J Korean Surg Soc.
2012 Mar;82(3):195-199. 10.4174/jkss.2012.82.3.195.
A hybrid operation in a patient with complex right subclavian artery aneurysm
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Vascular Surgery, Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. dikim@skku.edu
- 2Department of Radiology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Thoracic & Cardiovascular Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2212223
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2012.82.3.195
Abstract
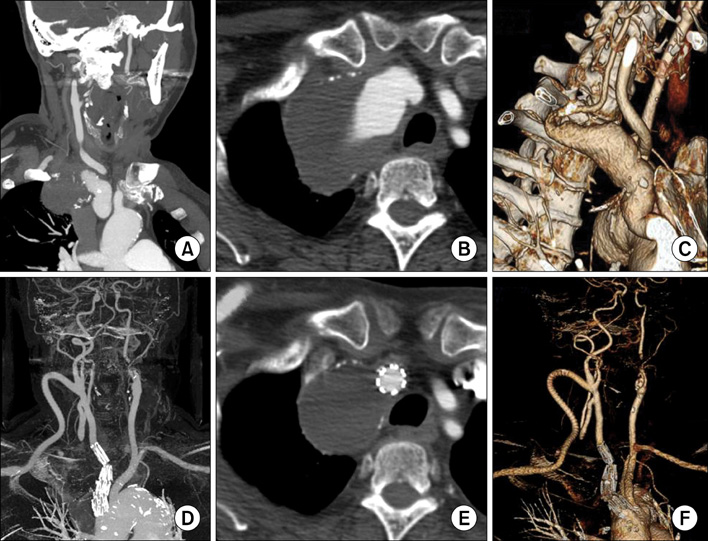
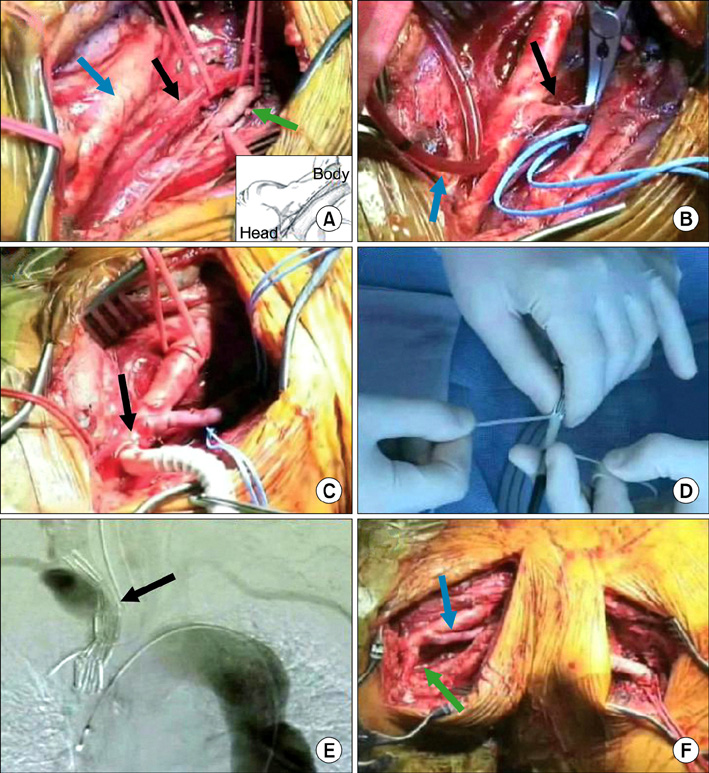
- We report a hybrid surgery including endovascular aneurysm repair and debranching procedures to treat a patient with a complex right subclavian artery aneurysm. The patient was a 70-year-old woman who presented with dry cough and hoarseness. The aneurysm was characterized by the absence of a proximal neck, and involvement of the origin of the right vertebral artery. She underwent carotid-vertebral artery bypass, stent graft from the innomiate artery to the common carotid artery and carotid-axillary artery bypass. Great saphenous vein was used for the carotid-vertebral artery bypass and 7 mm reinforced polytetrafluoroethylene graft was used for the carotid-axillary artery bypass. The postoperative course was uneventful.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Halldorsson A, Ramsey J, Gallagher C, Meyerrose G. Proximal left subclavian artery aneurysms: a case report and review of the literature. Angiology. 2007. 58:367–371.2. Dougherty MJ, Calligaro KD, Savarese RP, DeLaurentis DA. Atherosclerotic aneurysm of the intrathoracic subclavian artery: a case report and review of the literature. J Vasc Surg. 1995. 21:521–529.3. McCollum CH, Da Gama AD, Noon GP, DeBakey ME. Aneurysm of the subclavian artery. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 1979. 20:159–164.4. Bin HG, Kim MS, Kim SC, Keun JB, Lee JH, Kim SS. Intrathoracic aneurysm of the right subclavian artery presenting with hoarseness: a case report. J Korean Med Sci. 2005. 20:674–676.5. Salo JA, Ala-Kulju K, Heikkinen L, Bondestam S, Ketonen P, Luosto R. Diagnosis and treatment of subclavian artery aneurysms. Eur J Vasc Surg. 1990. 4:271–274.6. Becker GJ, Benenati JF, Zemel G, Sallee DS, Suarez CA, Roeren TK, et al. Percutaneous placement of a balloon-expandable intraluminal graft for life-threatening subclavian arterial hemorrhage. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 1991. 2:225–229.7. Hilfiker PR, Razavi MK, Kee ST, Sze DY, Semba CP, Dake MD. Stent-graft therapy for subclavian artery aneurysms and fistulas: single-center mid-term results. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2000. 11:578–584.8. Kasirajan K, Matteson B, Marek JM, Langsfeld M. Covered stents for true subclavian aneurysms in patients with degenerative connective tissue disorders. J Endovasc Ther. 2003. 10:647–652.9. Resch TA, Lyden SP, Gavin TJ, Clair DG. Combined open and endovascular treatment of a right subclavian artery aneurysm: a case report. J Vasc Surg. 2005. 42:1206–1209.10. Van Leemput A, Maleux G, Heye S, Nevelsteen A. Combined open and endovascular repair of a true right subclavian artery aneurysm without proximal neck. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2007. 6:406–408.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hybrid Operation of a Kommerell's Diverticulum with Left Aberrant Subclavian Artery
- Hybrid Treatment for Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Combined with Aberrant Right Subclavian Artery
- Total Arch Replacement for Chronic Aortic Aneurysmal Dissection Patient with Aberrant Subclavian Artery
- Hybrid Treatment of an Aortic Arch Aneurysm with an Aberrant Right Subclavian Artery
- Mycotic Aneurysm of the Left Subclavian Artery Presenting as Mediastinal Abscess: Case Report