J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2015 Apr;56(4):515-520. 10.3341/jkos.2015.56.4.515.
Comparison of Ocular Biometry and Postoperative Refraction in Cataract Patients between Galilei-G6(R) and IOL Master(R)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Hanyang University Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Guri, Korea. ocularimmunity@gmail.com
- KMID: 2215701
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2015.56.4.515
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare the axial lengths, anterior chamber depths, and keratometric measurements and to predict postoperative refractions of Dual Scheimpflug analyzer Galilei G6(R) and intra ocular lens (IOL) Master(R).
METHODS
A total of 50 eyes in 50 patients who received cataract surgery were included in the present study. The axial length, anterior chamber depth, and keratometry were measured using 2 types of partial coherence interferometries (Galilei G6(R) and IOL Master(R)). The SRK/T formula was used to calculate IOL power and the predictive error which subtracts predictive refraction from postoperative refraction was compared between the ocular biometry devices.
RESULTS
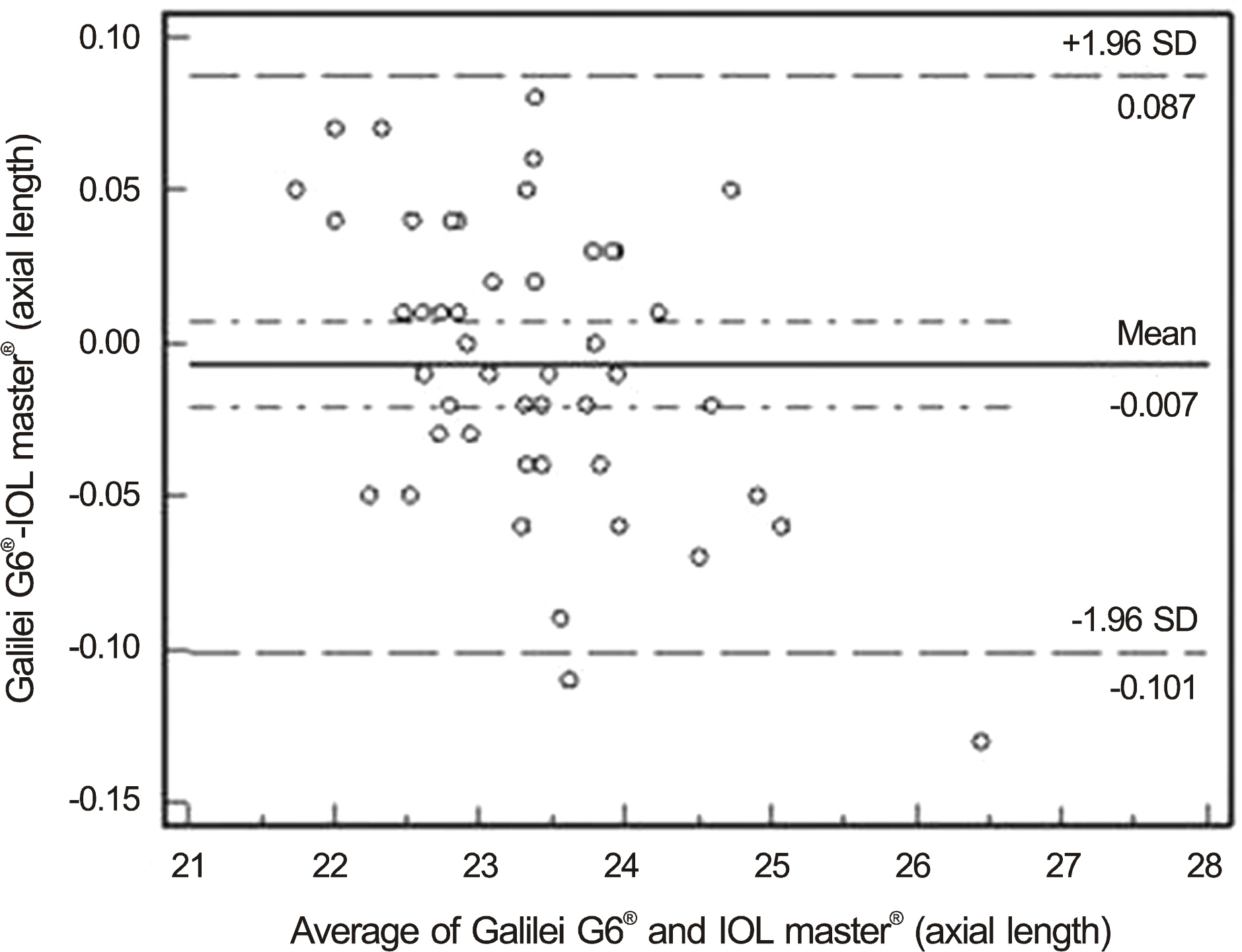
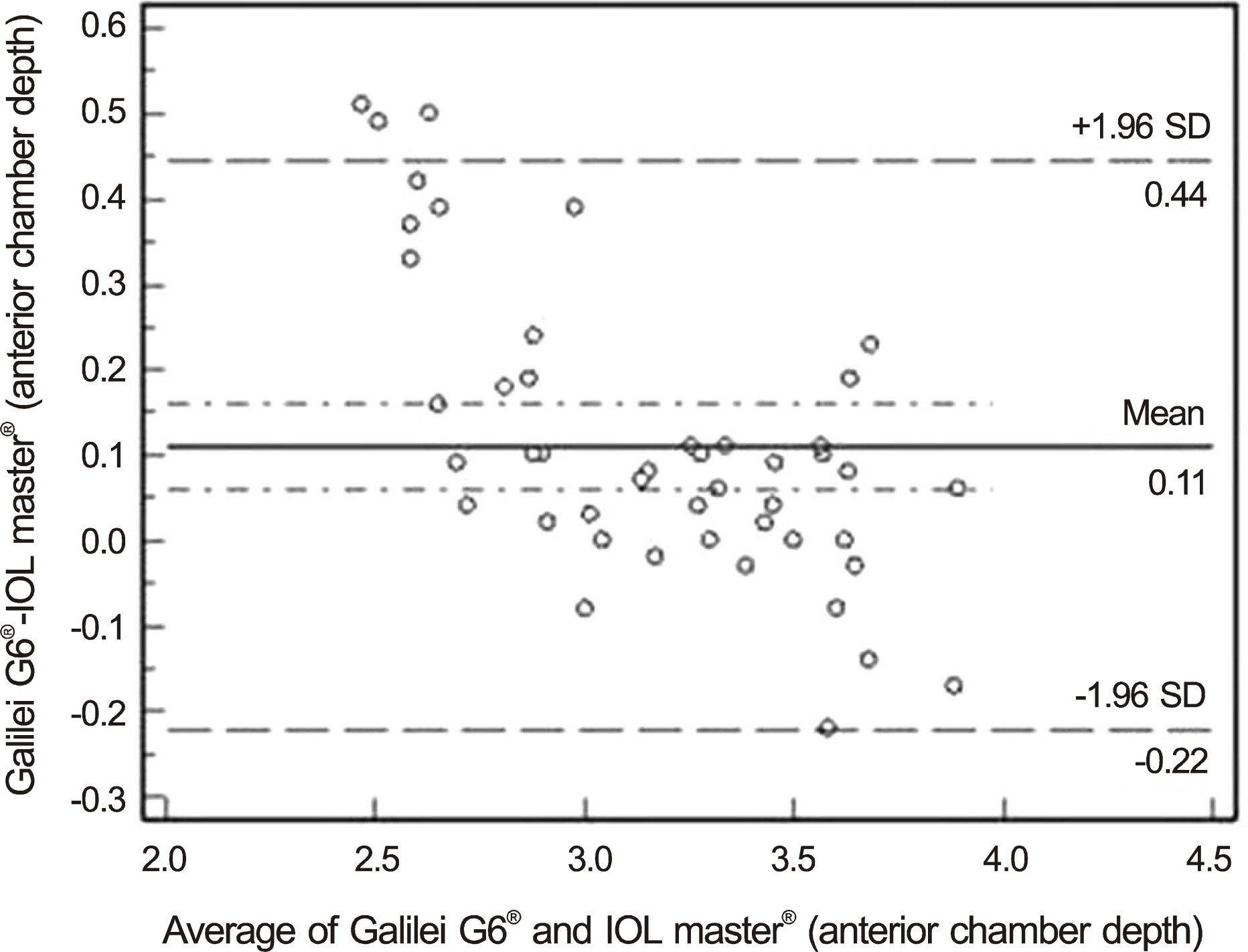
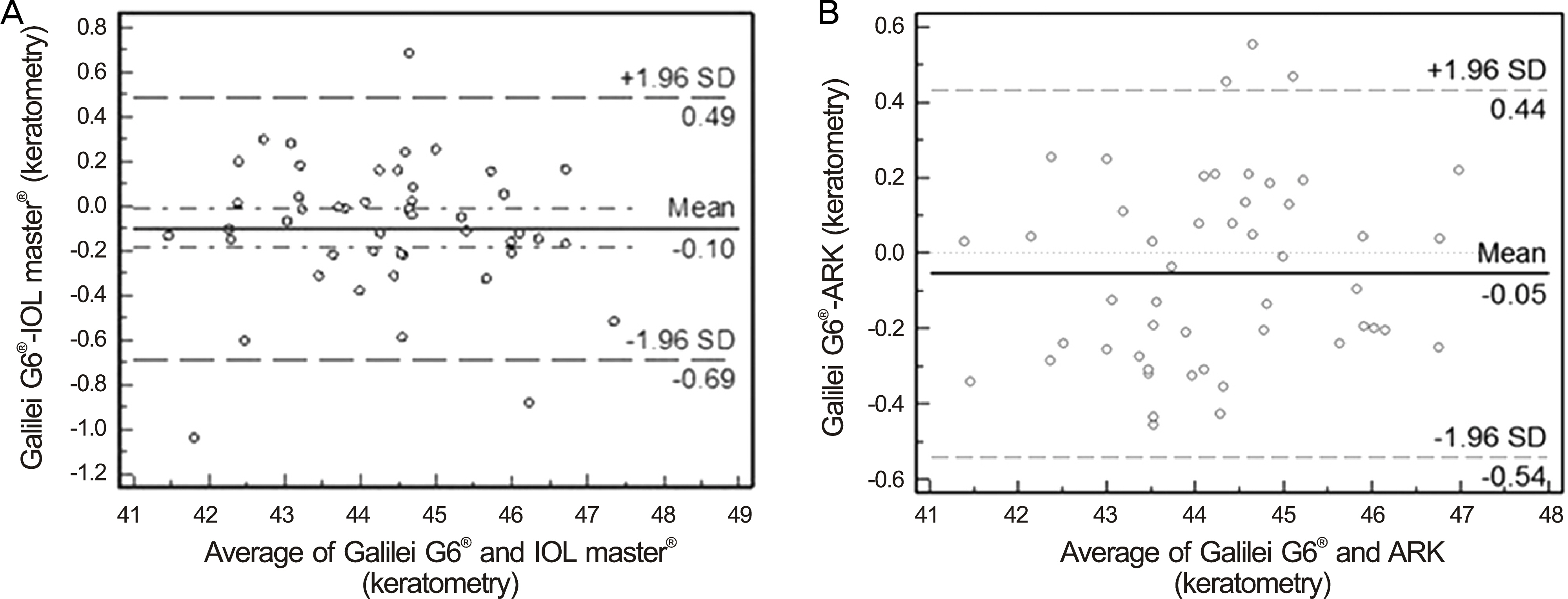
Axial lengths were 23.36 +/- 0.80 mm and 23.36 +/- 0.90 mm measured by Galilei G6(R) and IOL Master(R), respectively. Axial length measured by Galilei G6(R) was not statistically significant compared with IOL Master(R) (p = 0.321). The anterior chamber depth and keratometry were 3.22 +/- 0.35 mm and 44.29 +/- 1.40 D measured by Galilei G6(R) and 3.11 +/- 0.46 mm and 44.39 +/- 1.41 D measured by IOL Master(R), respectively. The differences of anterior chamber depth and keratometry between the 2 devices were statistically significant (p < 0.001 and p = 0.028, respectively). The mean absolute prediction errors were 0.45 +/- 0.37 D and 0.49 +/- 0.39 D in Galilei G6(R) and IOL Master(R), respectively and was not statistically significantly different (p = 0.423).
CONCLUSIONS
The ocular biometric measurements and prediction of postoperative refraction using Galilei G6(R) were as accurate as with IOL Master(R).
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Olsen T. Sources of error in intraocular lens power calculation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1992; 18:125–9.
Article2. Gimbel HV, Sun R. Accuracy and predictability of intraocular lens power calculation after laser in situ keratomileusis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2001; 27:571–6.
Article3. Holzer MP, Mamusa M, Auffarth GU. Accuracy of a new partial coherence interferometry analyser for biometric measurements. Br J Ophthalmol. 2009; 93:807–10.
Article4. Hwang JS, Lee JH. Comparison of the IOL Master(R) and A-scan ultrasound: refractive results of 96 consecutive cases. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007; 48:27–32.5. Lam AK, Chan R, Pang PC. The repeatability and accuracy of axial length and anterior chamber depth measurements from the IOLMaster. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2001; 21:477–83.6. Choi JH, Roh GH. The reproducibility and accuracy of biometry parameter measurement from IOL Master (R). J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2004; 45:1665–73.7. Olsen T, Thorwest M. Calibration of axial length measurements with the Zeiss IOLMaster. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005; 31:1345–50.
Article8. Shin JA, Chung SK. Comparison of the refractive results measured by ultrasound and partial coherence interferometers. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013; 54:723–7.
Article9. Patel RP, Pandit RT. Comparison of Anterior Chamber Depth Measurements from the Galilei Dual Scheimpflug Analyzer with IOLMaster. J Ophthalmol. 2012; 2012:430249.
Article10. Lopez de la Fuente C, Sanchez-Cano A, Segura F, Pinilla I. Comparison of anterior segment measurements obtained by three different devices in healthy eyes. Biomed Res Int. 2014; 2014:498080.
Article11. Santodomingo-Rubido J, Mallen EA, Gilmartin B, Wolffsohn JS. A new non-contact optical device for ocular biometry. Br J Ophthalmol. 2002; 86:458–62.
Article12. Kim SI, Kang SJ, Oh TH, et al. Accuracy of ocular biometry and postoperative refraction in cataract patients with AL-Scan(R). J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013; 54:1688–93.13. Shin JW, Seong MC, Kang MH, et al. Comparison of ocular biometry and postoperative refraction in cataract patients between Lenstar® and IOL Master®. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2012; 53:833–8.14. Buckhurst PJ, Wolffsohn JS, Shah S, et al. A new optical low coherence reflectometry device for ocular biometry in cataract patients. Br J Ophthalmol. 2009; 93:949–53.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Ocular Biometry and Postoperative Refraction in Cataract Patients Between Lenstar(R) and IOL Master(R)
- Comparison of Ocular Biometry and Refractive Outcomes Using IOL Master 700, IOL Master 500, and Ultrasound
- Accuracy of Ocular Biometry and Postoperative Refraction in Cataract Patients with AL-Scan(R)
- Comparison of Clinical Outcomes between Swept-source Optical Coherence Tomography Biometer and Partial Coherence Interferometer
- Comparison of Ocular Biometry and Refractive Outcomes Using IOL Master 500, IOL Master 700, and Lenstar LS900