J Korean Soc Radiol.
2010 Jan;62(1):1-6. 10.3348/jksr.2010.62.1.1.
Hemodynamic Alteration of the Cervical Venous Circulation in a Patient Suffering From Atlantoaxial Degenerative Osteoarthritis with Subluxation: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Busan Wooridul Spine Hospital, Korea. busan@wooridul.co.kr
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul Wooridul Hospital, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, Wooridul Spine Hospital, Korea.
- 4Department of Neurosurgery, Busan Wooridul Spine Hospital, Korea.
- KMID: 2208986
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2010.62.1.1
Abstract
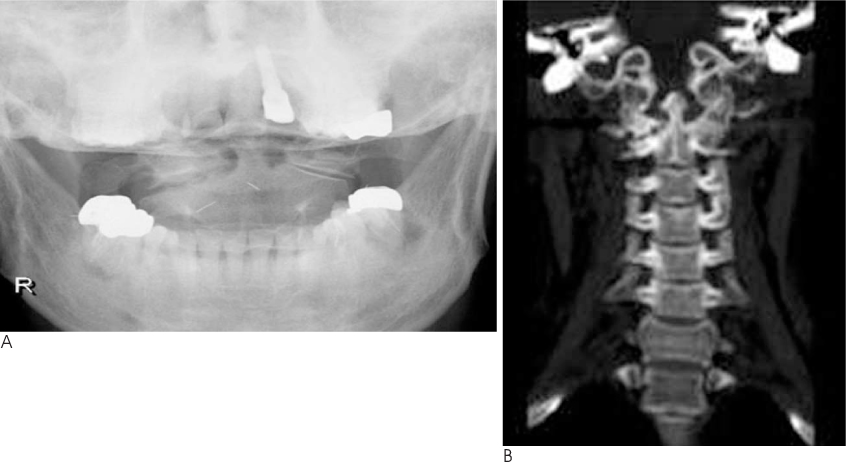
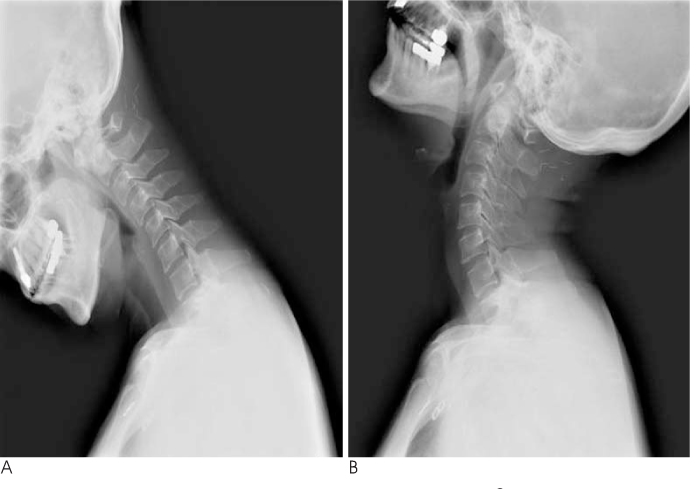
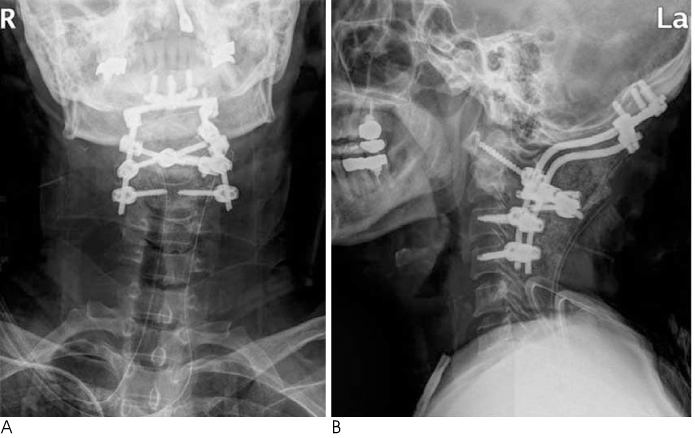
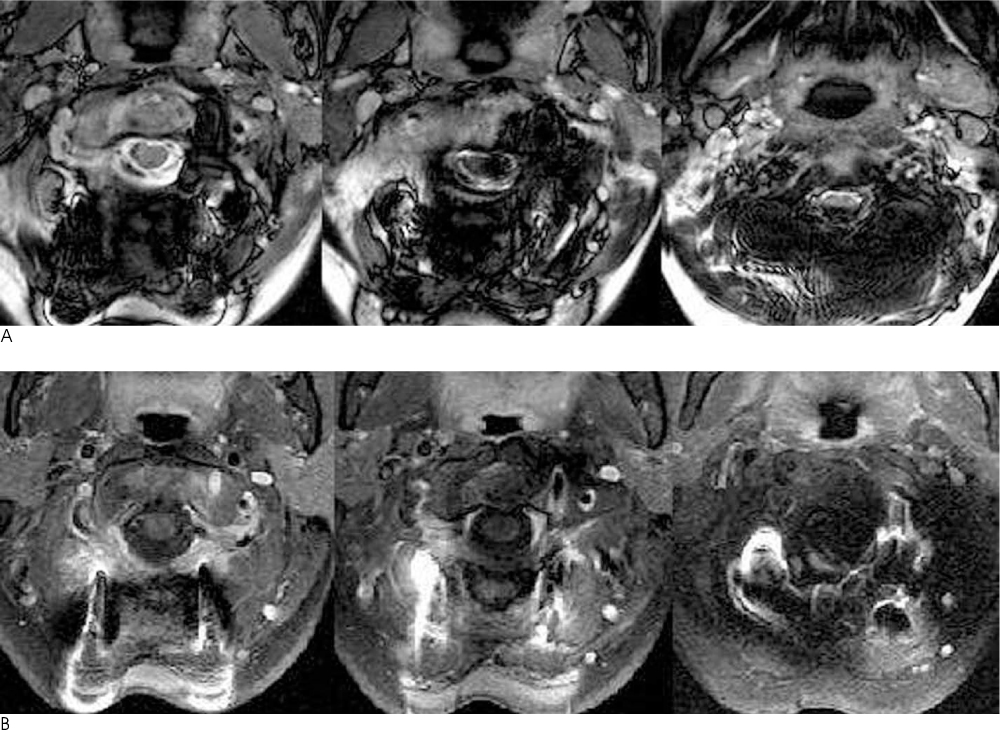
- A 52-year-old female patient was admitted to our hospital with severe occipitocervical pain. The radiographic examination revealed degenerative osteoarthritis and subluxation of the right atlantoaxial joint. Her pain was completely and immediately relieved after occipitocervical reduction and fusion. The marked dilatation of the extradural venous plexus around the vertebral artery and the enlarged deep cervical veins seen on the preoperative MR images had returned to normal dimensions on the postoperative MR images, and this explained the observed rapid pain relief. We report here on this case together with a review of the relevant literature.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Schaeren S, Jeanneret B. Atlantoaxial osteoarthritis: case series and review of the literature. Eur Spine J. 2005; 14:501–506.2. Christensen DM, Eastlack RK, Lynch JJ, Yaszemski MJ, Currier BL. C1 anatomy and dimensions relative to lateral mass screw placement. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007; 32:844–848.3. Mascalchi M, Scazzeri F, Prosetti D, Ferrito G, Salvi F, Quilici N. Dural arteriovenous fistula at the craniocervical junction with perimedullary venous drainage. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1996; 17:1137–1141.4. Caruso RD, Smith MV, Chang JK, Wasenko JJ, Rosenbaum AE. Giant cervical epidural veins after craniectomy for head trauma. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998; 19:903–906.5. Arnautović KI, Al-Mefty O, Pait TG, Krisht AF, Husain MM. The suboccipital cavernous sinus. J Neurosurg. 1997; 86:252–262.6. Parke WW, Valsamis MP. The ampulloglomerular organ: an unusual neurovascular complex in the suboccipital region. Anat Rec. 1967; 159:193–198.7. Yousry I, Förderreuther S, Moriggl B, Holtmannspötter M, Naidich TP, Straube A, et al. Cervical MR imaging in postural headache: MR signs and pathophysiological implications. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001; 22:1239–1250.8. Rabin BM, Roychowdhury S, Meyer JR, Cohen BA, LaPat KD, Russell EJ. Spontaneous intracranial hypotension: spinal MR findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998; 19:1034–1039.9. Mokri B. Spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid leaks: from intracranial to cerebrospinal fluid hypovolaemia: evolution of a concept. Mayo Clin Proc. 1999; 74:1113–1123.10. Clarot F, Callonnec F, Douvrin F, Hannequin D, Simonet J, Proust B, et al. Giant cervical epidural veins after lumbar puncture in a case of intracranial hypotension. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000; 21:787–789.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cervical Myelopathy Resulting From Non-Rheumatoid Atlantoaxial Subluxation
- Surgical Treatment of the Atlantoaxial Osteoarthritis
- A Case of Rheumatoid Arthritis Presenting Initially as Atlantoaxial Subluxation
- Upper Cervical Compression Myelopathy Caused by the Retro-Odontoid Pseudotumor With Degenerative Osteoarthritis and Calcium Pyrophosphate Dihydrate Disease: A Case Report and Literature Review
- Indirect Decompression using Segmental Screw Fixation for Cervical Myelopathy Caused by C1-2 Subluxation: Technical Note