J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2008 Jan;49(1):104-110. 10.3341/jkos.2008.1.104.
Multifocal Electroretinogram before and after Epiretinal Membrane Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Sungmo Eye Hospital, Pusan, Korea. heesyoon@dreamwiz.com
- KMID: 2211189
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2008.1.104
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: To assess macular function before and after vitrectomy and membrane removal in epiretinal membranes by means of multifocal electroretinogram (mfERG).
METHODS
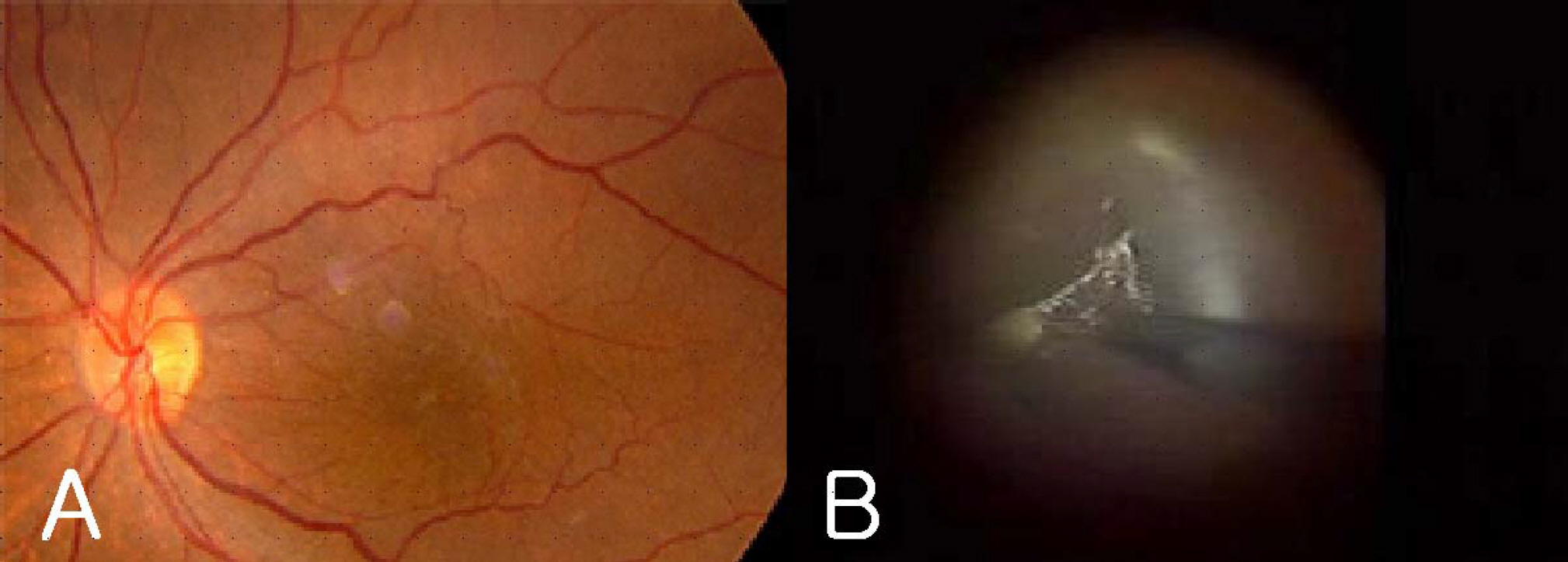
The mfERGs (RETIscan(R), Roland, Germany) of 28 consecutive patients (28 eyes) with idiopathic epiretinal membranes were recorded before epiretinal membrane surgery and 3 to 6 months after surgery. The average retinal response density and implicit time of each local response were estimated as anatomic macular areas corresponding roughly to 5 rings. Preoperative and postoperative responses of mfERG were compared. The correlation of the change of retinal response density and postoperative macular configuration on optical coherent tomography (OCT) was statistically analyzed.
RESULTS
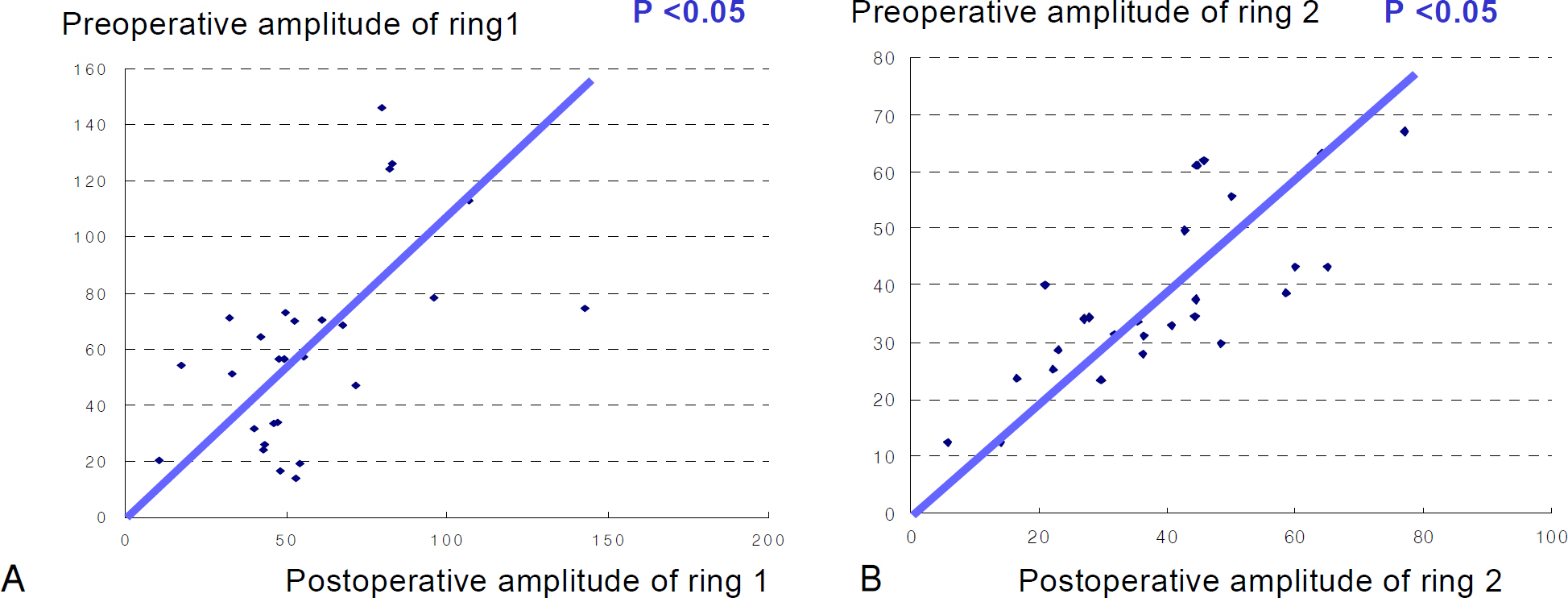
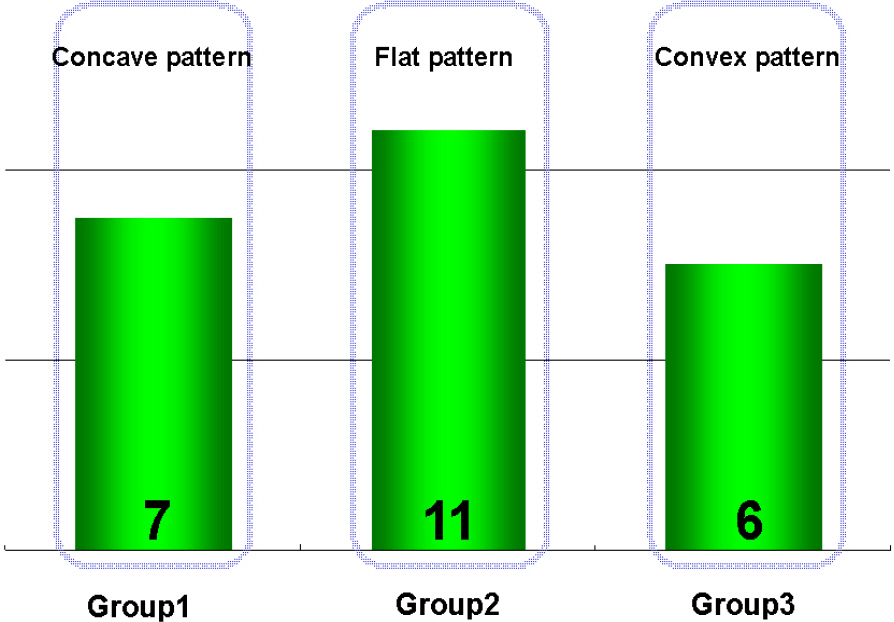
The postoperative value of P1 amplitude and implicit time were not statistically correlated with the preoperative value (p>0.05). There were no significant correlations between the changes of rings 1 and 2 with regard to the retinal response density of the mfERGs and visual acuity. There was no significant correlation between the change of retinal response density and postoperative macular configuration according to OCT.
CONCLUSIONS
The use of mfERGs does not seem useful for predicting clinical prognosis after epiretinal membrane surgery. Further studies of influence of internal limiting membrane removal on mfERG response should be conducted.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Morphologic and Functional Evaluation before and after Vitrectomy in Idiopathic Epiretinal Membrane Patients Using Microperimetry
Sam Seo, Han Woong Lim, Yong Un Shin, Min Ho Kang, Min Cheol Seong, Hee Yoon Cho
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013;54(6):893-901. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2013.54.6.893.
Reference
-
References
1. Wise GN. Clinical features of idiopathic preretinal macular fibrosis. Am J Ophthalmol. 1975; 79:349–7.
Article2. Choi YK, Yoo JS, Kim MH. Result of surgery for epiretinal membrane and their recurrence. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2000; 41:2357–62.3. Michels RG. Vitrectomy for macular pucker. Ophthalmology. 1984; 91:1384–8.
Article4. Hillenkamp J, Saikia P, Gora F, et al. Macular function and morphology after peeling of idiopathic epiretinal membrane with and without the assistance of indocyanine green. Br J Ophthalmol. 2005; 89:437–43.
Article5. Fish GE, Birch DG. The focal electroretinogram in the clinical assessment of macular disease. Ophthalmology. 1989; 96:109–14.
Article6. Moschos M, Apostolopoulos M, Ladas J, et al. Multifocal ERG changes before and after macular hole surgery. Doc Ophthalmol. 2001; 102:31–40.7. Kondo M, Miyake Y, Horiguchi M, et al. Clinical evaluation of multifocal electroretinogram. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1995; 36:2146–56.8. Ohn YH, Ahn YS. Clinical applications of multifocal electroretinography (mfERG). J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2002; 43:1901–17.9. Moschos M, Apostolopoulos M, Ladas J, et al. Assessment of macular function by multifocal electroretinogram before and after epimacular membrane surgery. Retina. 2001; 21:590–5.
Article10. Nagatomo A, Nao-i N, Maruiwa F, et al. Multifocal electroretinograms in normal subjects. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 1998; 42:129–35.
Article11. Hood DC. Assessing retinal function with the multifocal technique. Pro Retin Eye Res. 2000; 19:607–46.
Article12. Li D, Horiquchi M, Kishi S. Tomographic and multifocal electroretinographic features of idiopathic epimacular membranes. Arch Ophthalmol. 2004; 122:1462–7.13. Lee YD, Bae SR. Normal values of positive wave in the multifocal electroretinography in Korean. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003; 44:850–6.14. Lai TY, Kwok AK, Au AW, Lam DS. Assessment of macular function by multifocal electroretinography following epiretinal membrane surgery with indocyanine green-assisted internal limiting membrane peeling. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2007; 245:148–54.
Article15. Ueno S, Kondo M, Piao CH, et al. Selective amplitude reduction of the PhNR after macular hole surgery: ganglion cell damage related to ICG-assisted ILM peeling and gas tamponade. Invest Ophthalmo Vis Sci. 2006; 47:3545–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Choroidal Thickness Changes Following Vitrectomy in Epiretinal Membrane Based on the Optical Coherence Tomography Pattern
- Epiretinal Membrane of Combined Hamartoma of Retina and Retinal Pigment Epithelium Versus Idiopathic Epiretinal Membrane
- The Electron Microscopic Feature of Idiopathic and Complicated Epiretinal Membrane
- Surgical Management and Electron Microscopic Features of Idiopathic Epiretinal Membranes
- Electron Microscopic Features of Epiretinal Membrane in Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment