J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2001 Sep;8(3):235-241. 10.4184/jkss.2001.8.3.235.
Evaluation of Posterolateral Fusion Mass at Lumbosacral Junction Using Standard AP and Ferguson Radiographs
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. shmoon@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2209740
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2001.8.3.235
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: To evaluate the reliance of standard AP radiograph and Ferguson radiograph in assessment of instrumented lumbosacral fusion mass with interobserver and intraobserver reproducibilities.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
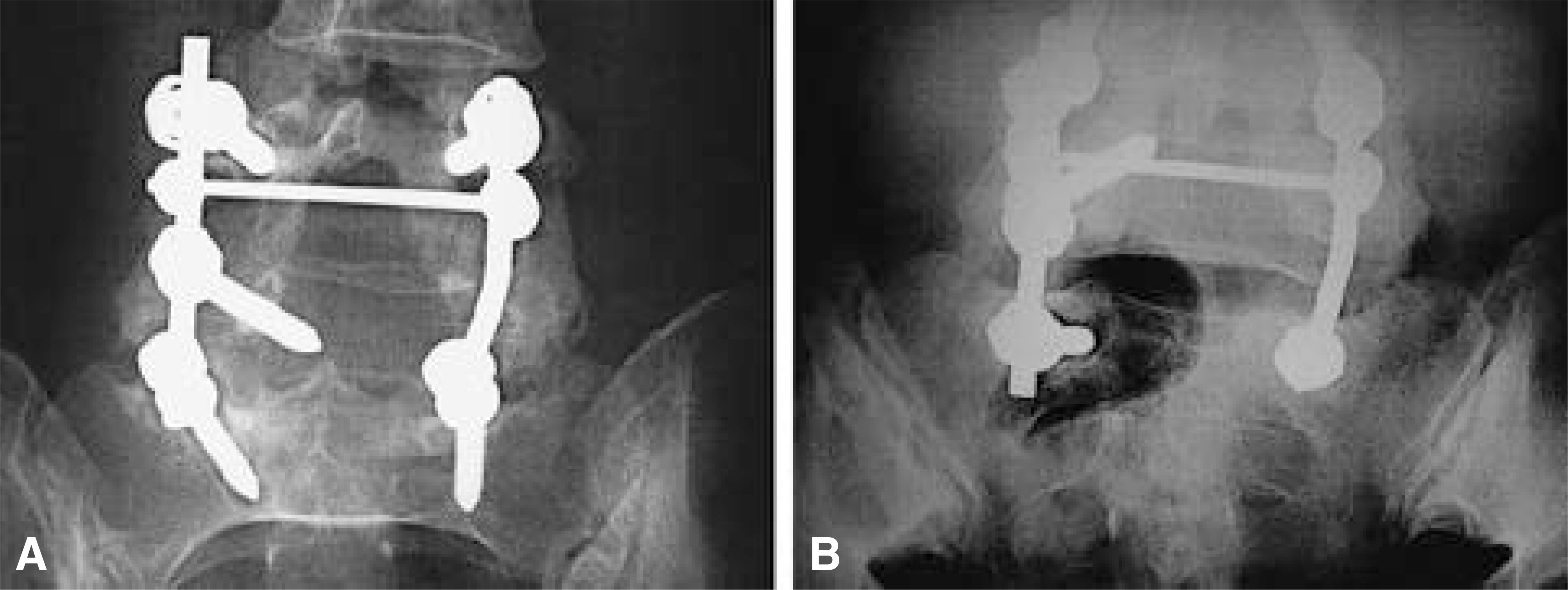
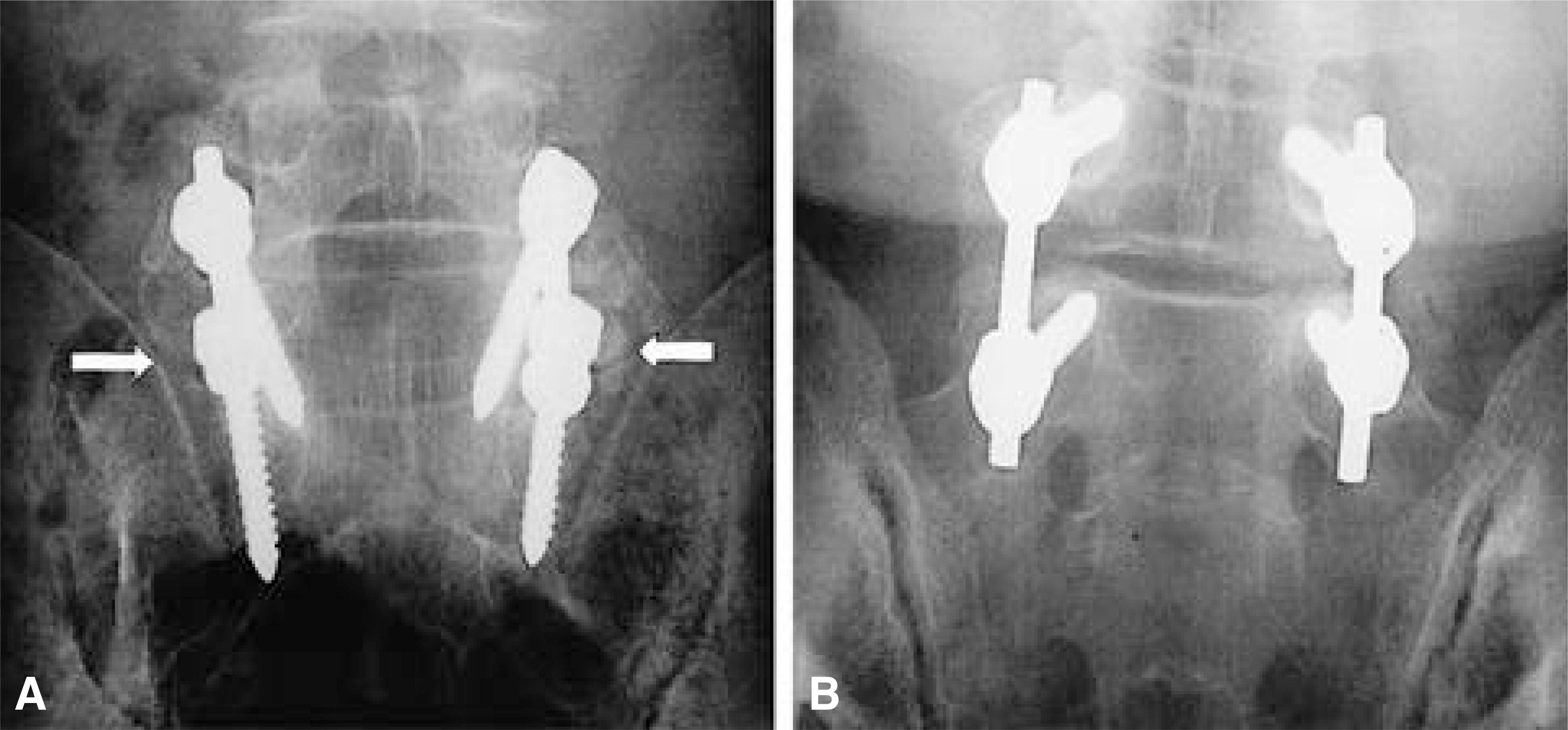
Postoperative standard AP radiograph and Ferguson radiograph were used to evaluate the fusion mass at the lumbosacral region of 44 consecutive patients who underwent posterolateral L4-S1 or L5-S1 instrumented fusion with pedicle screws & autogenous iliac bone graft. Ferguson radiograph was performed with the x-ray beam oriented toward the cranial portion at 40degree relative to the x-ray table. All observations were performed independently by three observers, blinded to the history, diagnosis, and patient identity. The fusion mass was graded as solid, pseudarthrosis or questionable. A second review was repeated at 2 weeks after index review. Interobserver and intraobserver reproducibilities were analyzed with Fleiss'method.
RESULTS
Ferguson radiographs were more reliable than standard AP radiographs in detecting the fusion mass. Kappa values with the interobserver reproducibility were higher in Ferguson radiographs than in the standard AP radiographs. Kappa values with the intraobserver reproducibility of all three observers were higher in Ferguson radiographs than in the standard AP radiographs. The questionable fusion masses in the standard AP radiographs were revealed solid or pseudarthrosis in Ferguson radiographs in 67%.
CONCLUSIONS
Ferguson radiograph is a more reliable method than standard AP radiograph in evaluating instrumented posterolateral fusion mass in lumbosacral region.
Figure
Reference
-
1). Albee FH. Transplantation of a portion of the tibia into the spine for Pott's disease: A preliminary report. JAMA. 42(11):885–886. 1911.2). Blumenthal SL, Gill K. Can lumbar spine radiographs accurately determine fusion in postoperative patients?: correlation of routine radiographs with a second surgical look at lumbar fusions. Spine. 18(9):1186–1189. 1993.3). Brodsky AE, Evan SK, Momtaz AK. Correlation of radiographic assessment of lumbar spine fusions with surgical exploration. Spine. 16:S261–265. 1991.4). Chafetz N, Cann CE, Morris JM, Steinbach LS, Goldbert HI. Pseudarthrosis following lumbar fusion; Detection by direct coronal CT scanning. Radiology. 162:803–805. 1987.
Article5). Christensen FB, Laursen M, Gelineck J, Eiskjær SP, Thomsen K, Bunger CE. Interobserver and intraobserver agreement of radiograph interpretation with and without pedicle screw implants; the need for a detailed classification system in posterolateral spinal fusion. Spine. 26(5):538–544. 2001.6). Dawson EG, Clader TJ, Bassett LW. A comparison of different methods used to diagnose pseudarthrosis following posterior spinal fusion for scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg. 67-A:1153–1159. 1985.
Article7). Deguchi M, Rapoff AJ, Zdeblick T. Posterolateral fusion for isthmic spondylolithesis in adults: analysis of fusion rate and clinical results. J Spinal Disord. 11(6):459–464. 1998.8). DePalma AF, Rothman RH. The nature of pseudarthrosis. Clin Orthop. 59:113–118. 1968.
Article9). Ebraheim NA, Xu R. Assessment of lumbosacral fusion mass by angled radiography: technical notes. Spine. 23(7):842–843. 1998.10). Fleiss JL. Statistical methods for rates and proportions. 2nd ed.New York, John Wiley & Sons: Inc.;p. 229–232. 1981.11). Frymoyer JW, Hanley EN, Howe J, Kuhlmann D, Matteri RE. A comparison of radiographic findings in fusion and nonfusion patients ten or more years following lumbar disc surgery. Spine. 4:435–440. 1979.
Article12). Greenfield RT, Capen DA, Thomas JC, Nelson R, Na-gelberg S, Rimoldi RL, Haye W. Pedicle screw fixation for arthrodesis of the lumbosacral spine in the elderly: an outcome study. Spine. 23(13):1470–1475. 1998.13). Hamill CL, Simmons ED. Interobserver variability in grading lumbar fusions. J Spinal Disord. 10(5):387–390. 1997.
Article14). Hibbs RA. An operation for progressive spinal deformities: A preliminary report of three cases from the service of the orthopaedic hospital. N Y Med J. 93(21):1013–1016. 1911.15). Landis RJ, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 33:159–174. 1977.
Article16). Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Bullis D, Betz RR, Baldus C, Schoenecker PL. Results of in situ fusion for isthmic spondylolithesis. J Spinal Disord. 5(4):433–442. 1992.17). Nachemson A, Zdeblick TA, O'Brien JP. Controversy, Lumbar disc disease with discogenic pain; what surgical treatment is most effective? Spine. 21(15):1835–1838. 1996.18). Rothman RH, Booth R. Failures of spinal fusion. Orthop Clin North Am. 6:299–303. 1971.
Article19). Schwab FJ, Nazarian DG, Mahmud F, Michelsen CB. Effects of spinal instrumentation on fusion of the lumbosacral spine. Spine. 20(18):2023–2028. 1995.
Article20). Stauffer RN, Coventry MB. Posterolateral lumbar spine fusion. J Bone Joint Surg. 54-A:1195–1204. 1972.21). Steinmann JC, Herkowitz HN. Pseudarthrosis of spine. Clin Orthop. 284:80–90. 1992.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Posterolateral Fusion for Unstable Thoracolumbar Junction
- Analysis of Anterior-posterior Distance of Sacral Canal on MRI to See the Possibility of Sacral Laminar Hook Insertion
- Posterior Agumentation with Rectangle Luque for the Treatment of Tuberculosis of the Lumbosacral Junction in Adults
- Radiologic Comparison of the Sacroiliac Joint Degeneration Following Lumbar or Lumbosacral Fusion
- Pelvic Stress Fracture After Long Posterolateral Lumbosacral Fusions: A Case Report