J Korean Rheum Assoc.
2010 Mar;17(1):100-102. 10.4078/jkra.2010.17.1.100.
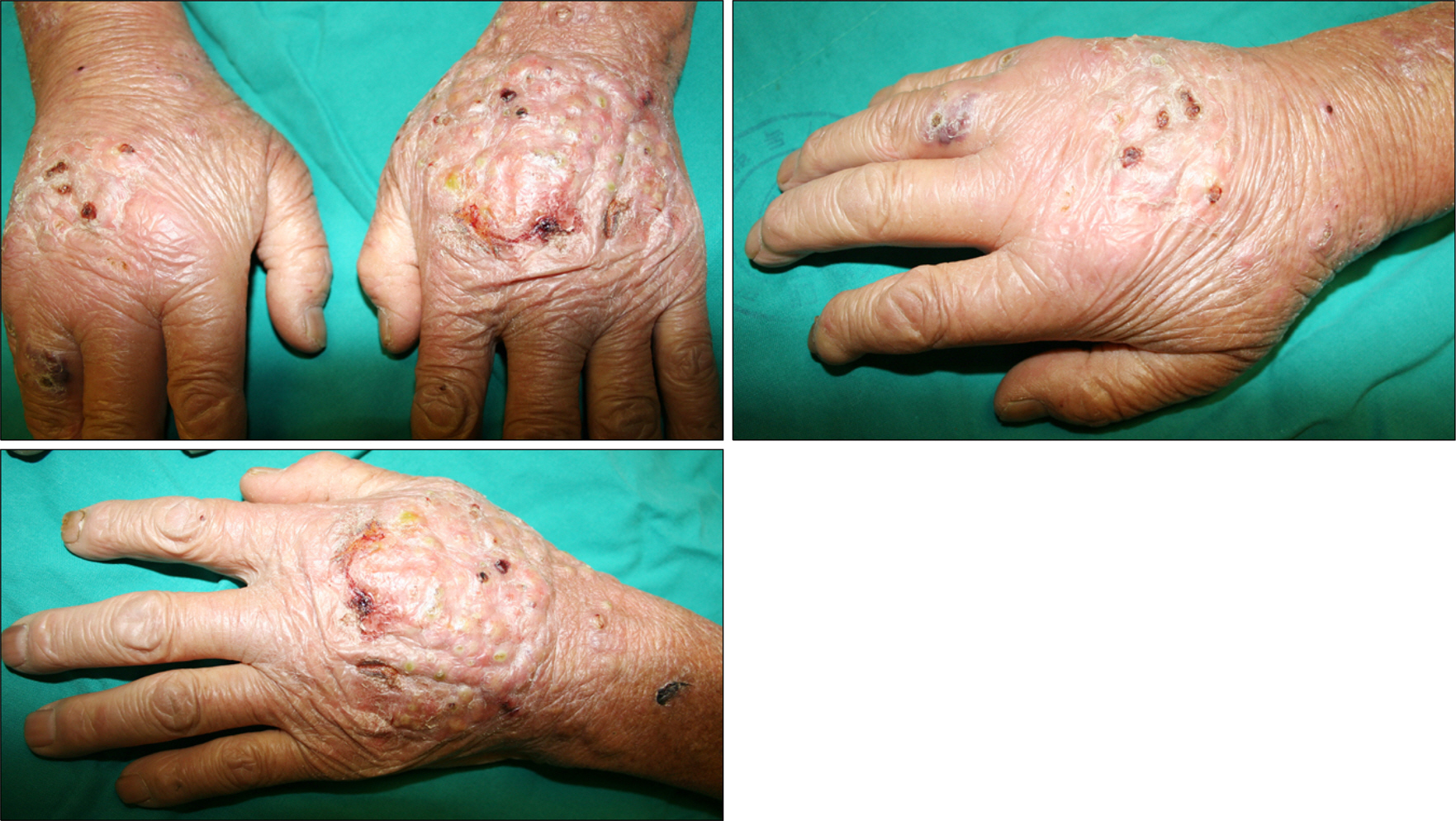
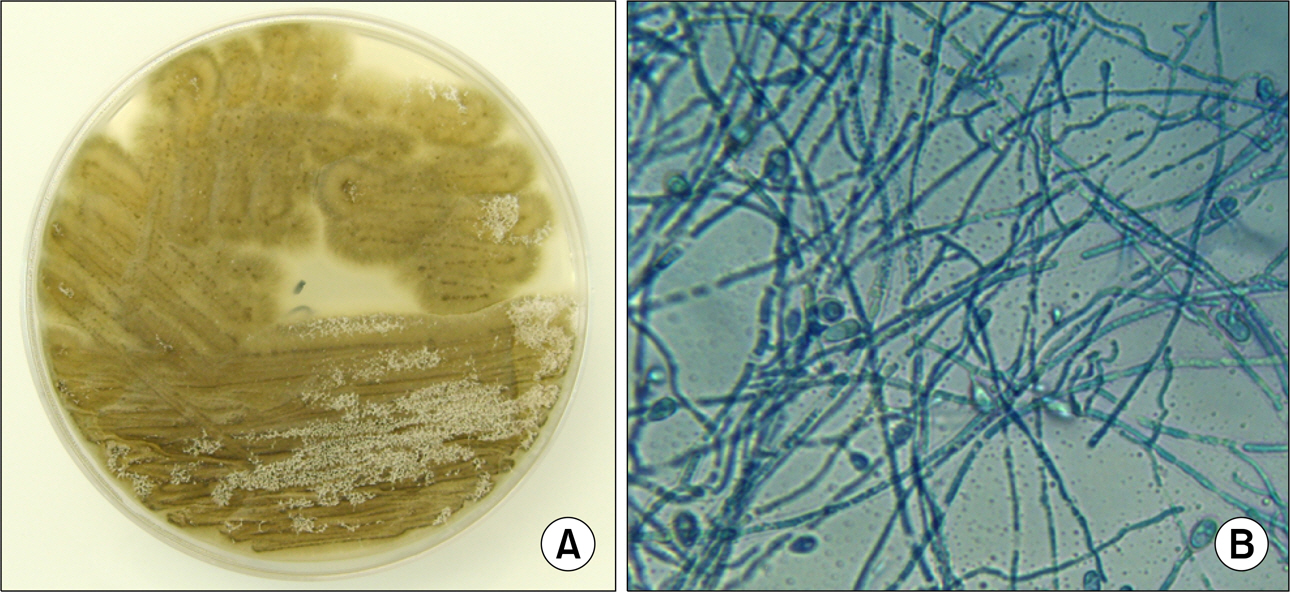
A Case of Localized Skin Infection Due to Scedosporium apiospermum in a Patient with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea. tykang@yonsei.ac.kr
- KMID: 2202002
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jkra.2010.17.1.100
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Cortez KJ., Roilides E., Quiroz-Telles F., Meletiadis J., Antachopoulos C., Knudsen T, et al. Infections caused by Scedosporium spp. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2008. 21:157–97.2). Lee YH., Kim SH., Suh MK., Ko WT., Ha GY., Kim JR. A case of localized skin infection due to Scedosporium apiospermum. Korean J Dermatol. 2007. 45:1060–3.3). Chaveiro MA., Vieira R., Cardoso J., Afonso A. Cutaneous infection due to Scedosporium apiospermum in an immunosuppressed patient. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2003. 17:47–9.
Article4). Choi YL., Lee KJ., Park JH., Rho NK., Lee DY., Lee ES. A case of cutaneous Scedosporium apiospermum infection. Korean J Dermatol. 2005. 43:704–6.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Localized Skin Infection Due to Scedosporium Apiospermum
- Localized Cutaneous Infection due to Scedosporium apiospermum
- A Case of Skin Infection due to Scedosporium apiospermum Treated with Voriconazole
- A Case of Localized Skin Infection Due to Scedosporium apiospermum
- A Case of Localized Skin Infection Due to Scedosporium apiospermum Diagnosed by DNA Sequencing of the Internal Transcribed Spacer Region