J Menopausal Med.
2015 Apr;21(1):41-46. 10.6118/jmm.2015.21.1.41.
A Pilot Study of the Impacts of Menopause on the Anogenital Distance
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Soonchunhyang University, College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea. heeobgy@schmc.ac.kr
- 2Department of Urology, Soonchunhyang University, College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Interdisciplinary Program in Biomedical Science, Soonchunhyang University, Asan, Korea.
- KMID: 2201021
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.6118/jmm.2015.21.1.41
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
It has been known that there is a difference in anogenital distance (AGD) in the animals and newborn depending on the exposure of androgenic hormones. The anatomical changes occur in the female genitalia in women after menopause. This was pilot study to find out whether the menopause affects AGD.
METHODS
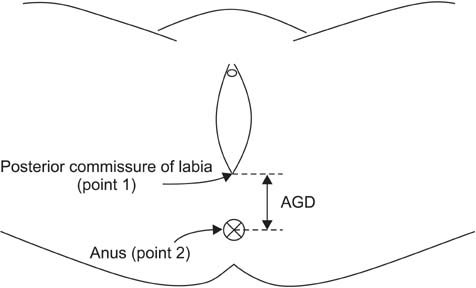
We evaluated a total of 50 women targeted for premenopausal and postmenopausal group in each 25 people. AGD was defined as a length between the posterior commissure of labia and anal center. AGD was measured in lithotomy position using sterile paper ruler. In order to control bias of the height and weight, which could influence the AGD, anogenital index (AGI) is defined as the weight divided by the AGD value. We used a Mann-Whitney U test to analyze the relationship between AGD and menopause for statistical analysis.
RESULTS
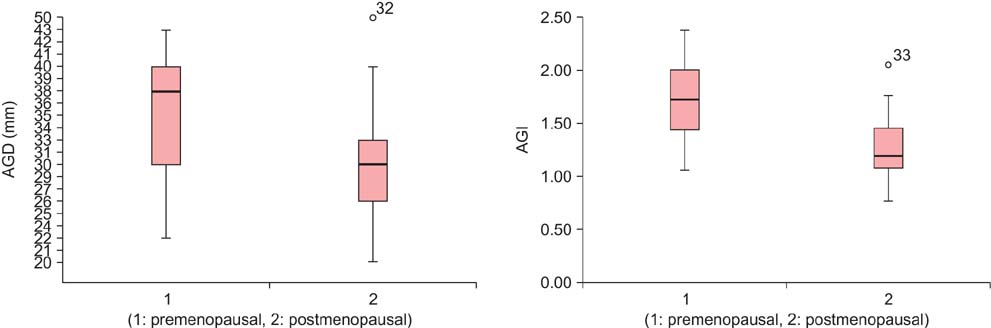
AGD was significantly longer in premenopausal women compared to postmenopausal women (34.8 +/- 6.4 vs. 30.3 +/- 6.6, P = 0.019). AGI was significantly higher in premenopausal women than postmenopausal women (1.7 +/- 0.4 vs. 1.3 +/- 0.3, P < or = 0.000).
CONCLUSION
The changes of AGD and AGI in postmenopausal women demonstrated to have potential to be used as on scale predicting the physical changes that may occur after menopause. This study could be used as the cornerstone of a large-scale studies in the future.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Comparison of Anogenital Distance and Correlation with Vulvo-vaginal Atrophy: A Pilot Study on Premenopausal and Postmenopausal Women
Lavinia Domenici, Angela Musella, Carlotta Bracchi, Francesca Lecce, Michele Carlo Schiavi, Vanessa Colagiovanni, Violante Di Donato, Claudia Marchetti, Federica Tomao, Innocenza Palaia, Ludovico Muzii, Pierluigi Benedetti Panici
J Menopausal Med. 2018;24(2):108-112. doi: 10.6118/jmm.2018.24.2.108.
Reference
-
1. Parks LG, Ostby JS, Lambright CR, Abbott BD, Klinefelter GR, Barlow NJ, et al. The plasticizer diethylhexyl phthalate induces malformations by decreasing fetal testosterone synthesis during sexual differentiation in the male rat. Toxicol Sci. 2000; 58:339–349.2. Mendiola J, Roca M, Mínguez-Alarcón L, Mira-Escolano MP, López-Espín JJ, Barrett ES, et al. Anogenital distance is related to ovarian follicular number in young Spanish women: a cross-sectional study. Environ Health. 2012; 11:90.3. Basaran M, Kosif R, Bayar U, Civelek B. Characteristics of external genitalia in pre- and postmenopausal women. Climacteric. 2008; 11:416–421.4. Swan SH, Main KM, Liu F, Stewart SL, Kruse RL, Calafat AM, et al. Decrease in anogenital distance among male infants with prenatal phthalate exposure. Environ Health Perspect. 2005; 113:1056–1061.5. Gray LE Jr, Wilson VS, Stoker T, Lambright C, Furr J, Noriega N, et al. Adverse effects of environmental antiandrogens and androgens on reproductive development in mammals. Int J Androl. 2006; 29:96–104.6. Barrett ES, Parlett LE, Sathyanarayana S, Liu F, Redmon JB, Wang C, et al. Prenatal exposure to stressful life events is associated with masculinized anogenital distance (AGD) in female infants. Physiol Behav. 2013; 114-115:14–20.7. Salazar-Martinez E, Romano-Riquer P, Yanez-Marquez E, Longnecker MP, Hernandez-Avila M. Anogenital distance in human male and female newborns: a descriptive, cross-sectional study. Environ Health. 2004; 3:8.8. Wilson VS, Blystone CR, Hotchkiss AK, Rider CV, Gray LE Jr. Diverse mechanisms of anti-androgen action: impact on male rat reproductive tract development. Int J Androl. 2008; 31:178–187.9. Mendiola J, Stahlhut RW, Jorgensen N, Liu F, Swan SH. Shorter anogenital distance predicts poorer semen quality in young men in Rochester, New York. Environ Health Perspect. 2011; 119:958–963.10. Eisenberg ML, Jensen TK, Walters RC, Skakkebaek NE, Lipshultz LI. The relationship between anogenital distance and reproductive hormone levels in adult men. J Urol. 2012; 187:594–598.11. Kim TH, Lee HH, Kim JM, Yang YJ, Kim SY, Hong YP. The routine value of anogenital distance as an anthropometric measurement in newborns. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol. 2014; 41:283–287.12. Hall G, Phillips TJ. Estrogen and skin: the effects of estrogen, menopause, and hormone replacement therapy on the skin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005; 53:555–568.13. Castelo-Branco C, Duran M, González-Merlo J. Skin collagen changes related to age and hormone replacement therapy. Maturitas. 1992; 15:113–119.14. Mun MJ, Kim JH, Kim TH, Hwang JY, Jang WC. Associations between estrogen receptor gene polymorphisms and endometriosis. J Korean Soc Menopause. 2013; 19:64–73.15. Brincat M, Kabalan S, Studd JW, Moniz CF, de Trafford J, Montgomery J. A study of the decrease of skin collagen content, skin thickness, and bone mass in the postmenopausal woman. Obstet Gynecol. 1987; 70:840–845.16. Barengolts EI, Berman M, Kukreja SC, Kouznetsova T, Lin C, Chomka EV. Osteoporosis and coronary atherosclerosis in asymptomatic postmenopausal women. Calcif Tissue Int. 1998; 62:209–213.17. Mitchell BD, Kammerer CM, Schneider JL, Perez R, Bauer RL. Genetic and environmental determinants of bone mineral density in Mexican Americans: results from the San Antonio Family Osteoporosis Study. Bone. 2003; 33:839–846.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Anogenital Distance and Correlation with Vulvo-vaginal Atrophy: A Pilot Study on Premenopausal and Postmenopausal Women
- Anogenital Index of Normal Children and Its Clinical Significance in Children with Constipation
- Adenoma of Anogenital Mammary-like Glands on the Labium Major
- Histiocytosis-X with Chronic Weeping Ulcers in the Anogenital Areas
- The Relationship of Hot Flush to Other Menopausal Symptoms and Chronic Disease Related to Menopause