J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2009 Jun;16(2):122-126. 10.4184/jkss.2009.16.2.122.
Multiple Extradural Arachnoid Cyst : A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Seoul Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. hananina@dreamwiz.com
- KMID: 2209606
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2009.16.2.122
Abstract
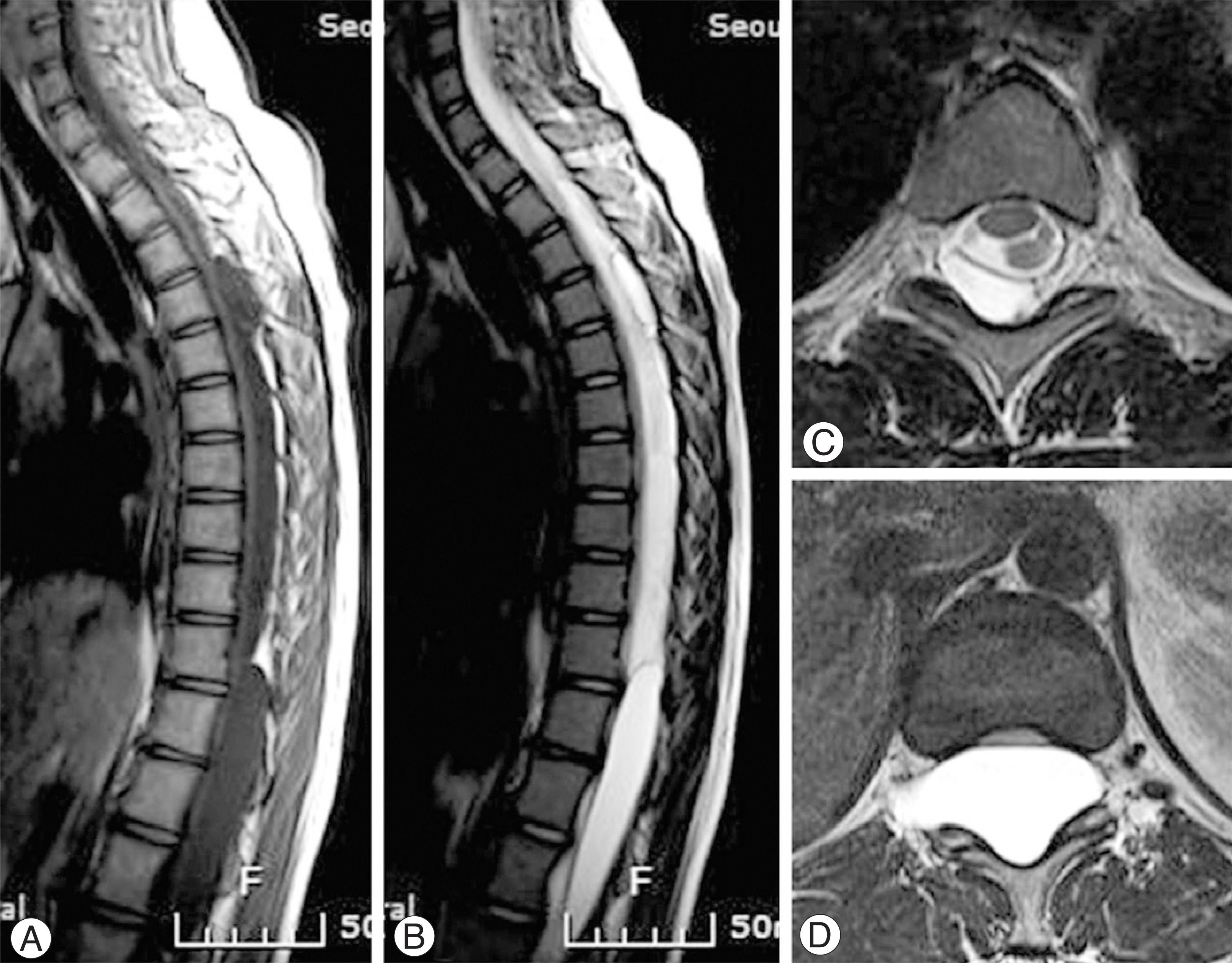
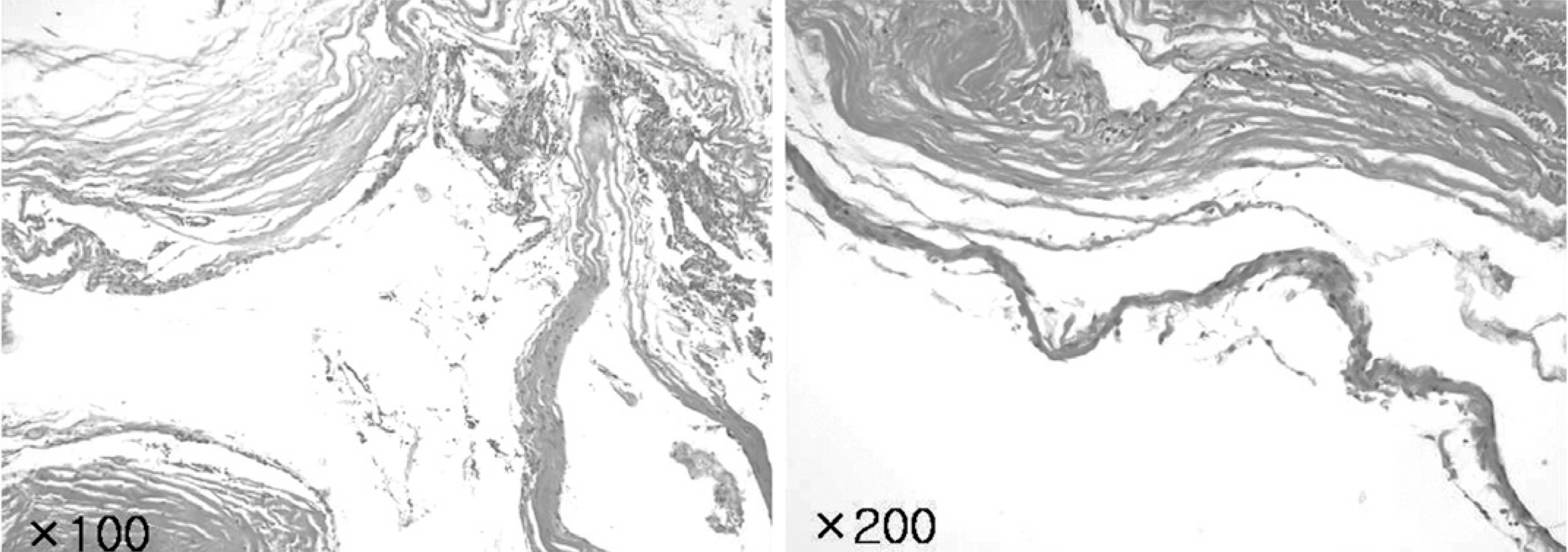
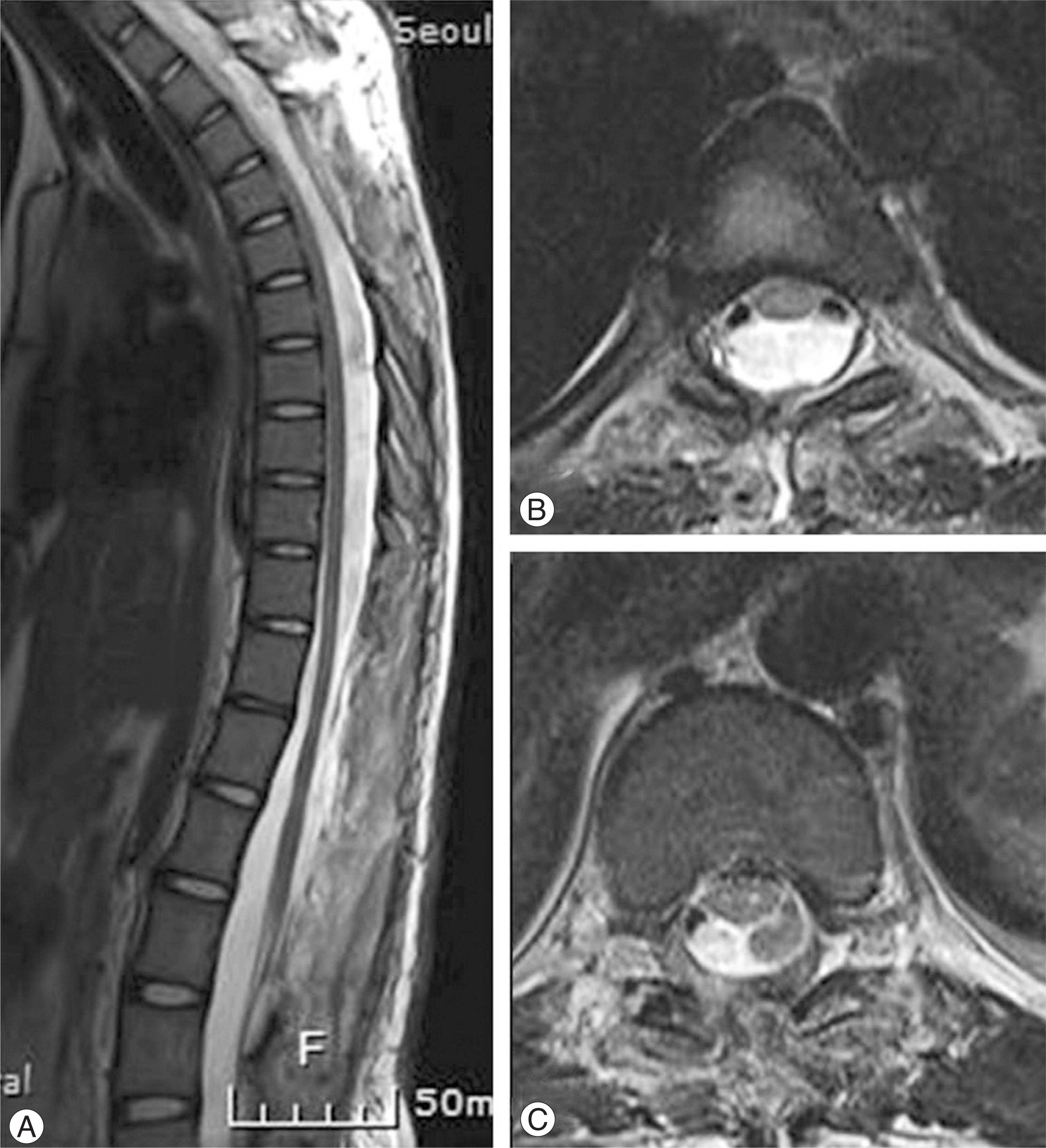
- Multiple extradural arachnoid cysts of the spine are extremely uncommon in children with only a few cases reported. The authors report a case of multiple extradural spinal arachnoid cysts in children with a review of the relevant literature.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Erisberg CA, Dyke CG, Brewer DE. Symptoms and diagnosis of extradural cysts. Bull Neurol Inst NY. 1934; 3:395–417.2). Rabb C, McComb J, Raffel C, Kennedy J. Spinal arachnoid cyst in the pediatric age group: an association with neural tube defect. J Neurosurg. 1992; 77:369–372.3). Spiller WG. A case of intradural spinal cyst with operation and recovery. Trans Coll Physicians Philadelphia. 1903; 25:1–18.4). Cilluffo JM, Gomez MR, Reese DF, Onofrio BM, Miller RH. Idiopathic (“congenital”) spinal arachnoid diverticula. Clinical diagnosis and surgical results. Myo Clin Proc. 1981; 56:93–101.5). Nabors MW, Pait TG, Byrd EB, Karim NO, Davis DO, Kobrine AI. Updated assessment and current classification of spinal meningeal cysts. J Neurosurg. 1988; 68:366–377.
Article6). Liu JK, Cole CD, Kan P, Schmidt MH. Spinal extradural arachnoid cysts: clinical, radiological, and surgical features. Neurosurg Focus. 2007; 22:6.
Article7). DiSclafani A 2nd, Canale DJ. Communicating spinal arachnoid cysts: diagnosis by delayed metrizamide computed tomography. Surg Neurol. 1985; 23:428–30.8). Fortuna A, La Torre E, Ciappetta P. Arachnoidal diverticula: a unitary approach to spinal cysts communicating with the cubarachnoid space. Acta Neurochir. 1977; 39:259–268.9). Bergland RM. Congenital intraspinal extradural syst. Report of three cases in one family. J Neurosurg. 1968; 28:495–499.10). Ersahin Y, Yildizhan A, Seber N. Spinal extradural arachnoid cyst. Childs Nerv Syst. 1993; 9:250–252.
Article11). Stechison MT, Hendrick EB, Cohen E. Spinal extradural arachnoid cyst: Pediatr Neurosci. 1989; 15:36–38.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Retroperitoneal Hematoma after Excision of Lumbar Extradural Arachnoid Cyst: Case Report
- Extradural Spinal Arachnoid Cyst as a Cause of Cauda Equina Syndrome in a Child
- Spinal Extradural Arachnoid Cyst: Minimally Invasive Surgical Treatment after Localization of Dural Defect Using Magnetic Resonance Myelogram
- Septated Extradural Arachnoid Cyst in Thoracolumbar Spine Causing Myelopathy
- Huge Thoracolumbar Extradural Arachnoid Cyst