Clinical Results and Some Problems of Multifocal Apodized Diffractive Intraocular Lens Implantation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Gangnam St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. mskim@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2211726
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2008.49.8.1235
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: To evaluate near and far visual outcomes, subjective visual symptoms, and patient satisfaction with AcrySof(R) ReSTOR(R) diffractive multifocal intraocular lenses (IOL), and to study the reasons for postoperative dissatisfaction.
METHODS
Twenty-three eyes of 19 patients received phacoemulsifications and implantation of AcrySof(R) ReSTOR(R) IOL. The main outcome measures, taken at postoperative 1 day, 1 week, 1 month, and 3 months, were uncorrected and corrected near and distant visual acuity, refractory errors, subjective visual symptoms (glare, halo, and night vision), and satisfaction.
RESULTS
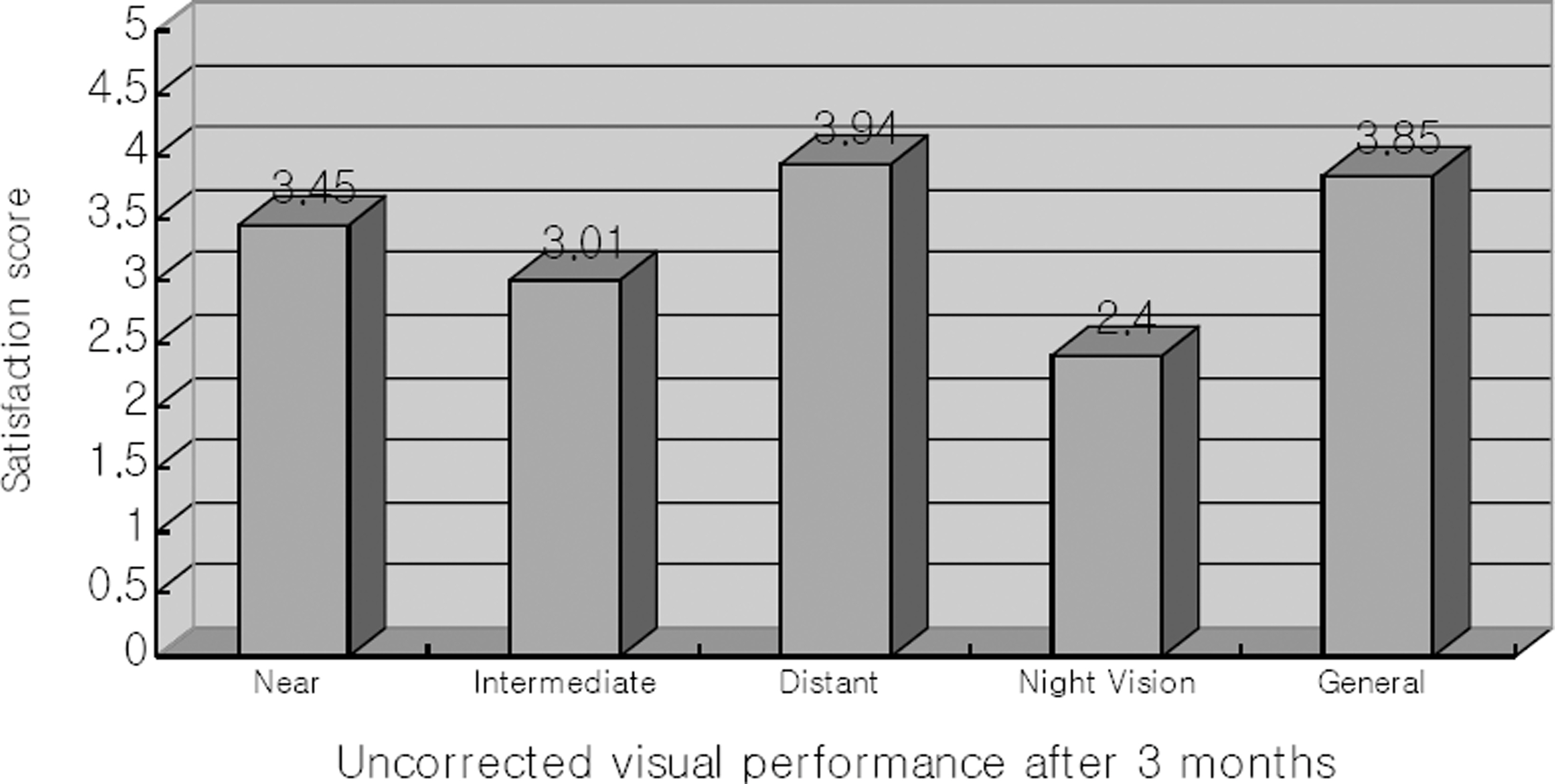
At the 3-month postoperative visit, the mean uncorrected near and distant visual acuities were 0.59+/-0.24 (0.25+/-0.22 LogMAR unit) and 0.78+/-0.27 (0.13+/-0.10 LogMAR unit), respectively. In addition, patients' satisfaction with uncorrected near vision, intermediate vision, far vision, and general visual performance were better than their satisfaction with night vision. Glare and halos were reported as severe by only 10.2% and 5.3% of patients, respectively. The seven eyes with poor patient satisfaction included eyes with a high incidence of preoperative ocular diseases or preoperative and postoperative high corneal astigmatisms of more than 1.0 diopter.
CONCLUSIONS
The AcrySof(R) ReSTOR(R) IOL demonstrated good near and distant visual acuity with good patient satisfaction. Previous ocular disease, corneal astigmatism less than 1.0 diopter, and patient lifestyle should be considered to enhance patient satisfaction.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 12 articles
-
Clinical Outcomes of Diffractive Aspheric Trifocal Intraocular Lens Implantation
Jung Hyun Lee, Young Joo Cho, Tae Hyung Lim, Kee Yong Choi, Beom Jin Cho
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2018;59(2):145-152. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2018.59.2.145.Comparisons of Visual Acuity, Spherical Aberration and Contrast Sensitivity among Spheric, Aspheric ReSTOR®, and Crystalens HD® Lenses
Eui Chun Kang, Eung Kweon Kim, Tai-im Kim
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2011;52(11):1275-1280. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2011.52.11.1275.Comparative Study of Clinical Outcomes Between 2 Types of Multifocal Aspheric Intraocular Lenses
Yu Li Park, Gyu Yeon Hwang, Choun Ki Joo
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013;54(8):1199-1207. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2013.54.8.1199.Clinical Outcomes of Diffractive Multifocal Toric Intraocular Lens Implantation
Jee Hyun Kim, Sung Yu, Sung Hyun Koo, Gwang Ja Lee, Kyoo Won Lee, Young Jeung Park
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014;55(8):1139-1149. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2014.55.8.1139.Clinical Results and Optical Quality of Diffractive Multifocal IOL Implantation after Myopic Refractive Surgery
Jae Hong Park, Dong Seob Ahn, Sang Jeong Moon, Dong Jun Lee, Sang Youp Han, Kyung Heon Lee
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014;55(12):1779-1786. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2014.55.12.1779.Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Refractive Aspheric Multifocal IOL Implantation
Sung Yu, Jee Hyun Kim, Gwang Ja Lee, Kyoo Won Lee, Young Jeung Park
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014;55(7):991-1000. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2014.55.7.991.Clinical Outcomes of Diffractive Aspheric Trifocal Intraocular Lens Implantation
Su Chan Lee, Jae Woo Kim, Tae Hyung Lim, Kee Yong Choi, Beom Jin Cho
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2015;56(9):1338-1344. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2015.56.9.1338.Clinical Outcomes of Diffractive Trifocal Intraocular Lens in Both Eyes: A 6-Month Follow-Up
Young Ki Kwon, Hong Kyun Kim, Jun Hun Lee
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2015;56(9):1331-1337. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2015.56.9.1331.Clinical Results and Optical Quality of Diffractive Multifocal Intraocular Lens
Jeong Jae Oh, Jin Seok Choi
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2015;56(12):1867-1873. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2015.56.12.1867.Comparison of Clinical Outcomes between Diffractive and Refractive Multifocal Intraocular Lens with Same Near Added
Jee Hyun Kim, Eun Joo Kim, Yong Il Kim, Gwang Ja Lee, Kyoo Won Lee, Young Jeung Park
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2015;56(6):875-884. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2015.56.6.875.A Case of Acute Angle Closure Caused by Dislocation of Accommodative Intraocular Lens
Hyun Ji Hwang, Young Hoon Hwang, Jung Jin Lee, Byoung Yeop Kim
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2016;57(9):1493-1497. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2016.57.9.1493.Clinical Efficacy of Bunny Multifocal Intraocular Lens after Cataract Surgery
Myung Ho Cho, Jae Yeong Park, Byung Gun Park, Jong Soo Lee
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2018;59(12):1129-1136. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2018.59.12.1129.
Reference
-
References
1. Kohnen T, Allen D, Boureau C. . European multicenter study of the AcrySof ReSTOR apodized diffractive intraocular lens. Ophthalmology. 2006; 113:578–84.
Article2. Toto L, Falconio G, Vecchiarino L. . Visual performance and biocompatibility of 2 multifocal diffractive IOLs:six-month comparative study. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007; 33:1419–25.3. Alfonso JF, Fernández-Vega L, Baamonde MB, Montés-Micó R. Prospective visual evaluation of apodized diffractive intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007; 33:1235–43.
Article4. Blaylock JF, Si Z, Vickers C. Visual and refractive status at different focal distances after implantation of the ReSTOR multifocal intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:1464–73.
Article5. Vander schueren I, Zeyen T, D'heer B. Multifocal IOL implantation: 16 cases. Br J Ophthalmol. 1991; 75:88–91.6. Sen HN, Sarikkola AU, Uusitalo RJ, Laatikainen L. Quality of vision after AMO Array multifocal intraocular lens implantation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004; 30:2483–93.
Article7. Davison JA, Simpson MJ. History and development of the apodized diffractive intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:849–58.
Article8. Slagsvold JE. 3M diffractive multifocal intraocular lens: eight year follow-up. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000; 26:402–7.
Article9. Vingolo EM, Grenga P, Iacobelli L, Grenga R. Visual acuity and contrast sensitivity: AcrySof ReSTOR apodized diffractive versus AcrySof SA60AT monofocal intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007; 33:1244–7.
Article10. Tochel CM, Morton JS, Jay JL, Morrison JD. Relationship between visual field loss and contrast threshold elevation in glaucoma. BMC Ophthalmol. 2005; 13:22–8.
Article11. Gardiner AM, Armstrong RA, Dunne MC, Murray PI. Correlation between visual function and visual ability in patients with uveitis. Br J Ophthalmol. 2002; 86:993–6.
Article12. Ellemberg D, Lewis TL, Maurer D. . Spatial and temporal vision in patients treated for bilateral congenital cataracts. Vision Res. 1999; 39:3480–9.
Article13. Hayashi K, Hayashi H, Nakao F, Hayashi F. Influence of astigmatism on multifocal and monofocal intraocular lenses. Am J Ophthalmol. 2000; 130:477–82.
Article14. Chiam PJ, Chan JH, Aggarwal RK, Kasaby S. ReSTOR intraocular lens implantation in cataract surgery: quality of vision. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:1459–63.
Article15. Randazzo A, Nizzola F, Rossetti L. . Pharmacological management of night vision disturbances after refractive surgery Results of a randomized clinical trial. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005; 31:1764–72.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pseudoaccomodation in Pseudophakic Eyes with 3M Multifocal Intraocular Lens
- Clinical Results of 3M Multifocal Intraocular Lens
- Multifocal Intraocular Lens Implantation after Pars Plana Vitrectomy to Treat Retinal Detachment
- Clinical Outcomes of Diffractive Multifocal Toric Intraocular Lens Implantation
- Comparison of the Visual Outcomes after Cataract Surgery with Implantation of a Bifocal and Trifocal Diffractive Intraocular Lens