J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2008 Apr;49(4):577-582. 10.3341/jkos.2008.49.4.577.
Intraocular Pressure Measurements Using Dynamic Contour Tonometer After Photorefractive Keratectomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1National Health Insurance Corporation Ilsan Hospital, Gyeonggi, Korea.
- 2The Institute of Vision Research, Department of Ophthalmology, College of Medicine, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea. eungkkim@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
- KMID: 2211487
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2008.49.4.577
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: To assess the performance of the dynamic contour tonometer (DCT) in eyes undergoing excimer laser photorefractive keratectomy (PRK).
METHODS
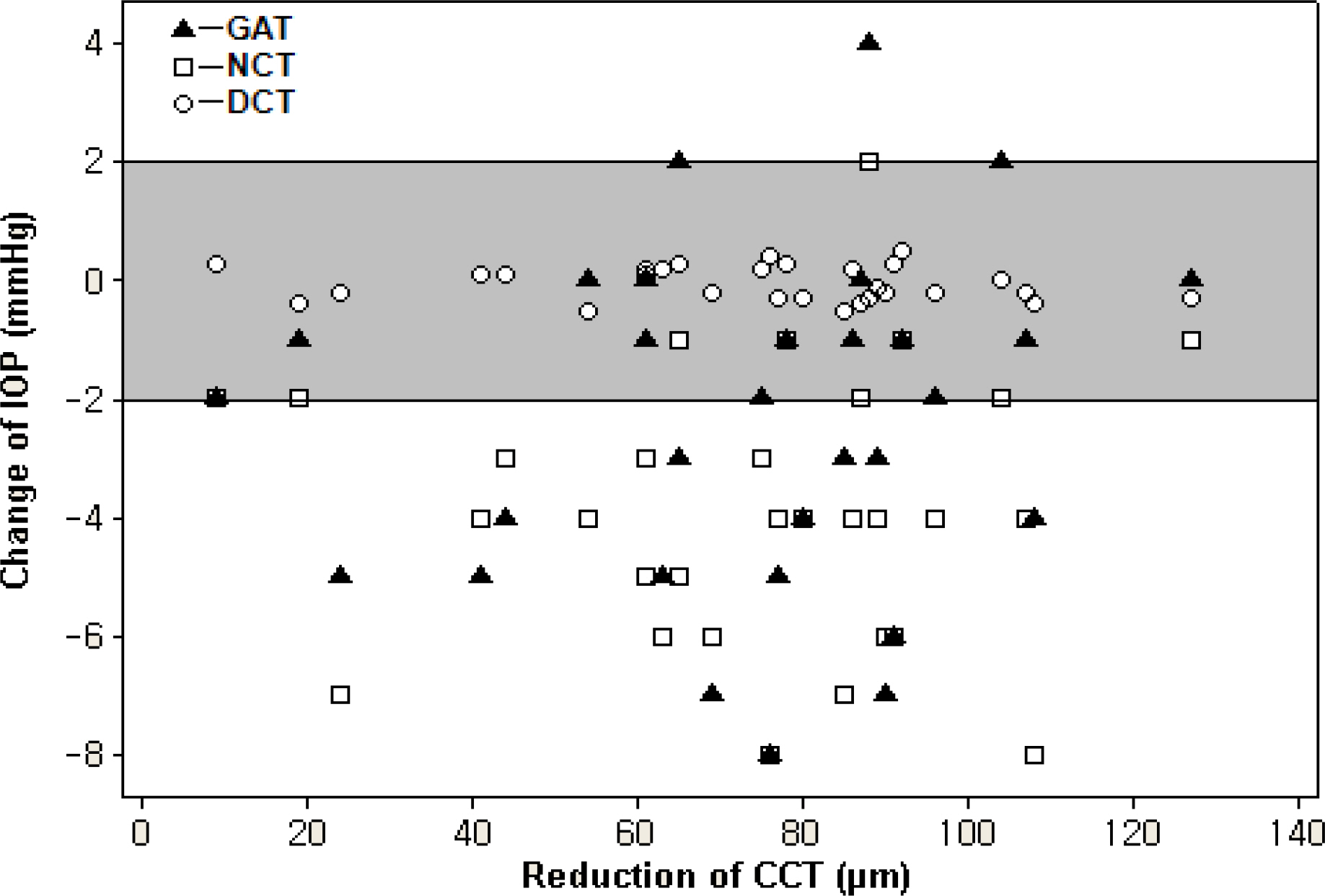
Intraocular pressure (IOP) was measured in 30 eyes after first time excimer laser PRK pre and three months post operatively using Goldmann applanation tonometer (GAT), noncontact air tonometer (NCT), and the DCT.
RESULTS
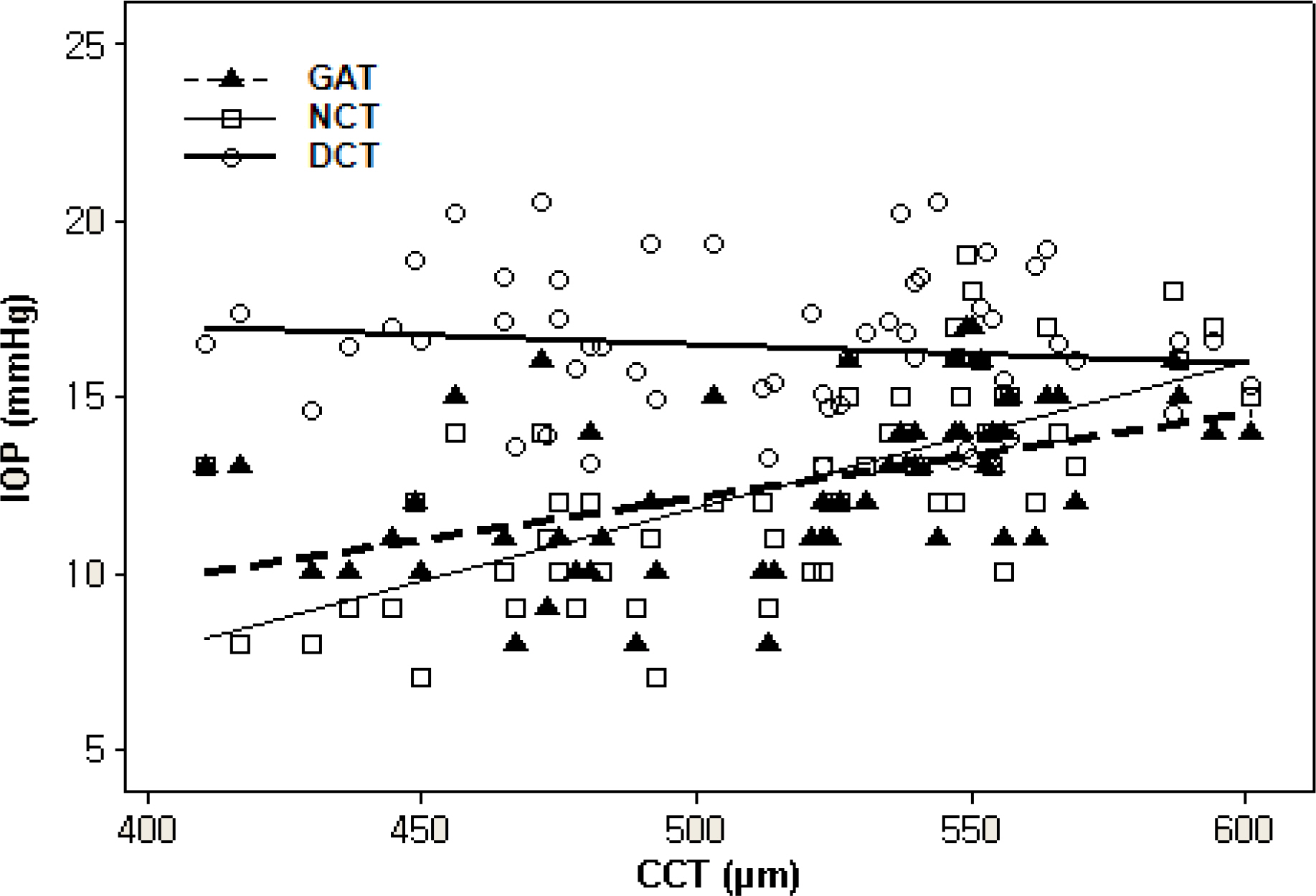
There was significant correlation between central corneal thickness (CCT) and IOP measurements by GAT and NCT (CCT vs GAT: r2=0.31, p<0.01, CCT vs NCT: r2=0.39, p<0.01). However, the correlation between CCT and IOP measurements by DCT was not significant (CCT vs DCT: r2=0.14, p=0.32). After PRK, the mean change in CCT and IOP measurements using GAT, NCT, DCT were 73.70+/-26.92 micrometer (mean+/-SD), 2.43+/-2.86 mmHg (p<0.01), 3.83+/-2.34 mmHg (p<0.01) and 0.44+/-1.51 mmHg (p=0.125), respectively. The preoperative and postoperative DCT measurements did not differ significantly.
CONCLUSIONS
The reduction in CCT induced by PRK doesn't appear to influence DCT measurements; therefore, DCT may be better suited over GAT or NCT for monitoring IOP in eyes that underwent refractive surgery.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Comparison of Dynamic Contour Tonometry and Goldmann Applanation Tonometry in Relation to Central Corneal Thickness
Min Kyo Kim, Si Yoon Park, Chan Yun Kim, Ji Hyun Kim
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2015;56(9):1392-1399. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2015.56.9.1392.Measurements of Dynamic Contour Tonometry After Penetrating Keratoplasty and EpiLASIK
Seung-Jin Lee, Hyun Soo Lee, Choun-Ki Joo
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009;50(5):749-755. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2009.50.5.749.
Reference
-
References
1. Wolfs RC, Klaver CC, Vingerling JR, et al. Distribution of central corneal thickness and its association with intraocular pressure: the Rotterdam Study. Am J Ophthalmol. 1997; 123:767–72.
Article2. Whitacre MM, Stein RA, Hassanein K. The effect of corneal thickness on applanation tonometry. Am J Ophthalmol. 1993; 115:592–6.
Article3. Robertritch M. Bruce shields. Glaucoma, Intraocular pressure and tonometry. 2nd ed.2. St. Louis: Mosby;1996. p. 407–28.4. Dimitrios SS, Georgios IP, Carlos M. Assessment of the Pascal dynamic contour tonometer in monitoring intraocular pressure in unoperated eyes and eyes after LASIK. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004; 30:746–51.5. Hamilton DR, Manche EE, Rich LF, Maloney RK. Steroid-induced glaucoma after laser in situ keratomileusis associated with interface fluid. Ophthalmology. 2002; 109:659–65.
Article6. Shaikh NM, Shaikh S, Singh K, Manche E. Progression to end-stage glaucoma after laser in situ keratomileusis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:356–9.
Article7. Levy Y, Hefetz L, Zadok D, et al. Refractory intraocular pressure increase after photorefractive keratectomy. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1997; 23:593–4.
Article8. Kaufmann C, Bachmann LM, Thiel MA. Intraocular Pressure Measurements Using Dynamic Contour Tonometry after Laser In Situ Keratomileusis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003; 44:3790–4.
Article9. Kniestedt C, Nee M, Stamper RL. Dynamic Contour Tonometry, A Comparative study on Human Cadaver Eyes. Arch Ophthalmol. 2004; 122:1287–93.10. Kaufmann C, Bachmann LM, Thiel MA. Comparison of Dynamic Contour Tonometry with Goldmann Applanation Tonometry. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004; 45:3118–21.
Article11. Shih CY, Graff Zivin JS, Trokel SL, Tsai JC. Clinical significance of central corneal thickness in the management of glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 2004; 122:1270–5.12. Koh SI, Kim SD, Kim JD. The effect of the changes in Central Corneal Thickness and Curvature on Measurement of Intraocular Pressure after LASIK. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:2464–72.13. Wittenberg S, Green MK. The effect of tears in intraocular pressure as measured with the NCT. Invest Ophthalmol. 1976; 15:139–42.14. Kwon GR, Kang SW, Kee CW. The influence of Central Corneal Thickness on Intraocular pressures Measured with Goldmann Applanation Tonometer and Non-contact Tonometer. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1998; 39:1494–8.15. Ehlers N, Bramsen T, Sperling S. Applanation tonometry and central corneal thickness. Acta Ophthalmol. 1975; 53:34–43.
Article16. Johnson M, Kass MA, Moses RA, Grodzki WJ. Increased corneal thickness simulating elevated intraocular pressure. Arch Ophthalmol. 1978; 96:664–5.
Article17. Ohmer F, Hikmet H, Nurullah C, Hikmet S. Relation between corneal thickness and intraocular pressure measurement by noncontact and applanation tonometry. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2001; 27:1787–91.18. Mardelli PG, Piebenga LW, Whitacre MM, Siegmund KD. The effect of excimer laser photorefractive keratectomy on intraocular pressure measurements using the Goldmann applanation tonometer. Ophthalmology. 1997; 104:945–9.
Article19. Faucher A, Gregoire J, Blondeau P. Accuracy of goldmann tonometry after refractive surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1997; 23:832–8.
Article20. Schipper I, Senn P, Thomann U, Suppiger M. Intraocular pressure after excimer laser photorefractive keratectomy for myopia. J Refract Surg. 1995; 11:366–70.
Article21. Chatterjee A, Shah S, Bessant DA, et al. Reduction in intraocular pressure after excimer laser photorefractive keratectomy; correlation with pretreatment myopia. Ophthalmology. 1997; 104:355–9.22. Schipper I, Senn P, Thomas U, Suppinger M. Intraocular pressure after excimer laser photorefractive keratectomy for myopia. J Refract Corneal Surg. 1995; 11:366–70.
Article23. Zadok D, Tran DB, Twa M, et al. Pneumotonometry versus Goldmann tonometry after laser in situ keratomileusis for myopia. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1999; 25:1344–8.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Difference between Goldmann Applanation and Topcon Noncontact Tonometer Measurements after Excimer Laser Photorefractive Keratectomy
- Clinical Comparision of the ProTon and the Goldmann Applanation Tonometer
- The Differences of IOP and Factors Influencing IOP Measured by Goldmann Applanation Tonometer after Photore fractive Keratectomy and Laser In Situ Keratomileusis in Myopic Eyes between -4~-7 Diopters
- A Case of Intraocular Pressure Rise with Iridocyclitis after Photorefractive Keratectomy
- The Result of Photorefractive Keratectomy Treated with 0.1% Fluorometholone and Tranilast Eye Drops