J Korean Soc Endocrinol.
2006 Aug;21(4):338-344. 10.3803/jkes.2006.21.4.338.
A Case of Pseudohypoparathyroidism Type I
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Incheon Christian Hospital, Korea.
- KMID: 2200850
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2006.21.4.338
Abstract
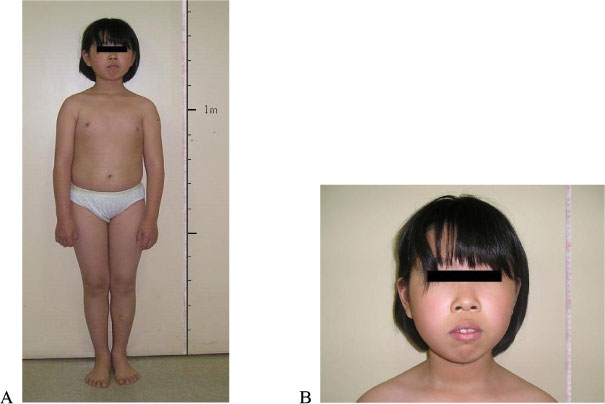
- Pseudohypoparathyroidism (PHP) is a rare clinical type of hypoparathyroidism. The patients with PHP show classic clinical and biochemical features of hypoparathyroidism, but elevated serum level of parathyroid hormone (PTH) and characteristic physical appearances termed 'Albright's hereditary osteodystrophy' (AHO). PHP is classified into types Ia, Ib, Ic and II according to the presence of AHO phenotype and the mechanism of PTH resistance. We experienced a case of PHP in a 12 year-old girl with carpopedal spasm, syncope and partial AHO. She showed very low serum calcium level (1.4 mmol/L), high phosphorus level (3.62 mmol/L) and high immunoreactive PTH level (186.6 ng/L). In the Ellsworth-Howard test, urinary cyclic adenosine monophosphate and phosphorus levels after an exogenous PTH injection remained unchanged. Therefore, we were able to classify the patient as either PHP type Ia or Ic. After the patient had been treated with daily calcium carbonate (1 g), cholecalciferol (250 IU) and calcitriol (0.5 microgram), her neurological signs and symptoms as well as her biochemical abnormalities of hypocalcemia and hyperphosphatemia were improved.
MeSH Terms
-
Adenosine Monophosphate
Calcitriol
Calcium
Calcium Carbonate
Child
Cholecalciferol
Female
Humans
Hyperphosphatemia
Hypocalcemia
Hypoparathyroidism
Parathyroid Hormone
Phenotype
Phosphorus
Pseudohypoparathyroidism*
Spasm
Syncope
Adenosine Monophosphate
Calcitriol
Calcium
Calcium Carbonate
Cholecalciferol
Parathyroid Hormone
Phosphorus
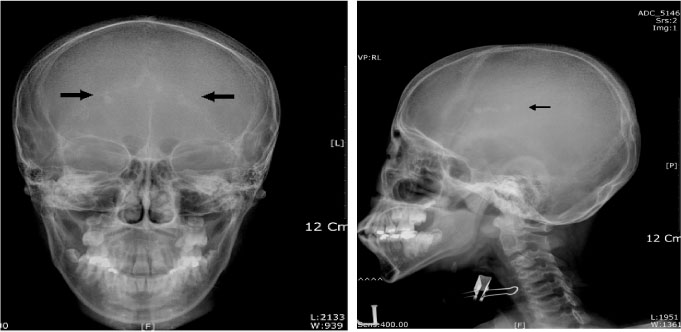
Figure
Reference
-
1. Albright FB, Burnett CH, Smith PH, Parson W. Pseudohypoparathyroidism: An example of the "Seabright-Bantam syndrome". Endocrinology. 1942. 30:922–932.2. Kang MH, Min YK, Chung YH, Hwang SD, Kim SY, Lee HK, Min HK. The variability of clinical and biochemical manifestation of pseudohypopara-thyroidism. Korean J Med. 1985. 28:103–108.3. Ko BG, Hong SG, Jin SH, Park DC, Cho JT, Lee JK. A case of pseudohypoparathyroidism with atypical feature of Albright's hereditary osteodystrophy. Korean J Med. 1986. 31:130–135.4. Kang MI, Park YB, Lee YK, Yoo SJ, Son HS, Yoon KH, Hong KS, Lee KW, Son HY, Kang SK. Pseudohypoparathyroism type Ia and type II. J Kor Soc Endocrinol. 1991. 6:170–178.5. Kim EY, Kim DK, Lee HJ, Jung EK, Park YB. A case of pseudohypoparathyroidism II. Korean J Pediatr. 1996. 39:1326–1330.6. Yoon JW, Han MH, Huh KB, Lee SY. A case of pseudo-pseudohypoparathyroidism. Korean J Med. 1976. 19:1123–1128.7. Ogata E, Yamamoto M, Matsumoto T, Fujita T, Fukase M, Kinoshita Y, Furukawa Y, Sohn HE, Nakajima H, Yasuda T. Standard procedure and the diagnostic criteria for the Ellsworth-Howard test using human PTH-(1-34). Nippon Naibunpi Gakkai Zasshi. 1984. 60:971–984.8. Kim YS. Interpretation and reading of endocrine function test. 2001. 1st ed. Seoul: Korea Medical Book Publisher;116–118.9. Farfel Z, Brickman AS, Kaslow HR, Brothers VM, Bourne HR. Defect of receptor-cyclase coupling protein in pseudohypoparathyroidism. N Engl J Med. 1980. 303:237–242.10. Farfel Z, Friedman E. Mental deficiency in pseudohypoparathyroidism type I is associated with Ns-protein deficiency. Ann Intern Med. 1986. 105:197–199.11. Bourne HR, Kaslow HR, Brickman AS, Farfel Z. Fibroblast defect in pseudohypoparathyroidism, type I: reduced activity of receptor-cyclase coupling protein. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981. 53:636–640.12. Farfel Z, Bourne HR. Deficient activity of receptor-cyclase coupling protein in platelets of patients with pseudohypoparathyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980. 51:1202–1204.13. Levine MA, Jap TS, Mauseth RS, Downs RW, Spiegel AM. Activity of the stimulatory guanine nucleotide-binding protein is reduced in erythrocytes from patients with pseudohypoparathyroidism and pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism: biochemical, endocrine, and genetic analysis of Albright's hereditary osteodystrophy in six kindreds. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986. 62:497–502.14. Beaudet AL. Complex imprinting. Nat Genet. 2004. 36:793–795.15. Bastepe M, Juppner H. GNAS locus and pseudohypoparathyroidism. Horm Res. 2005. 63:65–74.16. Liu J, Litman D, Rosenberg MJ, Yu S, Biesecker LG, Weinstein LS. A GNAS1 imprinting defect in pseudohypoparathyroidism type IB. J Clin Invest. 2000. 106:1167–1174.17. Barrett D, Breslau NA, Wax MB, Molinoff PB, Downs RW Jr. New form of pseudohypo- parathyroidism with abnormal catalytic adenylate cyclase. Am J Physiol. 1989. 257:E277–E283.18. Linglart A, Carel JC, Garabedian M, Le T, Mallet E, Kottler ML. GNAS1 lesion in pseudohypoparathyroidism Ia and Ic: genotype phenoype relationship and evidence of the maternal transmission of the hormonal resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002. 87:189–197.19. Drezner M, Neelson FA, Levovitz HE. Pseudohypoparathyroidism type II: a possible defect in the reception of the cyclic AMP signal. N Engl J Med. 1973. 289:1056–1060.20. Silve C. Pseudohypoparathyroidism syndromes: the many faces of parathyroid hormone resistance. Eur J Endocrinol. 1995. 133:145–146.