J Korean Soc Radiol.
2013 Aug;69(2):153-156. 10.3348/jksr.2013.69.2.153.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings of Periosteal Interposition in a Distal Tibial Salter-Harris Type I Fracture with Surgical Correlation: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Chung-Ang University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. jyj907075@naver.com
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chung-Ang University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2208820
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2013.69.2.153
Abstract
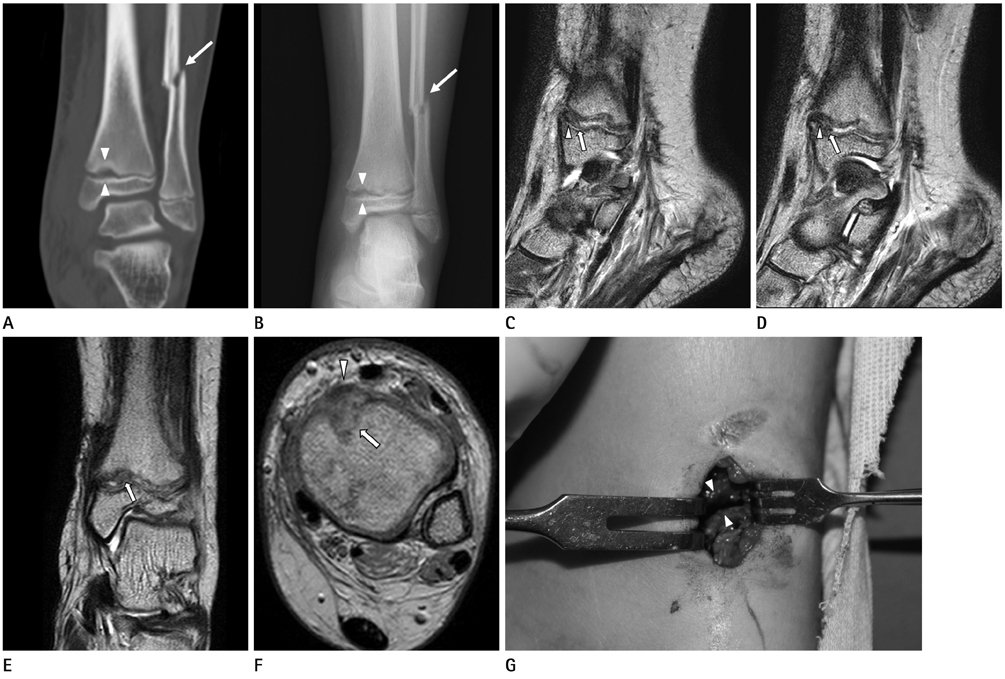
- The complication of growth disturbance after physeal fracture of the distal tibia has been well recognized. Although irreducible fractures of the physis due to trapped soft tissue, including periosteum, are not common, it could still cause growth disturbances. Therefore, the detection of periosteal interposition with physeal injury on imaging study is important. We present a case of a 10-year-old girl with surgically confirmed periosteal interposition in the distal tibial Salter-Harris type I fracture, through magnetic resonance imaging findings.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mann DC, Rajmaira S. Distribution of physeal and nonphyseal fractures in 2,650 long-bone fractures in children aged 0-16 years. J Pediatr Orthop. 1990; 10:713–716.2. Kay RM, Matthys GA. Pediatric ankle fractures: evaluation and treatment. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2001; 9:268–278.3. Whan A, Breidahl W, Janes G. MRI of trapped periosteum in a proximal tibial physeal injury of a pediatric patient. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003; 181:1397–1399.4. Barmada A, Gaynor T, Mubarak SJ. Premature physeal closure following distal tibia physeal fractures: a new radiographic predictor. J Pediatr Orthop. 2003; 23:733–739.5. Grace DL. Irreducible fracture-separations of the distal tibial epiphysis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1983; 65:160–162.6. Leary JT, Handling M, Talerico M, Yong L, Bowe JA. Physeal fractures of the distal tibia: predictive factors of premature physeal closure and growth arrest. J Pediatr Orthop. 2009; 29:356–361.7. Gruber HE, Phieffer LS, Wattenbarger JM. Physeal fractures, part II: fate of interposed periosteum in a physeal fracture. J Pediatr Orthop. 2002; 22:710–716.8. Phieffer LS, Meyer RA Jr, Gruber HE, Easley M, Wattenbarger JM. Effect of interposed periosteum in an animal physeal fracture model. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000; 15–25.9. Shi DP, Zhu SC, Li Y, Zheng J. Epiphyseal and physeal injury: comparison of conventional radiography and magnetic resonance imaging. Clin Imaging. 2009; 33:379–383.10. Raman S, Wallace EC. MRI diagnosis of trapped periosteum following incomplete closed reduction of distal tibial Salter-Harris II fracture. Pediatr Radiol. 2011; 41:1591–1594.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Interposition of Periosteum in Distal Tibial Physeal Fractures of Children
- Treatment of Distal Tibial Epiphyseal fracture Salter-Harris Type I & II
- Periosteal Impingement in Salter-Harris Type II Injury of proximal Tibial Epiphysis
- Bilateral Salter-Harris Type II Proximal Tibial Epiphtyseal Fracture: A Case
- Salter-Harris Type IV Physeal Fracture of the Distal Radius: A Case Report