J Clin Neurol.
2006 Jun;2(2):146-148. 10.3988/jcn.2006.2.2.146.
Isolated Weakness of Middle, Ring, and Little Fingers due to a Small Cortical Infarction in the Medial Precentral Gyrus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Seoul Veterans Hospital, Seoul, Korea. hippocam@naver.com
- KMID: 1700749
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2006.2.2.146
Abstract
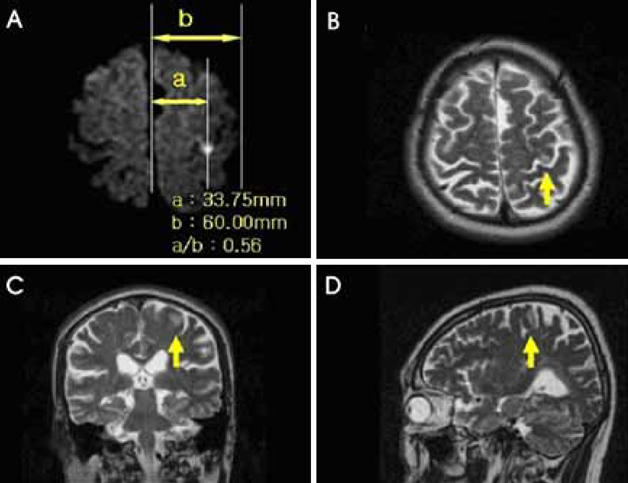
- Small cortical strokes can produce predominant isolated weakness in a particular group of fingers: radial or ulnar. The traditional views are of point-to-point representations of each finger to neurons located in the precentral gyrus of the motor cortex such that the neurons of the radial fingers are located laterally and those of the ulnar fingers are located medially. We present a case of isolated weakness of middle, ring, and little fingers due to a small cortical infarction in the medial precentral gyrus.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Ipsilateral Tilt and Contralateral Sensory Change of Neck in Cortical Infarction
Suk Yun Kang, Hyeo-Il Ma, Mi Jeong Lee, Seok-Beom Kwon, San Jung, Yun Joong Kim, Sung Hee Hwang
J Clin Neurol. 2011;7(3):156-158. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2011.7.3.156.
Reference
-
1. Lampl Y, Gilad R, Eshel Y, Sarova-Pinhas I. Strokes mimicking peripheral nerve lesions. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 1995. 97:203–207.
Article2. Lhermitte J. De la valeur sémiologique des troubles de la sensibilité á disposition radiculaire dans les lésions de l'encephale. Sem Med. 1909. 24:277.3. Yousry TA, Schmid UD, Alkadhi H, Schmidt D, Peraud A, Buettner A, et al. Localization of the motor and hand area to a knob on the precentral gyrus. A new landmark. Brain. 1997. 120:141–157.
Article4. Phan TG, Evans BA, Huston J. Pseudoulnar palsy from a small infarct of the precentral knob. Neurology. 2000. 54:2185.
Article5. Lee PH, Han SW, Heo JH. Isolated weakness of the fingers in cortical infarction. Neurology. 1998. 50:823–824.
Article6. Kim JS, Chung JP, Ha SW. Isolated weakness of index finger due to small cortical infarction. Neurology. 2002. 58:985–986.
Article7. Penfield W, Boldrey E. Somatic motor and sensory representation in the cerebral cortex of man as studied by electrical stimulation. Brain. 1937. 60:389–443.
Article8. Kim JS. Predominant involvement of a particular group of fingers due to small, cortical infarction. Neurology. 2001. 56:1677–1682.
Article9. Kwan HC, MacKay WA, Murphy JT, Wong YC. Spatial organization of precentral cortex in awake primates. II Motor outputs. J Neurophysiol. 1978. 41:1120–1131.
Article10. Sanes JN, Donoghue JP, Thangaraj V, Edelman RR, Warach S. Shared neural substrates controlling hand movements in human motor cortex. Science. 1995. 268:1775–1777.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Isolated Shoulder Weakness due to a Small Cortical Infarction
- Weakness of Index, Middle and Ring Fingers Due to Precentral Gyrus Infarction
- Isolated Weakness of Radial-side Fingers Due to a Small Cortical Infarction
- Cortical Infarction with Weakness of Individual Intrinsic Hand Muscles
- Cerebral Infarction Producing Sudden Isolated Foot Drop