Effects of Anterior Chamber Depth and Axial Length on Refractive Error after Intraocular Lens Implantation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. eschung@skku.edu
- KMID: 2213140
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2010.51.2.195
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To investigate the error tendency between preoperative expected refraction and postoperative manifest refraction based on anterior chamber depth (ACD) and axial length (AXL) in cataract surgery cases and to report how ACD and AXL affect determination of intraocular lens (IOL) power.
METHODS
We retrospectively studied 82 eyes of 62 patients who underwent cataract surgery in our hospital between August 2008 and January 2009. Anterior chamber depth and AXL were measured using IOL Master(R), and IOL power was calculated using the SRK II and SRK/T formulae. Patients were divided into three groups based on ACD and into another three based on AXL. Refractive error (RE) was analyzed one month after surgery.
RESULTS
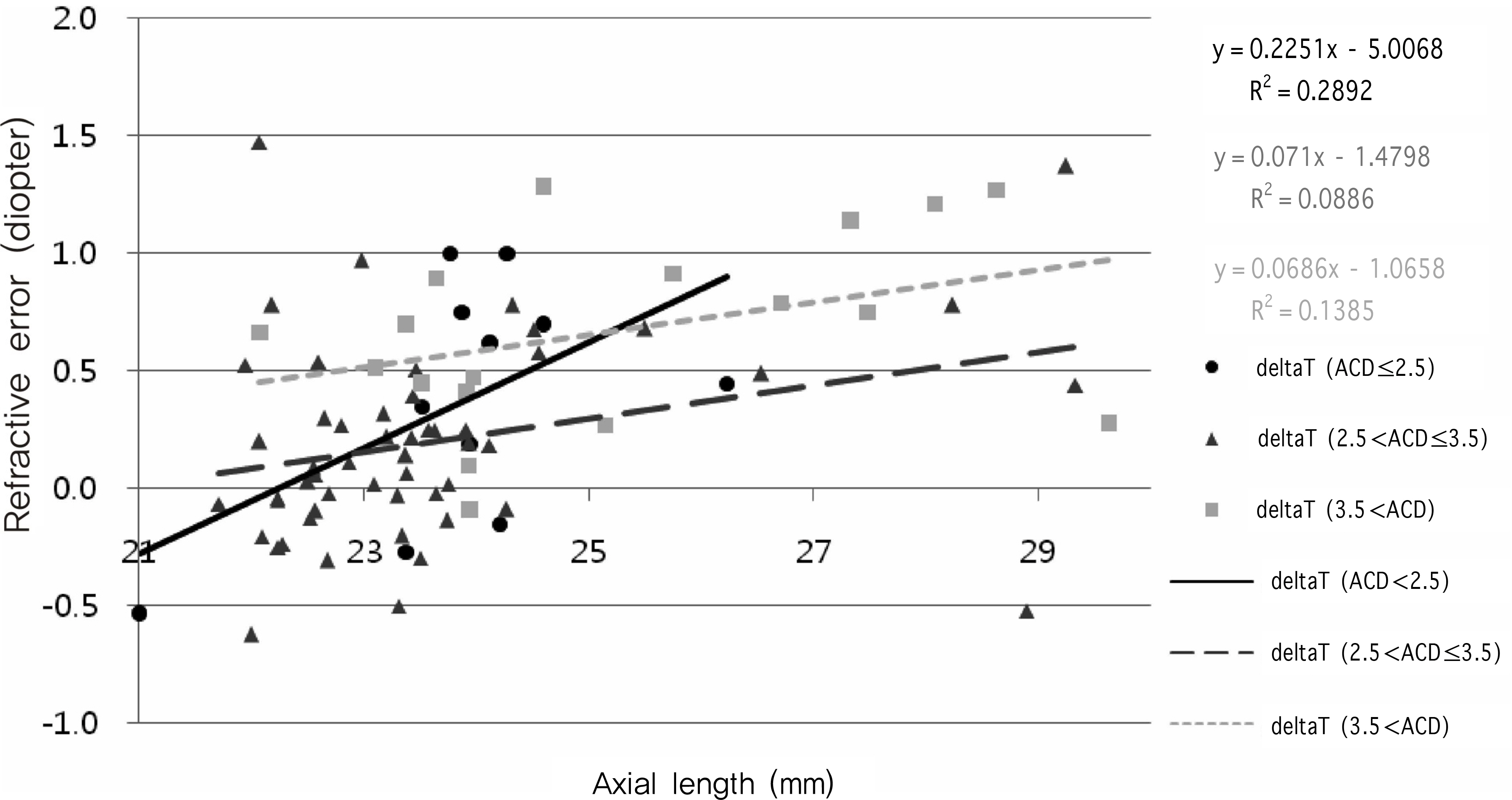
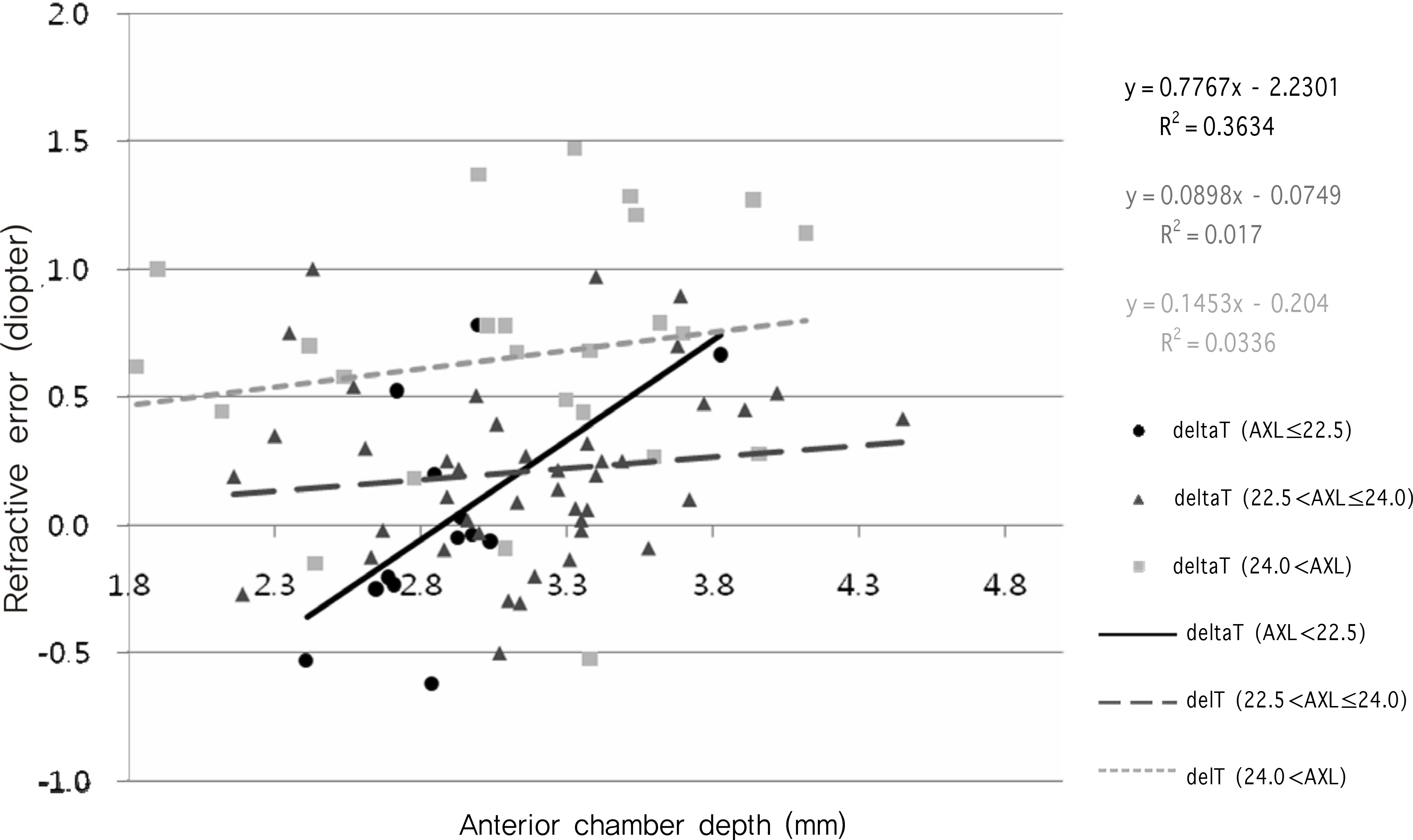
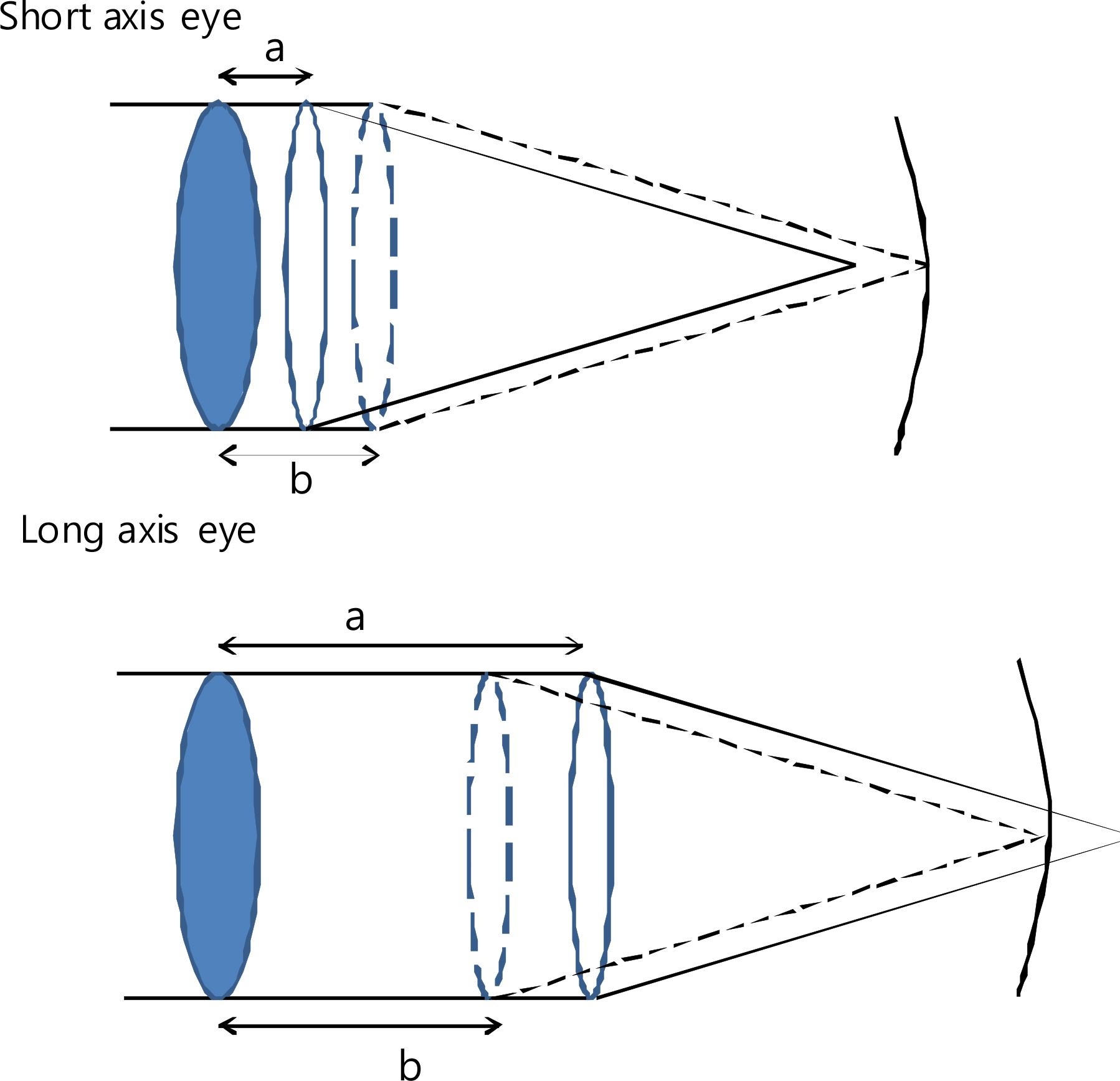
Though the RE of each group showed a tendency for hyperopic shifts, only those obtained with the SRK/T formula showed statistically significant differences between groups (p<0.05). Using the SRK/T formula, we found that an increasing AXL was associated with an increased hyperopic shift. This was more pronounced in those with shallow ACD (<2.5 mm), though the difference was not statistically significant. Similarly, an increase in ACD was associated with an increased hyperopic shift, and this difference was more pronounced in those with short AXL (<22.5 mm), and this time the difference was statistically significant.
CONCLUSIONS
As ACD and AXL significantly affect RE, both should be considered when investigating postoperative RE tendency and when determining IOL power. Postoperative RE will be greatly affected by a short AXL or a shallow ACD, and therefore these factors should be considered in IOL power determination.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 11 articles
-
Refractive Error Induced by Combined Phacotrabeculectomy
Jun Seok Lee, Chong Eun Lee, Ji Hae Park, Sam Seo, Kyoo Won Lee
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2018;59(12):1173-1180. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2018.59.12.1173.Comparison of Three Formulas for Intraocular Lens Power Formula Accuracy
Ki Woong Lee, Jinsoo Kim, Dong Hyun Kim
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2020;61(1):27-33. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2020.61.1.27.Accuracy of the Haigis Formula Based on Axial Length and Anterior Chamber Depth
Chan-Hui Yi, Sung-Ho Choi, Eui-Sang Chung, Tae-Young Chung
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2011;52(2):175-181. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2011.52.2.175.Comparison of the Refractive Outcomes According to the Differences of Biometry and Keratometry Reading
Kang Hoon Lee, Na Rae Kim, Kyoung Yul Seo
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013;54(9):1345-1352. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2013.54.9.1345.Effects of Axial Length and Vitrectomy on Refractive Error after Cataract Surgery Using SRK/T Formula
Min Kyu Lee, Kyu Yeon Hwang, Man Soo Kim
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013;54(2):257-264. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2013.54.2.257.Refractive Eerror According to the Anterior Chamber Depth and Corneal Refractive Power in Short Eyes
Jeong Ah Shin, Kyu Yeon Hwang, Man Soo Kim
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013;54(1):65-71. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2013.54.1.65.Analysis of Factors that Influence on Accuracy of Intraocular Lens Power Calculation
Bo Hyuck Kim, Won Ryang Wee, Mee Kum Kim
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014;55(2):173-181. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2014.55.2.173.Formula Comparison for Intraocular Lens Power Calculation Using IOL Master and Ultrasound for the ZCB00 IOL
Dong Hoon Shin, Dong Hui Lim, Ja Young You, Eui Sang Chung, Tae Young Chung
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014;55(4):527-533. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2014.55.4.527.Comparative Analysis of Corneal Refractive Power Measured with AL-Scan®, Autokeratometer, and Pentacam®
Sung Jin Park, Sung Hyup Lim, Ho Young Lee
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014;55(7):984-990. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2014.55.7.984.Comparison of Refractive Power and Astigmatism between Digital Keratometer and Autorefractor
Jae Won Choi, Sang Youp Han, Kyung Heon Lee
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2017;58(1):21-26. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2017.58.1.21.Influence of Biometric Variables on Refractive Outcomes after Cataract Surgery in Angle-closure Glaucoma Patients
Kyoung Nam Kim, Hyung Bin Lim, Jong Joo Lee, Chang-Sik Kim
Korean J Ophthalmol. 2016;30(4):280-288. doi: 10.3341/kjo.2016.30.4.280.
Reference
-
References
1. Holladay JT, Prager TC, Ruiz RS, et al. Improving the aberrations of intraocular lens power calculations. Arch Ophthalmol. 1986; 104:539–41.2. Mamalis N. Complications of foldable intraocular lenses requiring explanation or secondary intervention–1998 survey. J aberrations Refract Surg. 2000; 26:766–72.3. Olsen T. Sources of error in intraocular lens power calculation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1992; 18:125–9.
Article4. Hitzenberger CK. Optical measurement of the axial eye length by laser Doppler interferometry. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1991; 32:616–24.5. Drexler W, Findl O, Menapace R, et al. Dual beam optical aberrations tomography: signal identification for ophthalmologic aberrations. J Biomed Opt. 1998; 3:55–65.6. Vogel A, Dick HB, Krummenauer F. Reproducibility of optical biometry using partial coherence interferometry: intraobserver and interobserver reliability. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2001; 27:1961–8.
Article7. Kiss B, Findl O, Menapace R, et al. Biometry of cataractous eyes using partial coherence interferometry: clinical feasibility study of a commercial prototype I. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:224–9.8. Lam AK, Chan R, Pang PC. The repeatability and accuracy of axial length and anterior chamber depth measurements from the IOLMaster. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2001; 21:477–83.9. Kielhorn I, Rajan MS, Tesha PM, et al. Clinical assessment of the Zeiss IOLMaster. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:518–22.
Article10. Choi JH, Roh GH. The reproducibility and accuracy of biometry parameter measurement from IOL Master. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2004; 45:1665–73.11. Kim HJ, Kim HJ, Joo CK. Comparison of IOL Master, A-scan and Orbscan II for measurement of axial length and anterior chamber depth. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003; 44:1519–27.12. Olsen T, Thim K, Corydon L. Theoretical versus SRK I and SRK II calculation of intraocular lens power. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1990; 16:217–25.
Article13. McEwan JR, Massengill RK, Friedel SD. Effect of keratometer and axial length measurement errors on primary implant power calculations. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1990; 16:61–70.
Article14. Olsen T. Prediction of the effective postoperative (intraocular lens) anterior chamber depth. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:419–24.
Article15. Weissman JL, Beatty RL, Hirsch WL, Curtin HD. Enlarged anterior chamber: CT finding of a ruptured globe. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1995; 16:936–8.16. Masket S. Alcon Restor multifocal-clinical pearls, mastering aberrations IOLs, the art and science. Thorofare, NJ: Slack, Inc.;2008. p. 125–9.17. Bogan SJ, Waring GO 3rd, Ibrahim O, et al. Classification of normal corneal topography based on computer-assisted aberrations. Arch Ophthalmol. 1990; 108:945–9.18. Rose LT, Moshegov CN. Comparison of the Zeiss IOLMaster and applanation A-scan ultrasound: biometry for intraocular lens calculation. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2003; 31:121–4.
Article19. Connors R 3rd, Boseman P 3rd, Olson RJ. Accuracy and aberrations of biometry using partial coherence aberrations. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:235–8.20. Eleftheriadis H. IOLMaster biometry: refractive results of 100 consecutive cases. Br J Ophthalmol. 2003; 87:960–3.
Article21. Hwang JS, Lee JH. Comparison of the IOL master and A-scan ultrasound: Results of 96 consecutive cases. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007; 48:27–32.22. Fedorov SN, Kolinko AI. A method of calculating the optical power of the intraocular lens. Vestn Oftalmol. 1967; 80:27–31.23. Holladay JT, Prager TC, Chandler TY, et al. A three-part system for refining intraocular lens power calculations. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1988; 14:17–24.
Article24. Retzlaff JA, Sanders DR, Kraff MC. Development of the SRK/T intraocular lens implant power calculation formula. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1990; 16:333–40.
Article25. Hoffer KJ. The Hoffer Q formula: a comparison of theoretic and regression formulas. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1993; 19:700–12.
Article26. Olsen T, Olesen H, Thim K, Corydon L. Prediction of aberrations anterior chamber depth with the newer IOL calculation formulas. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1992; 18:280–5.27. Narvaez J, Zimmerman G, Stulting RD, et al. Accuracy of aberrations lens power prediction using the Hoffer Q, Holladay 1, Holladay 2, and SRK/T formulas. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:2050–3.28. Lim LH, Lee SY, Ang CL. Factors affecting the predictability of SRK II in patients with normal axial length undergoing phacoemulsification surgery. Singapore Med J. 2009; 50:120–5.29. Haigis W. The Haigis formula. HJ S, editor. Intraocular lens power calculations. Thorofare, NJ: Slack;2004. chap. 5.30. Olsen T, Olesen H, Thim K, Corydon L. Prediction of aberrations intraocular lens chamber depth. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1990; 16:587–90.31. Olsen T, Corydon L, Gimbel H. Intraocular lens power aberrations with an improved anterior chamber depth prediction aberrations. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1995; 21:313–9.32. Olsen T. The Olsen formula. HJ S, editor. Intraocular Lens Power Calculations. Thorofare, NJ: Slack;2004. chap. 4.33. Sanders DR, Retzlaff JA, Kraff MC, et al. Comparison of the SRK/T formula and other theoretical and regression formulas. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1990; 16:341–6.
Article34. Olsen T. Calculation of intraocular lens power: a review. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2007; 85:472–85.
Article35. Yang CH, Hung PT. Intraocular lens position and anterior chamber angle changes after cataract extraction in eyes with primary angle-closure glaucoma. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1997; 23:1109–13.
Article36. Chang SW, Yu CY, Chen DP. Comparison of intraocular lens power calculation by the IOLMaster in phakic and eyes with hydrophobic acrylic lenses. Ophthalmology. 2009; 116:1336–42.
Article37. Kang SY, Hong S, Won JB, et al. Inaccuracy of intraocular lens power prediction for cataract surgery in angle-closure glaucoma. Yonsei Med J. 2009; 50:206–10.
Article38. Gavin EA, Hammond CJ. Intraocular lens power calculation in short eyes. Eye. 2008; 22:935–8.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Predictability of Postoperative Refractive Error after Secondary Lens Implantation
- Effects of Axial Length and Anterior Chamber Depth on Intrascleral Fixation Using a Fibrin Adhesive
- Posterior Chamber Intraocular Lens Implantation in High Myopia
- Change of Anterior Chamber Depth after Phacoemulsification with Posterior Chamber Intraocular Lens Implantation in High Myopia
- The Change of Anterior Chamber Depth According to the Types of Intraocular Lens