–5.
Article9. Omulecki W, Laudanska-Olszewska I, Synder A. Factors affecting patient cooperation and level of pain perception during phacoemulsification in topical and intracameral anesthesia. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2009; 19:977–83.
Article10. Yoon KC, Cho CW, Seo MS, Yang KJ. Comparision of Ocular pain between topical and retrobulbar anesthesia for cataract surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1996; 37:2041–7.11. Chylack LT Jr., Wolfe JK, Singer DM, et al. The Lens Opacities Classification System III. The Longitudinal Study of Cataract Study Group. Arch Ophthalmol. 1993; 111:831–6.
Article12. O'Brien PD, Fulcher T, Wallace D, Power W. Patient pain during different stages of phacoemulsification using topical anesthesia. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2001; 27:880–3.13. Bardocci A, Ciucci F, Lofoco G, et al. Pain during second eye cataract surgery under topical anesthesia: an intraindividual study. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2011; 249:1511–4.
Article14. Ursea R, Feng MT, Zhou M, et al. Pain perception in sequential cataract surgery: comparison of first and second procedures. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:1009–14.
Article15. Sharma NS, Ooi JL, Figueira EC, et al. Patient perceptions of second eye clear corneal cataract surgery using assisted topical anaesthesia. Eye (Lond). 2008; 22:547–50.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Topical versus Retrobulbar Anesthesia in Clear Corneal Cataract Surgery
- Comparision of Ocular pain Between Topical and Retrobulbar Anesthesia for Cataract Surgery
- The Comparison of Post-Operative Pain between Topical Anesthesia and Monitored Anesthesia Care in Cataract Surgery
- Comparison of Ocular Pain during Cataract Surgery Using a Scleral Pocket Incision under Pinpoint versus Intracameral Anesthesia
- Comparison of Effects of Topical, Pinpoint and Retrobulbar Anesthesin in Cataract Surgery using Clear Corneal Incision