J Lung Cancer.
2012 Jun;11(1):45-47. 10.6058/jlc.2012.11.1.45.
Multilocular Thymic Cyst with Prominent Lymphoid Follicular Hyperplasia: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hanjho@skku.edu
- 2Department of Thoracic Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2199876
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.6058/jlc.2012.11.1.45
Abstract
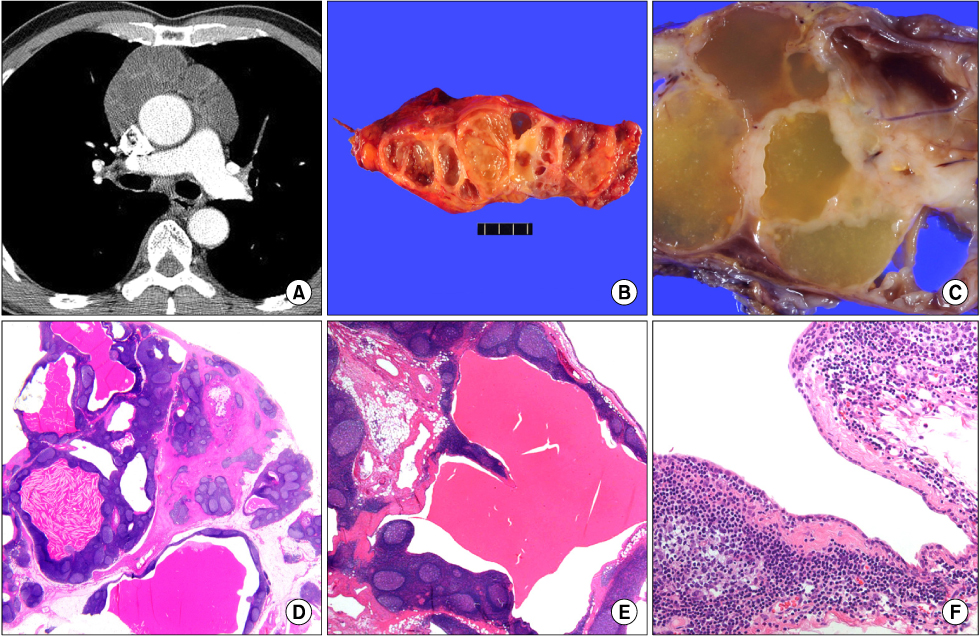
- We present herein an unusual case of multilocular thymic cyst, with prominent lymphoid follicular hyperplasia, in a 64-year-old man. It was incidentally founded as a mediastinal mass on chest radiography, during a routine health check-up. Computed tomography revealed a cystic lesion, which contains thick septa involving the thymus. The resected mass, 8x4 cm in diameter, involved the thymus and there is no adhesion or invasion into the adjacent tissue. The cut surface showed cystic spaces with thick white-tan firm wall, which cysts contained gelatinous material. Microscopically, the lesion was characterized by multiple cysts, lined by flattened cuboidal epithelium that was separated by thick walls, having a dense lymphoid tissue with lymphoid follicles. The patient was discharged without any complication and is well without evidence of recurrence for sixteen months.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Suster S, Rosai J. Multilocular thymic cyst: an acquired reactive process: study of 18 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1991. 15:388–398.2. Sung CO, Han J, Kim JY, Shim YM, Kim TS. Squamous cell carcinoma arising in a thymic cyst: a brief case report. Korean J Pathol. 2009. 43:260–262.
Article3. Weissferdt A, Moran CA. Thymic carcinoma associated with multilocular thymic cyst: a clinicopathologic study of 7 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2011. 35:1074–1079.4. Mishalani SH, Lones MA, Said JW. Multilocular thymic cyst: a novel thymic lesion associated with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1995. 119:467–470.5. Izumi H, Nobukawa B, Takahashi K, et al. Multilocular thymic cyst associated with follicular hyperplasia: clinicopathologic study of 4 resected cases. Hum Pathol. 2005. 36:841–844.
Article6. Sugimoto S, Misao T, Nakano H, Yamane M. Mediastinal cyst with rim calcification. Jpn J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2004. 52:261–263.
Article7. Suster S, Barbuto D, Carlson G, Rosai J. Multilocular thymic cysts with pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia. Hum Pathol. 1991. 22:455–460.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Rare Case of Multilocular Thymic Cyst with Follicular Lymphoid Hyperplasia: Radiologic and Histopathologic Features
- Micronodular Thymoma with Lymphoid Stroma in a Multilocular Thymic Cyst: A Case Study
- Cystic Thymic Diseases: CT Manifestations
- A Case of Renal Multilocular Cyst
- Multilocular Thymic Cyst Associated with Mediastinal Teratoma: A Case Report