J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2010 Jun;51(6):809-815. 10.3341/jkos.2010.51.6.809.
Effects of Eye Registration on the Astigmatism Correction in the Surface Laser Ablation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. crisim@freechal.com
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Hongseong Medical Center, Hongseong, Korea.
- 3Hansol Eye Clinic Center, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 2213604
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2010.51.6.809
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare the effect of astigmatism correction upon Mel 80 excimer laser surgery with or without an eye registration system.
METHODS
This retrospective analysis investigates a group (eye registration group) of surface laser ablation surgeries for myopic astigmatism correction, with operation on 27 eyes from 15 patients with guidance of the eye registration system and 40 eyes from 29 patients without guidance from the eye registration system. The evaluation of astigmatism correction was performed by the Alpins method, measuring the amount and axis of astigmatism before and after the operations.
RESULTS
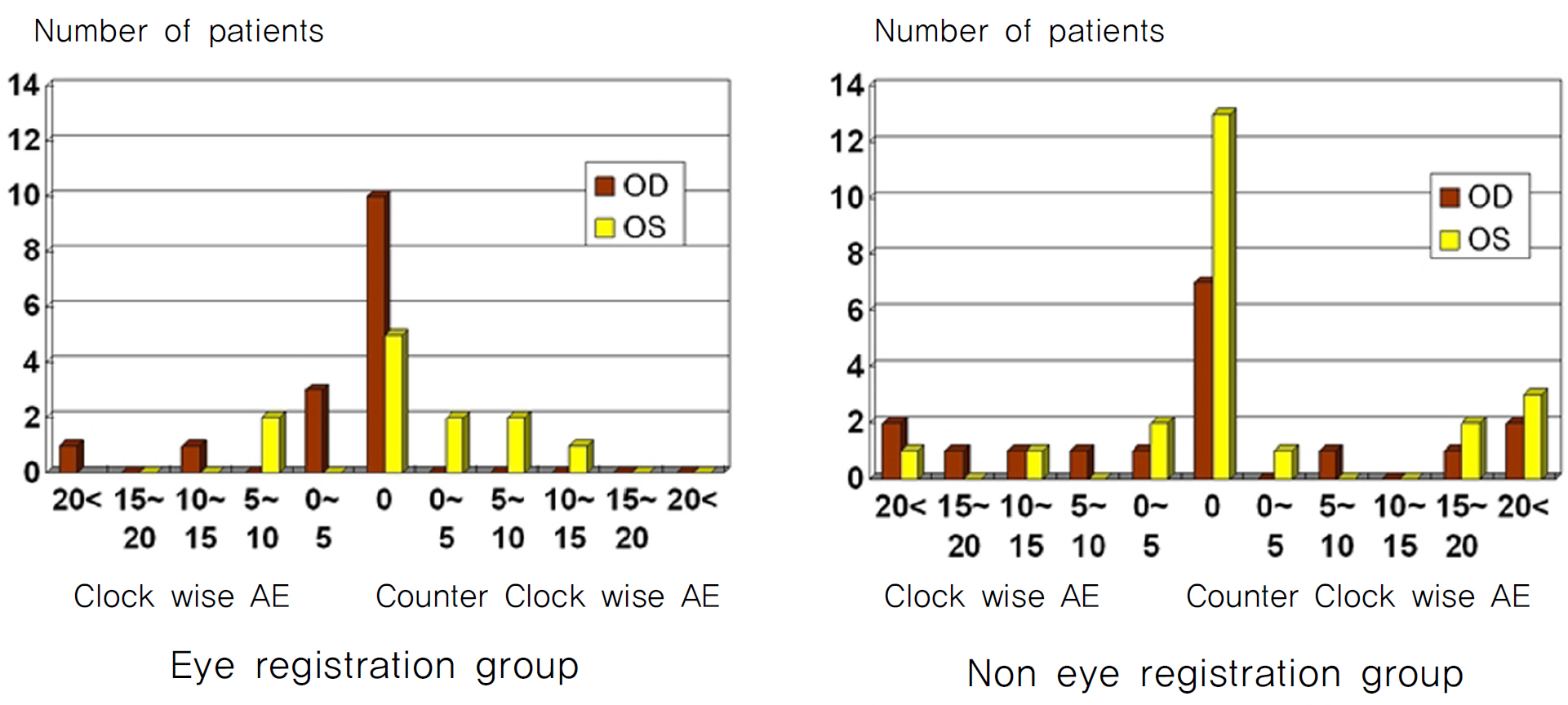
The average of the correction index (the ratio of the surgically induced amount of astigmatism correction to the intended amount of astigmatism correction) for the eye registration group was calculated to be 0.94+/-0.30 and, for non-eye registration group, was 0.92+/-0.41, showing no statistical significant difference between the two groups (p=0.762). However, the comparison of the index of success (the ratio of the difference vector to the intended amount of astigmatism correction) favorably demonstrated the effectiveness of eye registration (0.23+/-0.34 for eye registration group, 0.47+/-0.54 for non-eye registration group, p=0.03). The absolute angle of error (AE), a measure of difference in angle between the ablated axis of astigmatism correction and the desired axis of astigmatism correction, was lower on average for the eye registration group than for the non-eye registration group (3.52+/-7.69 to 12.5+/-20.69 degrees, p=0.015).
CONCLUSIONS
Eye registration-guided surface laser ablation is suggested to be beneficial for the reduction of errors in astigmatism correction.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Kohnen T, Mahmoud K, Bühren J. Comparison of corneal higher-order aberrations induced by myopic and hyperopic LASIK. Ophthalmology. 2005; 112:1692.
Article2. Bueeler M, Mrochen M, Seiler T. Maximum permissible lateral decentration in aberration-sensing and wavefront-guided corneal ablation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:257–63.
Article3. Bueeler M, Mrochen M, Seiler T. Maximum permissible torsional mis-alignment in aberration-sensing and wavefront-guided corneal ablation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004; 30:17–25.
Article4. Hersh PS, Fry K, Blaker JW. Spherical aberration after laser in situ keratomileusis and photorefractive keratectomy. Clinical results and theoretical models of etiology. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:2096–104.5. Kohnen T, Bühren J, Kuhne C, Mirshahi A. Wavefront-guided LASIK with the Zyoptix 3.1 system for the correction of myopia and compound myopic astigmatism with 1-year follow-up: clinical outcome and change in higher order aberrations. Ophthalmology. 2004; 111:2175–85.6. Hori-Komai Y, Sakai C, Toda I, et al. Detection of cyclotorsional rotation during excimer laser ablation in LASIK. J Refract Surg. 2007; 23:911–5.
Article7. Guirao A, Williams DR, Cox IG. Effect of rotation and translation on the expected benefit of an ideal method to correct the eye’s higher-order aberrations. J Opt Soc Am A Opt Image Sci Vis. 2001; 18:1003–15.
Article8. Bará S, Mancebo T, Moreno-Barriuso E. Positioning tolerances for phase plates compensating aberrations of the human eye. Appl Opt. 2000; 39:3413–20.
Article9. Viestenz A, Seitz B, Langenbucher A. Evaluating the eye’s rotational stability during standard photography: Effect on determining the axial orientation of toric intraocular lenses. J Refract Surg. 2005; 31:557–61.10. Chernyak DA. Cyclotorsional eye motion occurring between wave-front measurement and refractive surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004; 30:633–8.
Article11. Mrochen M, Eldine MS, Kaemmerer M, et al. Improvement in photo-refractive corneal laser surgery results using an active eye tracking system. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2001; 27:1000–6.12. McDonald MB, Deitz MR, Frantz JM, et al. Photorefractive keratectomy for low to moderate myopia and astigmatism with a small-beam, tracker-directed excimer laser. Ophthalmol. 1999; 106:1481–8.13. Ciccio AE, Durrie DS, Stahl JE, Schwendeman F. Ocular cyclotorsion during customized laser ablation. J Refract Surg. 2005; 21:S772–4.
Article14. Kohnen T, Kühne C, Cichocki M, Strenger A. Cyclorotation of the eye in wavefront-guided LASIK using a static eyetracker with iris recognition. Ophthalmologe. 2007; 104:60–5.15. Park SH, Kim M, Joo CK. Measurement of pupil centroid shift and cyclotorsional displacement using iris registration. Ophthalmologica. 2009; 223:166–71.
Article16. Chang J. Cyclotorsion during laser in situ keratomileusis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:1720–6.
Article17. Ghosh S, Couper TA, Lamoureux E, et al. Evaluation of iris recognition system for wavefront-guided laser in situ keratomileusis for myopic astigmatism. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:215–21.
Article18. Khalifa M, El-Kateb M, Shaheen MS. Iris registration in wave-front-guided LASIK to correct mixed astigmatism. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:433–7.
Article19. Zhang J, Zhou YH, Wang NL, Li R. Comparison of visual performance between conventional LASIK and wavefrontguided LASIK with irisregistration. Chin Med J (Engl). 2008; 121:137–42.
Article20. Wu F, Yang Y, Dougherty PJ. Contralateral comparison of wave-front-guided LASIK surgery with iris recognition versus without iris recognition using the MEL80 Excimer laser system. Clin Exp Optom. 2009; 92:320–7.
Article21. Moshirfar M, Chen MC, Espandar L, et al. Effect of iris registration on outcomes of LASIK for myopia with the VISX CustomVue platform. J Refract Surg. 2009; 25:493–502.
Article22. Tantayakom T, Lim JN, Purcell TL, et al. Visual outcomes after wave-front-guided laser in situ keratomileusis with and without iris registration. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:1532–7.
Article23. Prakash G, Ashok Kumar D, Agarwal A, et al. Predictive factor analysis for successful performance of iris recognition-assisted dynamic rotational eye tracking during laser in situ keratomileusis. Am J Ophthalmol. 2010; 149:229–37.
Article24. Alpins N. Astigmatism analysis by the Alpins method. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2001; 27:31–49.
Article25. Alpins N. Vector analysis of astigmatism changes by flattening, steepening, and torque. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1997; 23:1503–14.
Article26. Alpins N. A new method of analyzing vectors f or changes in astigmatism. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1993; 19:524–33.27. Stokes GG. 19th meeting of the British association for the advancement of science. Transactions of the sections. 1849. 10–1.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Excimer laser photorefractive keratectomy for astigmatism
- Result of Schwind Excimer Photoastigmatic Refractive Keratectomy(One year follow up)
- Influence of Surface Fluid during Photorefractive Keratectomy Using a 213-nm Solid-State Laser
- Clinical Outcomes of Combined Procedure of Astigmatic Keratotomy and Laser in situ Keratomileusis
- Effect of Excimer Laser Photorefractive Keratectomy on the Induction of Astigmatism in Rabbits