J Korean Soc Magn Reson Med.
2014 Dec;18(4):357-361. 10.13104/jksmrm.2014.18.4.357.
Rapid Regression of White Matter Changes in Hypoglycemic Encephalopathy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Dankook University Hospital, Cheonan, Korea. sonsangw@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2206933
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13104/jksmrm.2014.18.4.357
Abstract
- PURPOSE
In a previous report, it took several days for white matter lesions to regress in hypoglycemic encephalopathy. We present a case of rapid diffusion-weighted image (DWI) changes in hypoglycemic encephalopathy.
CASE REPORT
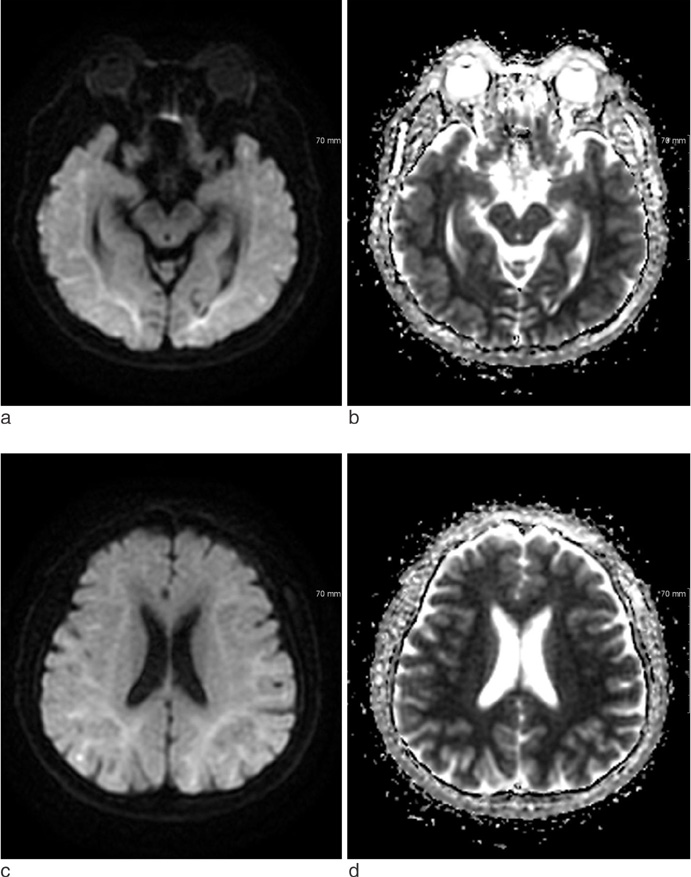
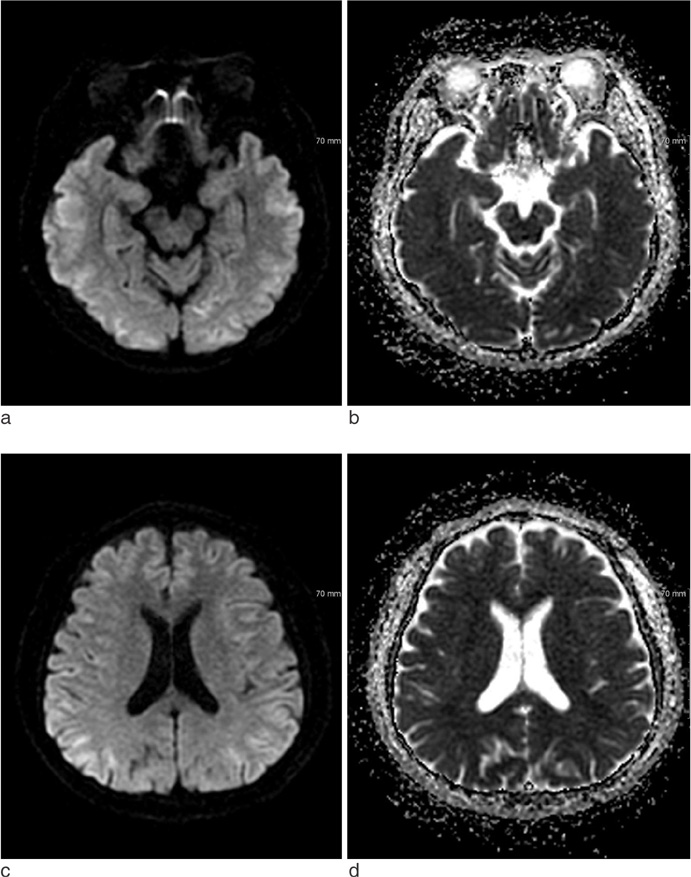
A 58-year-old male patient was found semi-comatous with the only abnormality in his laboratory tests showing hypoglycemia (44 mg/dL). After rapid correction of glucose level, immediate brain DWI showed bilateral subcortical white matter lesions. After about 5 hours, follow-up DWI showed resolved subcortical white matter lesions, with newly-appeared bilateral fronto-temporo-parietal cortical lesions.
CONCLUSION
Both white matter and cortex involvement in hypoglycemic encephalopathy has been shown in several reports, but rapid regression of white matter changes in hypoglycemic encephalopathy has been rarely reported. It is important to know that MR imaging changes in hypoglycemic encephalopathy can be made as quick as just a few-hour-long.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee CY, Liou KC, Chen LA. Serial magnetic resonance imaging changes in hypoglycemic encephalopathy. Acta Neurol Taiwan. 2013; 22:22–25.2. Auer RN. Progress review: hypoglycemic brain damage. Stroke. 1986; 17:699–708.3. Pelligrino D, Almquist LO, Siesjo BK. Effects of insulin-induced hypoglycemia on intracellular pH and impedance in the cerebral cortex of the rat. Brain Res. 1981; 221:129–147.4. Ma JH, Kim YJ, Yoo WJ, et al. MR imaging of hypoglycemic encephalopathy: lesion distribution and prognosis prediction by diffusion-weighted imaging. Neuroradiology. 2009; 51:641–649.5. Yoneda Y, Yamamoto S. Cerebral cortical laminar necrosis on diffusion-weighted MRI in hypoglycaemic encephalopathy. Diabet Med. 2005; 22:1098–1100.6. Hasegawa Y, Formato JE, Latour LL, et al. Severe transient hypoglycemia causes reversible change in the apparent diffusion coefficient of water. Stroke. 1996; 27:1648–1655.7. Aoki T, Sato T, Hasegawa K, Ishizaki R, Saiki M. Reversible hyperintensity lesion on diffusion-weighted MRI in hypoglycemic coma. Neurology. 2004; 63:392–393.8. Hassel B, Boldingh KA, Narvesen C, Iversen EG, Skrede KK. Glutamate transport, glutamine synthetase and phosphateactivated glutaminase in rat CNS white matter. A quantitative study. J Neurochem. 2003; 87:230–237.9. Fujioka M, Okuchi K, Hiramatsu KI, Sakaki T, Sakaguchi S, Ishii Y. Specific changes in human brain after hypoglycemic injury. Stroke. 1997; 28:584–587.10. Mori F, Nishie M, Houzen H, Yamaguchi J, Wakabayashi K. Hypoglycemic encephalopathy with extensive lesions in the cerebral white matter. Neuropathology. 2006; 26:147–152.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hyperperfusion in DWI Abnormality in a Patient with Acute Symptomatic Hypoglycemic Encephalopathy
- An Atypical Case of Neonatal Hypoglycemic Encephalopathy with Extensive White Matter Lesions
- A Case of Metronidazole-Induced Encephalopathy: Atypical Involvement of the Brain on MRI
- A Case of Severe Hypoglycemic Encephalopathy with Extensive Brain Lesions in Non-diabetics and Alcoholism
- Cortical Atrophy Following Delayed Encephalopathy After Carbon Monoxide Poisoning