J Korean Acad Periodontol.
2009 Sep;39(3):293-301. 10.5051/jkape.2009.39.3.293.
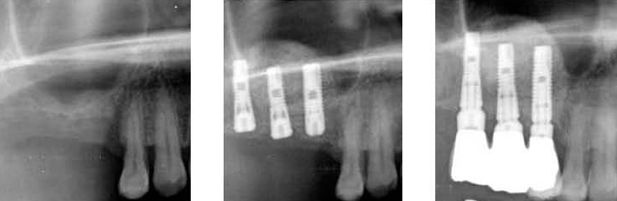
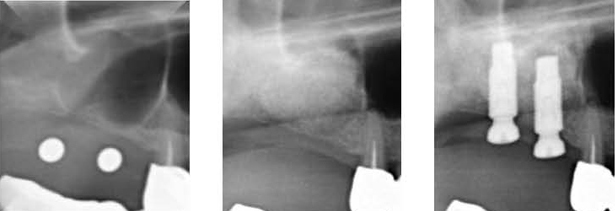
The retrospective study of survival rate of implants with maxillary sinus floor elevation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Periodontology, Research Institute for Periodontal Regeneration, College of Dentistry, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea. kscho@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Periodontology, Dental Medical Center, Seoul Veterans Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2212143
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5051/jkape.2009.39.3.293
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to show the total survival rate of implants with maxillary sinus floor elevation and the effects that reach the survival rate by classifying types of graft materials, implant surface, operation method, bone height.
METHODS
In a total of 131 patients, 251 implants with sinus floor elevation were installed simultaneously or after regular healing. Various bone grafts (autograft, xonograft, allograft, alloplast) and implant surface (MTX-HA implant, chemical etching implant, Titanium oxide surface implant, resorbable blasting media implant, resorbable blast texturing implant, HA-coated implant) were used. All implants were investigated clinically and radiographically, being with 1 to 5 years follow-up period after installation.
RESULTS
The survival rate of 251 implants with maxillary sinus floor elevation was 94%. The types of implant, surface, graft material, bone height have no statistically signi-ficant differencies.
CONCLUSIONS
It can be suggested that maxillary sinus floor elevation may have predictable result with various bone graft materials and implant surface.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Albrektsson T, Zarb G, Worthington P, Eriksson AR. The long-term efficacy of currently used dental implants:a review and proposed criteria of success. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1986. 1:11–25.2. Chanavaz M. Maxillary sinus anatomy, physiology, surgery and bone grafting related to implantology-eleven years surgical experience(1979-1990). J Oral Implantol. 1990. 16:199–209.3. Boyne PJ, James RA. Grafting of the maxillary sinus floor with autogenous marrow and bone. J Oral Surg. 1980. 38:613–616.4. Tatum HJ. Maxillary and sinus implant reconstructions. Dent Clin North Am. 1986. 30:207–229.5. Summers RB. A new concept in maxillary implant surgery: the osteotome technique. Compend contin Educ Dent. 1994. 15:152–162.6. Misch CE. Maxillary sinus augmentation for endosteal implants: organized alternative treatment plans. Int J Oral Implantol. 1987. 4:49–58.7. Smiler DG, Holmes RE. Sinus lift procedure using porous hydroxyapatite:a preliminary clinical report. J Oral Implantol. 1987. 13:239–253.8. Wood RM, Moore DL. Grafting of the maxillary sinus with intraorally harvested autogenous bone prior to implant placement. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1988. 3:209–214.9. Jensen OT, Shulman LB, Block MS, Iacono VJ. Report of the sinus consensus conference of 1996. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1998. 13:suppl. 11–45.10. Hising P, Bolin A, Branting C. Reconstruction of severely resorbed alveolar crests with dental implants using a bovine bone mineral for augmentation. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2001. 16:90–97.11. Froum SJ, Tarnow DP, Wallace SS, Rohrer MD, Cho SC. Sinus floor elevation using anorganic bovine bone materials with and without autogenous bone:a clinical, histologic, radiographic and histomorphometric analysis-Part 2 of an ongoing prospective study. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 1998. 18:528–543.12. Lee JH, Jung UW, Kim CS, Choi CH, Cho KS. Maxillary sinus augmentation using calcium phosphate(MBCP):three case report with histologic evaluation. J Korean Acad Periodontol. 2007. 37:277–286.13. Kim JS, Lee SK, Chae GJ, et al. A radiographic evaluation of graft height changes after maxillary sinus augmentation and placement of dental implants. J Korean Acad Periodontol. 2007. 37:277–286.
Article14. Rosen PS, Summers R, mellado JR, et al. The bone-added osteotome sinus floor elevation technique:multicenter retrospective report of consecutively treated patients. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1999. 14:853–858.15. Rosenberg ES, Cho SC, Elian N, et al. A comparison of characteristics of implant failure and survival in periodontally compromised and periodontally healthy patients:a clinical report. Int J Oral maxillofac Implants. 2004. 19:873–879.16. Jensen OT, Greer R. Laney WR, Tolman DE, editors. Immediate placement of osseointegrating implants into the maxillary sinus augmented with mineralized cancellous allograft and Gore-Tex:second-stage surgical and histologic findings. Tissue Integration in Oral, Orthopedic, and Maxillofacial Reconstruction. 1992. Chicago: Quintessence Publishing Co Inc;321–333.17. Peleg M, Garg AK, Mazor Z. Predictability of simultaneous implants placement in the severely atrophic posterior maxilla: a 9-year longitudinal experience study of 2,132 implants placed into 731 human sinus grafts. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2006. 21:94–102.18. Nkenke E, Schelgel A, Schultze-Mosgau S, Neukam FW, Wiltfang J. The endoscopically controlled osteotome sinus floor elevation:a preliminary prospective study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2002. 17:557–566.19. Winter AA, Pollack AS, Odrich RB. Placement of implants in the severely atrophic posterior maxilla using localized management of the sinus floor:a preliminary study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2002. 17:687–695.20. Van den Bergh JP, Ten Bruggenkate CM, Krekeler G, Tuinzing DB. Sinus floor elevation and grafting with autogenous iliac crest bone. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1998. 9:429–435.
Article21. Ferrigno N, Laureti M, Fanali S. Dental implants in conjuction with osteotome sinus floor elevation:a 12-year life-table analysis from a prospective study on 588 ITI implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006. 17:194–205.
Article22. Cavicchia F, Bravi F, Petrelli G. Localized augmentation of the maxillary sinus floor through a coronal approach for the placement or implants. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2001. 21:475–485.23. Toffler M. Osteotome-mediated sinus floor elevation:a clinical report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2004. 19:266–273.24. Herzberg R, Dolev E, Schwarz-Arad D. Implant marginal bone loss in maxillary sinus grafts. Int J Oral maxillofac Implants. 2006. 21:103–110.25. Aaboe M, Pinholt EM, Hjorting-Hansen E. Healing of experimentally created defects: a review. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1995. 33:312–318.
Article26. Coombs CJ, Mutimer KL, Holmes AD, et al. Osseointegration in sinus-forming bone. Plast and Reconstr Surg. 1995. 95:866–875.
Article27. Schelgel AK. Long term results with Bio-oss bone replacement material. Schweiz Monatsschr Zahnmed. 1996. 106:141–149.28. McAllister BS, Marqolin MD, Cogan AG, et al. Eighteen-month radiographic and histologic evaluation of sinus grafting with anorganic bovine in the chimpanzee. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1999. 14:361–368.29. Hallman M, Sennerby L, Lundgren S. A clinical and histologic evaluation of implant integration in the posterior maxilla after sinus floor augmentation with autogenous bone, bovine hydroxyapatite, or a 20:80 mixture. Int J Oral maxillofac Implants. 2002. 17:635–643.30. Lee JH, Jung UW, Kim CS, et al. Maxillary sinus augmentation using macroporous biphasic calcium phosphate (MBCP): three case report with histologic evaluation. J Korean Acad Periodontol. 2006. 36:567–577.
Article31. Kim MS, Choi SH, Cho KS, et al. A cumulative survival of implants installed on posterior maxilla augmented using MBCP after 2 years of loading: a retrospective clinical study. J Korean Acad Periodontol. 2008. 38:669–678.
Article32. Buser D, Schenk RK, Steinemann S, et al. Influence of surface characteristics on bone integration of titanium implants. A histomorphometric study in miniature pigs. J Biomed Mater Res. 1992. 26:831–833.
Article33. Wallace SS, Froum SJ. Effect of maxillary sinus augmentation on the survival of endosseous dental implants. A systemic review. Ann Periodontol. 2003. 8:328–343.
Article34. Hong SB, Chai GJ, Jung UW, et al. Clinical evaluation of Brnemark Ti-unite implants and ITI SLA implant in the post maxillary area with sinus evaluation technique. J Korean Acad Periodontol. 2005. 35:813–822.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical evaluation of Branemark Ti-Unite implant and ITI SLA implant in the post maxillary area with sinus elevation technique
- Results of Maxillary Sinus Elevation for Endosseous Implant Placement
- The use of Autologous Venous Blood for Maxillary Sinus Floor Augmentation in Conjunction with the Sinus Membrane Elevation: An Experimental Study
- Survival rate of Astra Tech implants with maxillary sinus lift
- Resorption of bone graft after maxillary sinus grafting and simultaneous implant placement