J Korean Soc Magn Reson Med.
2014 Dec;18(4):362-365. 10.13104/jksmrm.2014.18.4.362.
Isolated Weakness of Radial-side Fingers Due to a Small Cortical Infarction
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, School of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. hsyoon96@medimail.co.kr
- KMID: 2206934
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13104/jksmrm.2014.18.4.362
Abstract
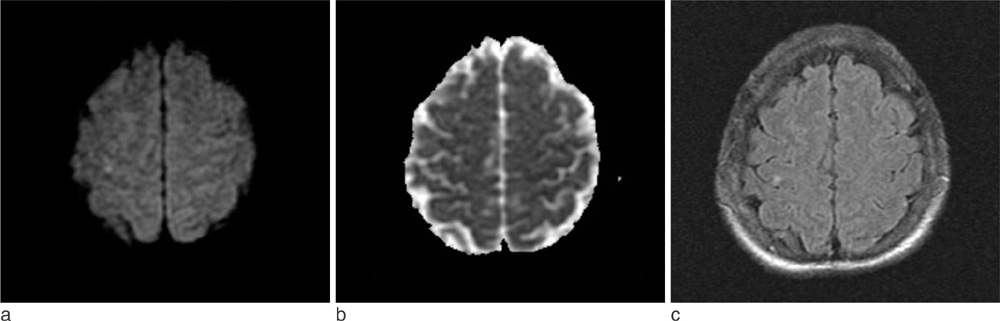
- Predominant involvement of a particular group of fingers due to a central nervous system lesion has been described as pseudoperipheral palsy. Two patients visited our hospital with isolated weakness of a particular group of fingers due to small cortical infarctions. A 51-year-old woman suddenly developed weakness in her left index and middle fingers. The brain MRI showed a small infarct in the right frontal cortex. A 67-year-old man was sudden difficulty using his chopsticks and had weakness in his right thumb and index finger. The brain MRI showed a small infarct in the left precentral cortex.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim JS. Predominant involvement of a particular group of fingers due to small, cortical infarction. Neurology. 2001; 56:1677–1682.2. Uematsu S, Lesser R, Fisher RS, et al. Motor and sensory cortex in humans: topography studied with chronic subdural stimulation. Neurosurgery. 1992; 31:59–71. discussion 71-2.3. White LE, Andrews TJ, Hulette C, et al. Structure of the human sensorimotor system. I: Morphology and cytoarchitecture of the central sulcus. Cereb Cortex. 1997; 7:18–30.4. Kim JS, Chung JP, Ha SW. Isolated weakness of index finger due to small cortical infarction. Neurology. 2002; 58:985.5. Kleinschmidt A, Nitschke MF, Frahm J. Somatotopy in the human motor cortex hand area. A high-resolution functional MRI study. Eur J Neurosci. 1997; 9:2178–2186.6. Grafton ST, Woods RP, Mazziotta JC. Within-arm somatotopy in human motor areas determined by positron emission tomography imaging of cerebral blood flow. Exp Brain Res. 1993; 95:172–176.7. Buys EJ, Lemon RN, Mantel GW, Muir RB. Selective facilitation of different hand muscles by single corticospinal neurones in the conscious monkey. J Physiol. 1986; 381:529–549.8. Schieber MH. Somatotopic gradients in the distributed organization of the human primary motor cortex hand area: evidence from small infarcts. Exp Brain Res. 1999; 128:139–148.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Isolated Weakness of Middle, Ring, and Little Fingers due to a Small Cortical Infarction in the Medial Precentral Gyrus
- Isolated Shoulder Weakness due to a Small Cortical Infarction
- Weakness of Index, Middle and Ring Fingers Due to Precentral Gyrus Infarction
- Isolated Distal Leg Weakness due to a Small Cerebral Infarction Masquerading as a Spinal Lesion
- Acute Pontine Infarction Presenting with Isolated Unilateral Masticatory Muscle Weakness