J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2010 Nov;51(11):1525-1527. 10.3341/jkos.2010.51.11.1525.
A Case of Alcaligenes xylosoxidans Keratitis in a Soft Contact Lens Wearer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Science, St. Vincent's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. laty@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2213990
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2010.51.11.1525
Abstract
- PURPOSE
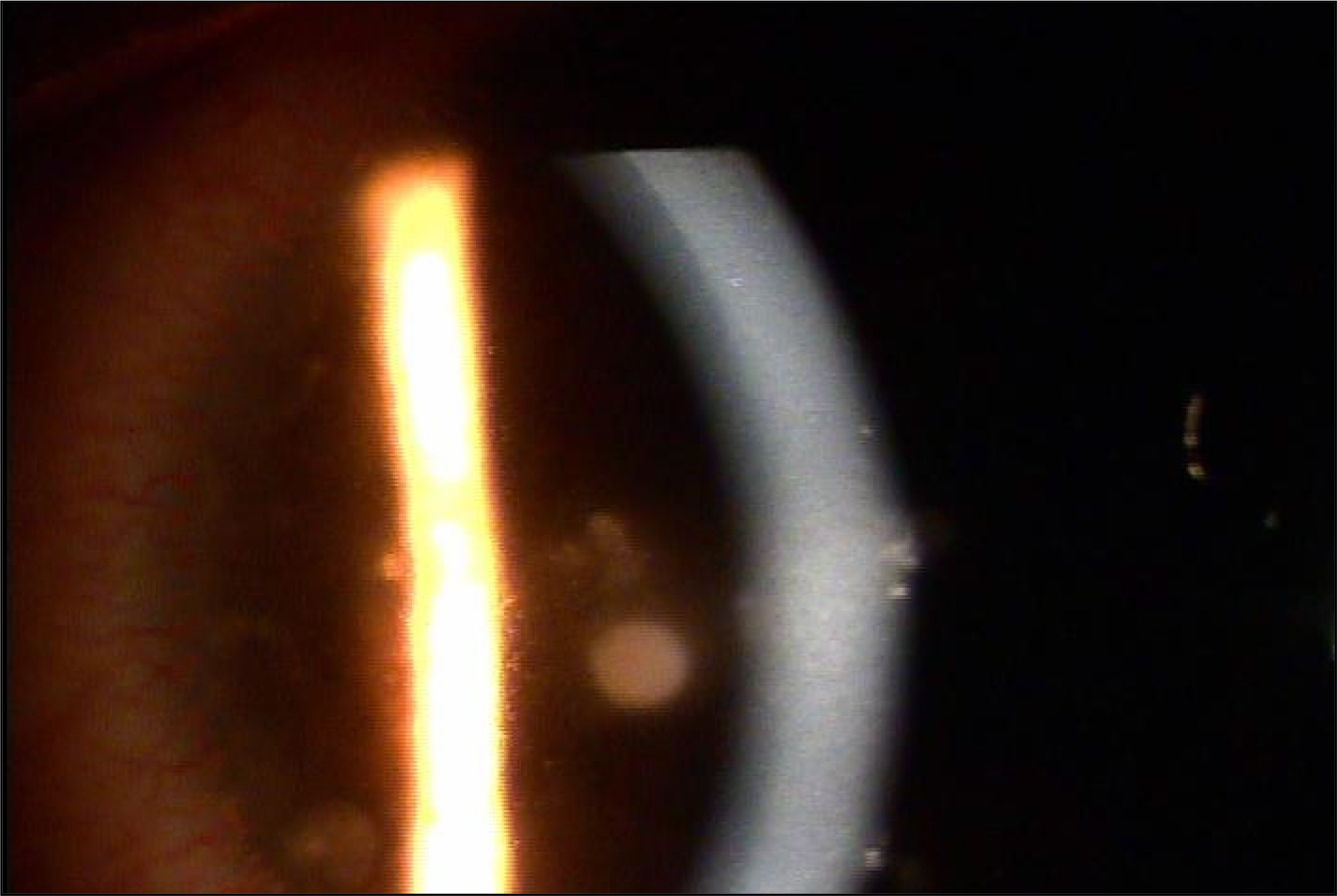
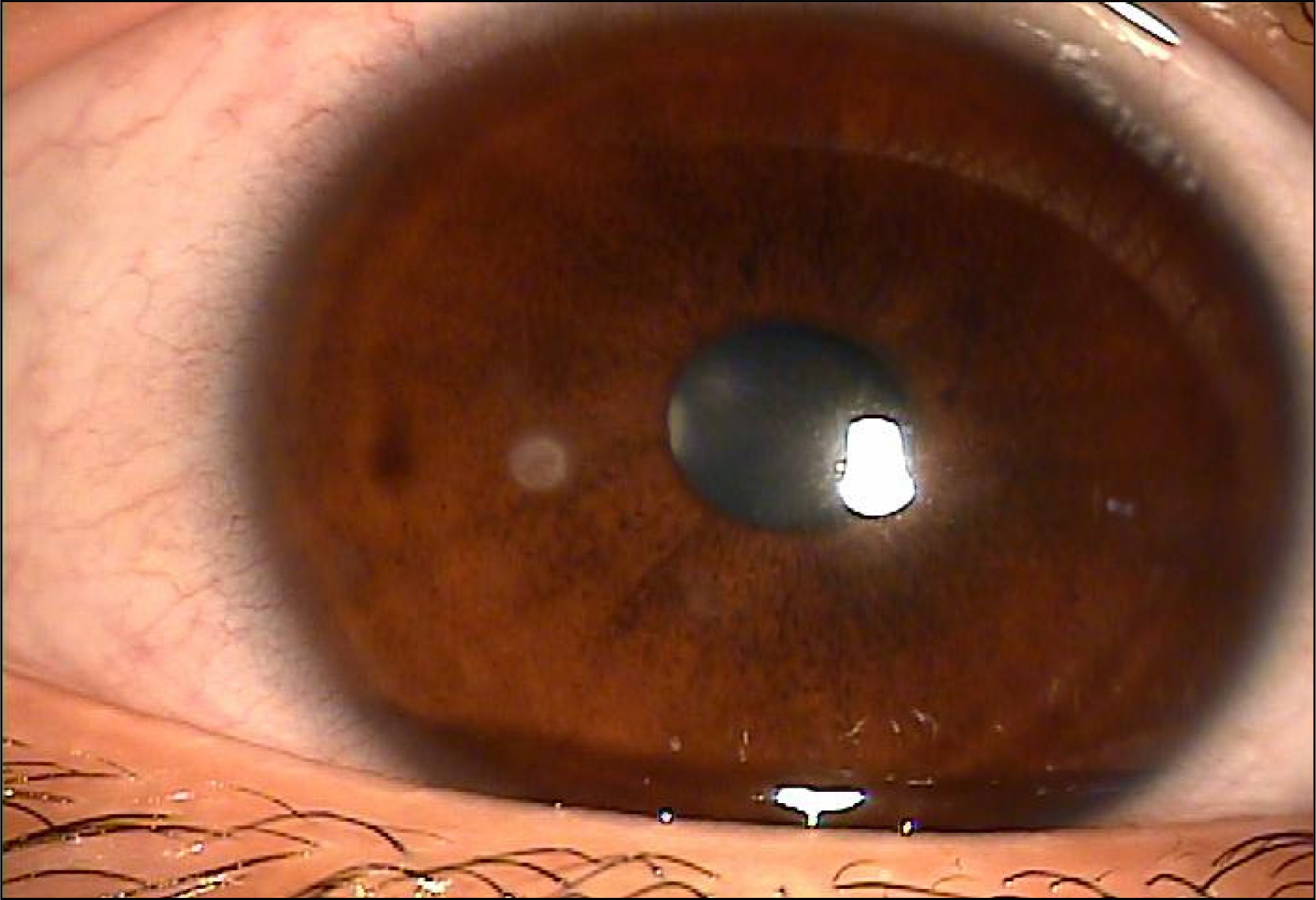
To report a case of corneal ulcer due to Alcaligenes xylosoxidans in a soft contact lens wearer.
CASE SUMMARY
A 20-year-old female patient presented with a corneal ulcer. The patient had been wearing soft contact lenses over 6 months. The ulcer had a typical appearance, similar to that of immune infiltration due to contact lenses. However, the corneal scraping and culture yielded Alcaligenes xylosoxidans, which is susceptible to ceftazidime and levofloxacine in the antibiotic susceptibility test. After treatment with topical antibiotics, her eye improved, with only a mild corneal scar remaining.
CONCLUSIONS
Alcaligenes xylosoxidans should be considered as a potential causal pathogen of keratitis upon wearing soft contact lenses. Additionally, any lesion should be suspected as a bacterial corneal ulcer, even if appearing as an immune infiltration due to contact lenses.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Holmes B, Snell JJ, Lapage SP. Strains of Achromobacter xylosoxidans from clinical material. J Clin Pathol. 1977; 30:595–601.
Article2. Han YS, Chung IY, Park JM. A case of Alcaligenes xylosoxidans endophthalmitis after cataract extraction. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:186–9.3. Oh J-Y, Shin YJ, Wee WR. A case of Epidemic keratoconjunctivitis complicated by Alcaligenes xylosoxidans infection. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2005; 19:233–4.
Article4. Hwang JH, Kim MJ, Kweon EY, et al. A case of corneal ulcer by Alcaligenes Faecalis. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:1414–7.
Article5. Fiscella R, Noth J. Achromobacter xylosoxidans corneal ulcer in a therapeutic soft contact lens wearer. Cornea. 1989; 8:267–9.
Article6. Pan TH, Heidemann DG, Dunn SP, et al. Delayed onset and recurrent Alcaligenes xylosoxidans keratitis. Cornea. 2000; 19:243–5.
Article7. Lin A, Driebe WT, Polack P. Alcaligenes xylosoxidans keratiits post penetrating keratoplasty in a rigid gas permeable lens wearer. CLAO J. 1998; 24:239–41.8. Huang ZL, Chen YF, Chang SW, et al. Recurrent Alcalgenes xylosoxidans keratitis. Cornea. 2005; 24:489–90.9. Yabuuchi E, Ohyama A. Achromobacter xylosoxidans from human ear discharge. Jpn J Microbiol. 1971; 15:477–81.10. Newman PE, Heider P, Waring GO, et al. Corneal ulcer due to Achromobactere xylosoxidans. Br J Ophthalmol. 1984; 68:472–4.11. Reddy AK, Garg P, Shah V, Gopinathan U. Clinical, microbiological profile and treatment outcome of ocular infections caused by Achromobacter xylosoxidans. Cornea. 2009; 28:1100–3.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Achromobacter xylosoxidans Keratitis after Contact Lens Usage
- A Case of Alcaligenes xylosoxidans Endophthalmitis after Cataract Extraction
- Pseudomonas Keratitis Due to Mishandling of Soft Contact lenses
- Corneal Complications of Contact Lens Wearer
- A Case of Acinetobacter Baumannii Keratitis After Contact Lens Wearing