J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2008 May;49(5):811-818. 10.3341/jkos.2008.49.5.811.
A Study of the Anatomical Characteristics of External Ocular Muscles in Adults Cadavers
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, College of Medicine, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. eyeshin@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2211712
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2008.49.5.811
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: This research was performed to investigate if the insertion site of the rectus muscle and the type of the insertion anatomically correspond for both eyes in Korean cadavers.
METHODS
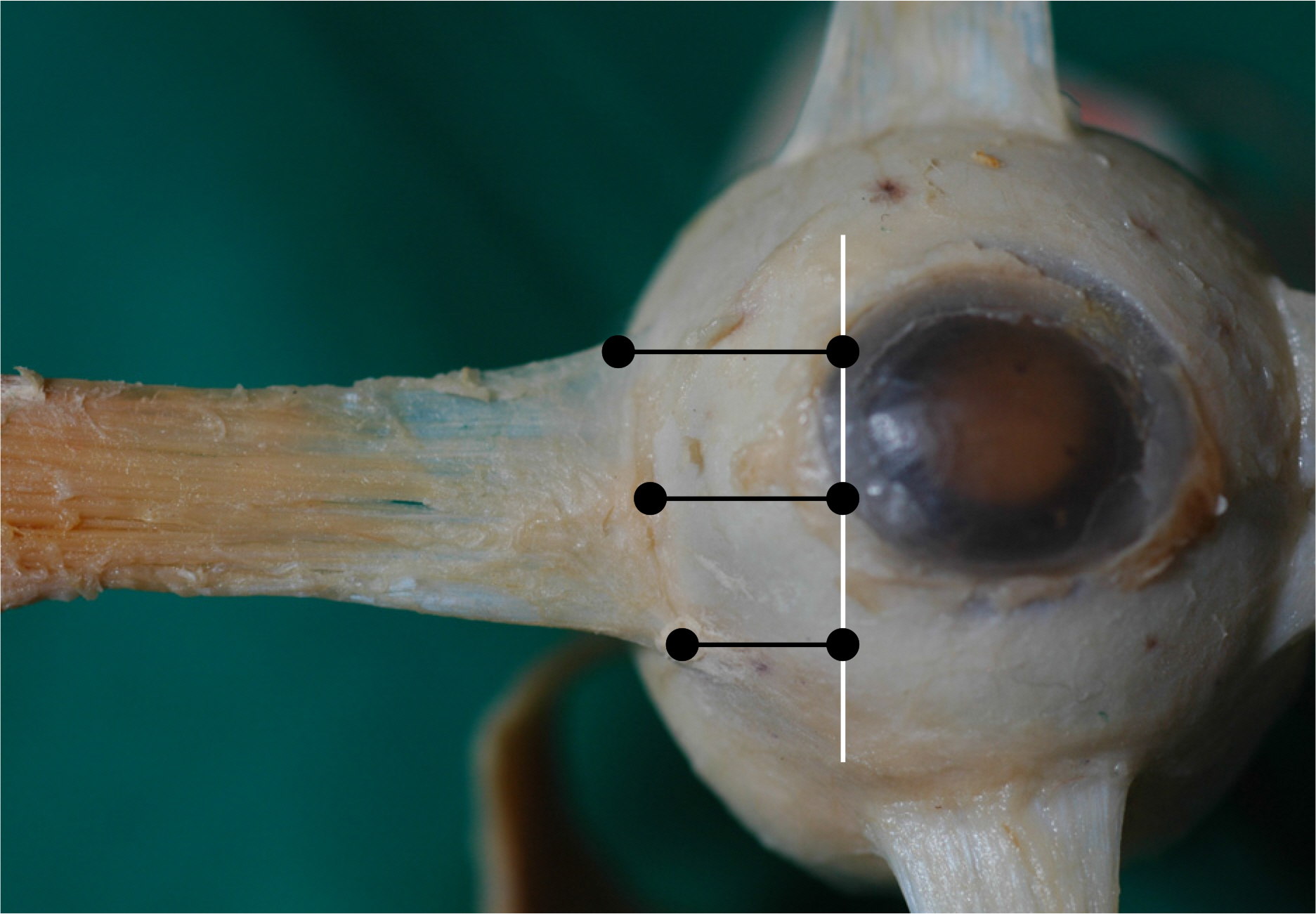
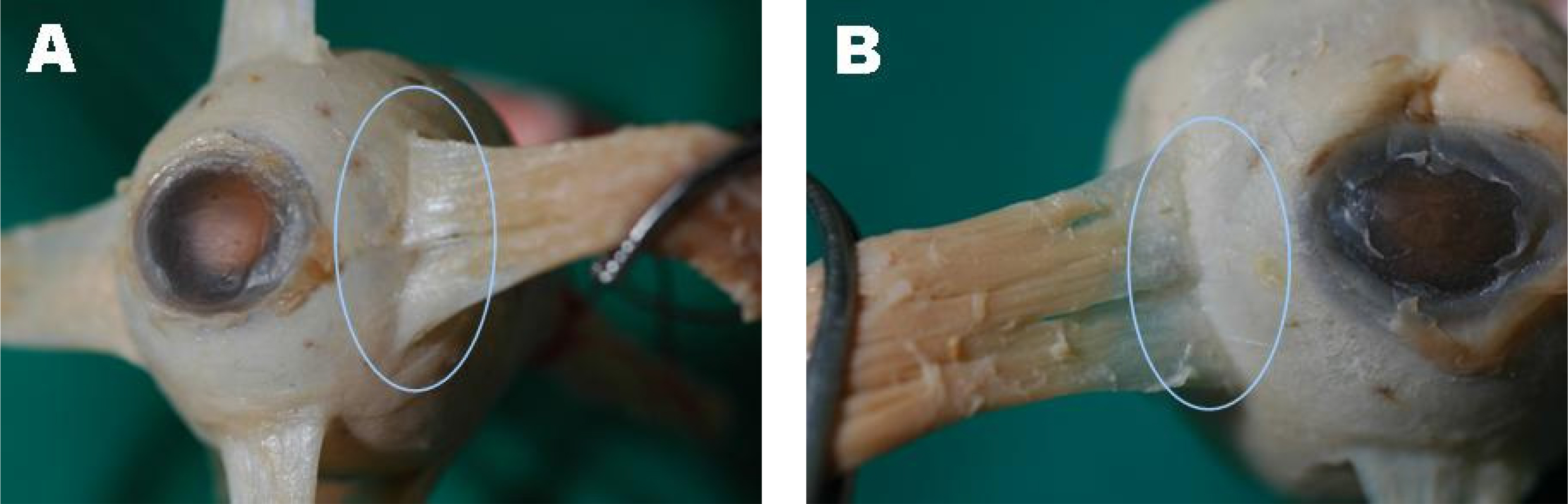
Thirty-four eyes from seventeen cadavers were anatomized for this research. We measured minimum distances from the insertion of each muscle to the tangential lines passing through the corneal limbus using a vernier caliper. Center, temporal, and nasal portions are used as an insertion for the vertical muscle, while center, upper, and lower portions are used as an insertion for the horizontal muscle. The average values of those minimum distances were compared for both eyes. Moreover, the type of the insertion of the rectus muscle is observed to determine whether it is identical for both eyes.
RESULTS
Anatomical data does not show a significant difference between the right and left eyes except for the distance from an insertion of the inferior and lateral rectus muscle to the corneal limbus. With regard to the morphologic type of the insertion, the most common types are oblique and nonspecific shapes in the vertical muscles, and straight and concave shapes in the horizontal muscles.
CONCLUSIONS
Although there was not a significant difference between the eyes, precautions should still be taken during eye operations due to possible anatomical differences between the eyes.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Chang BR. Insertion and width of the vertical rectus muscles in vertical strabismus. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1992; 33:176–9.2. Fuchs E. Beitrage zur normalen Anatomie des Augapfels. Albrecht zon Graefes Arch Klin Exp Ophthalmol. 1884; 30:1–21.3. Apt L. Anatomical reevaluation of rectus muscle insertion. Trans Am Ophthalmol. 1980; 78:365–76.4. Paik HJ, Cho YA. Insertion of horizontal rectus muscles in strabismus. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1989; 30:761–6.5. Weiss L. Uber das Wachstum des Menschlichen Auges und uber die Veranderung der Muskelinsertionen am wachsenden Auge. Anatomische Hefte. 1987; 8:193–248.6. Von Gat L. Ein bertrag zur Topographie des Anasatzes des vier geraden Augenmuskeln. Ophthalmologica. 1947; 114:43–51.7. Scobee RG. Anatomic factors in the etiology of heterotopia. Am J Ophthalmol. 1948; 31:781–5.8. Postic G. On the mechanism of action of supra- and infraposition insertions of the horizontal motor muscles in the surgical correction of the A and V syndrome in strabismus. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1963; 165:540–4.9. Kushner BJ, Morton GV. A randomized comparison of surgical procedures for infantile esotropia. Am J Ophthalmol. 1984; 98:50–61.
Article10. Jansson F. Measurements of intraocular distance by ultrasound. Acta Ophthalmol. 1963; 74:1–11.11. Yamamoto Y. A new study on the measurement of ocular axial length by ultrasound echography. Acta Soc Ophthalmol. 1960; 64:1333–8.12. Sorsby A. Ultrasonographic measurement of the components of ocular refraction in life. Vision Res. 1963; 3:499–507.
Article13. Duke Elder. System of Ophthalmology. CV Mosby: St. Louis;Vol. 2:1961. p. 81–90.14. Lee YC, Yang SW. Anatomical evaluations of the location and insertion shape of horizontal rectus muscle. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1995; 36:1357–62.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Satellite cell distribution in the medial rectus muscle in cadavers
- Profiles, tissue, and microbial integrity of cadavers used in medical faculties in South-western Uganda: implication in anatomical education
- Anatomical Study of Musculus Pyramidalis in Korean Adults
- The Study on the Menisci of Korean Adults
- Morphometric Study of Fibularis Brevis and Fibularis Digiti Quinti Muscles Insertion Patterns