J Korean Acad Prosthodont.
2009 Oct;47(4):376-384. 10.4047/jkap.2009.47.4.376.
The effect of Ca-P coatings of anodized implant surface on response of osteoblast-like cells in vitro
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Advanced Prosthodontics, Graduate School of Clinical Dentistry, Institute for Clinical Dental Research (ICDR), Korea University, Korea. swshin@korea.ac.kr
- 2Well Dental Clinic, Clinical researcher, Korea.
- 3School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Korea.
- KMID: 2195586
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jkap.2009.47.4.376
Abstract
- PURPOSE
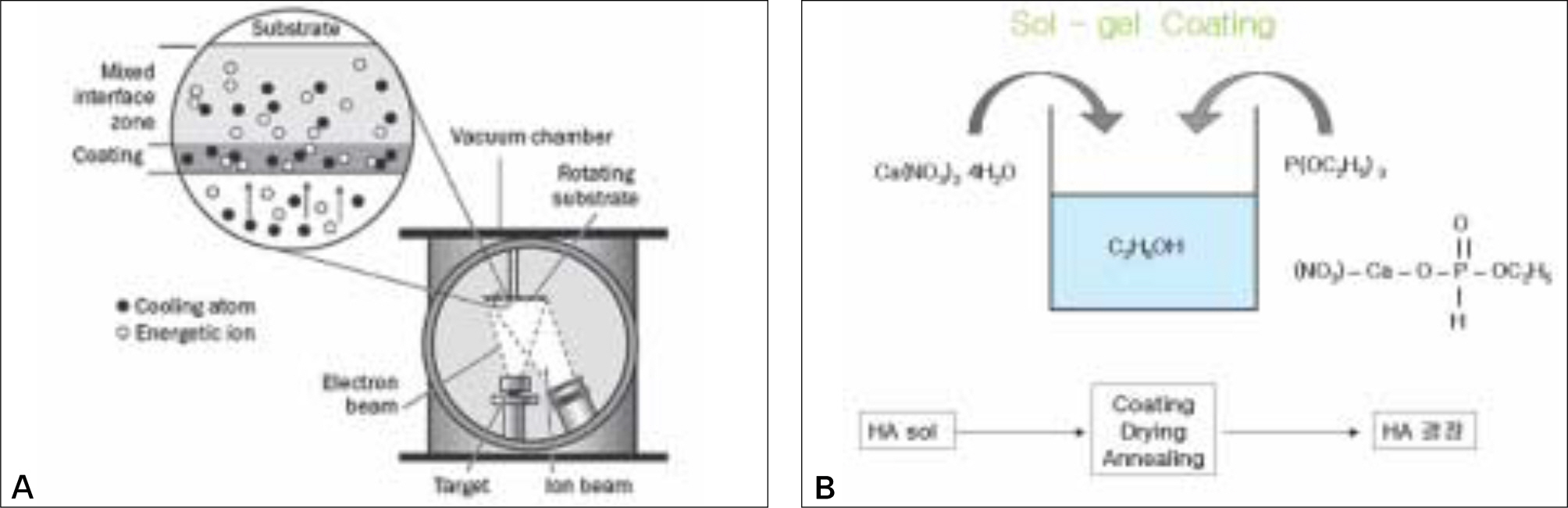
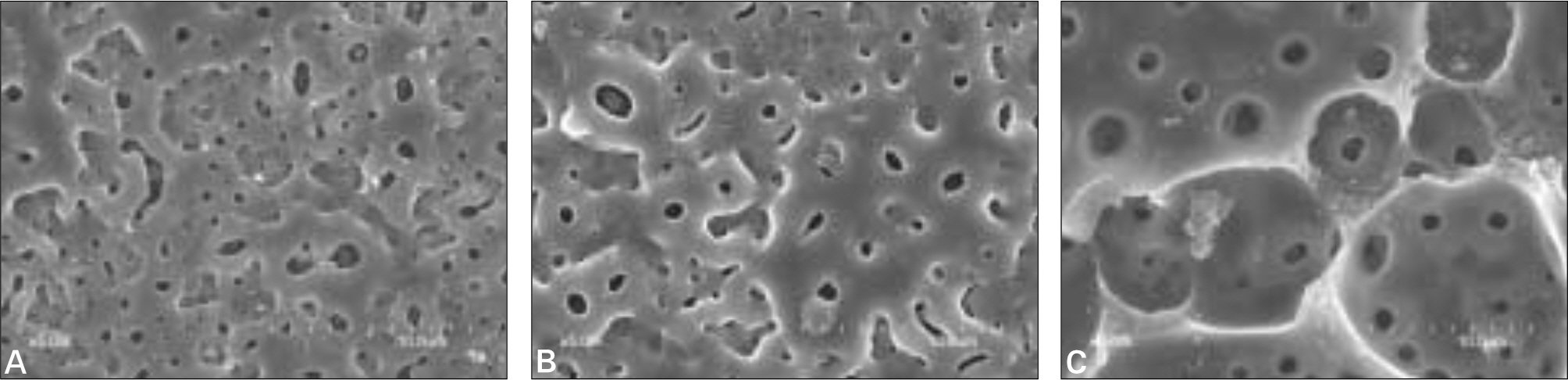
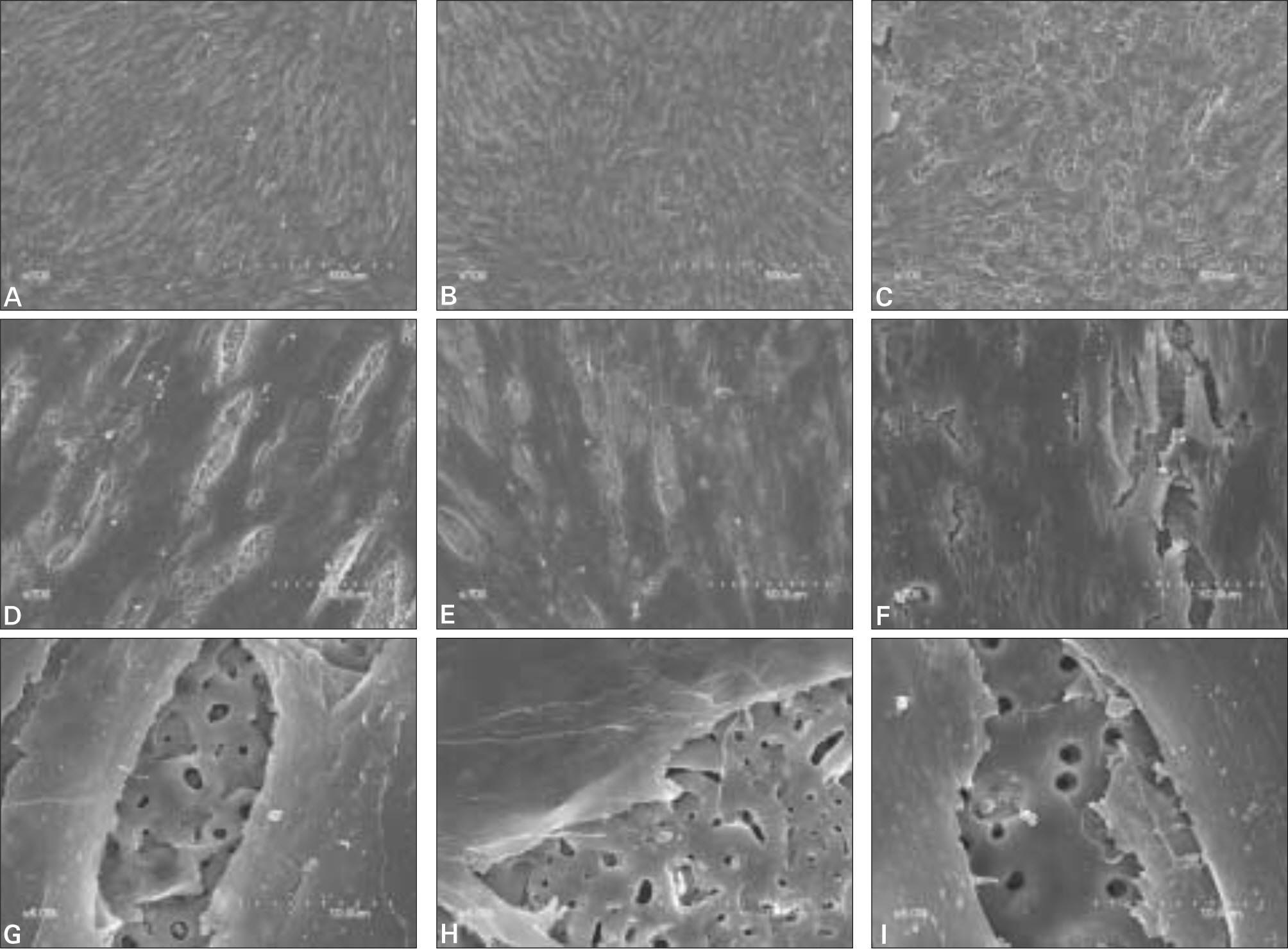
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the response of osteoblast-like cells to Ca-P coated surface obtained via Ion beam-assisted deposition (IBAD) method and Sol-Gel process on anodized surface by cellular proliferation and differentiation. MATERIAL AND METHODS: The surface of a commercially pure titanium (Grade IV) discs with dimension of 10mm diameter and 2 mm thickness was modified by anodic oxidation under a constant voltage of 300 V. The experimental groups were coated with Ca-P by the IBAD method and Sol-Gel process on anodized surface. The surface roughness (Ra) of specimens was measured by optical interferometer and each surface was examined by SEM. To evaluate cell response, MG63 cells were cultured and cell proliferation, ALP activity and the ability of cell differentiation were examined. Also, cell morphology was examined by SEM. The significant of each group was verified by Kruskal-Wallis Test (alpha= .05).
RESULTS
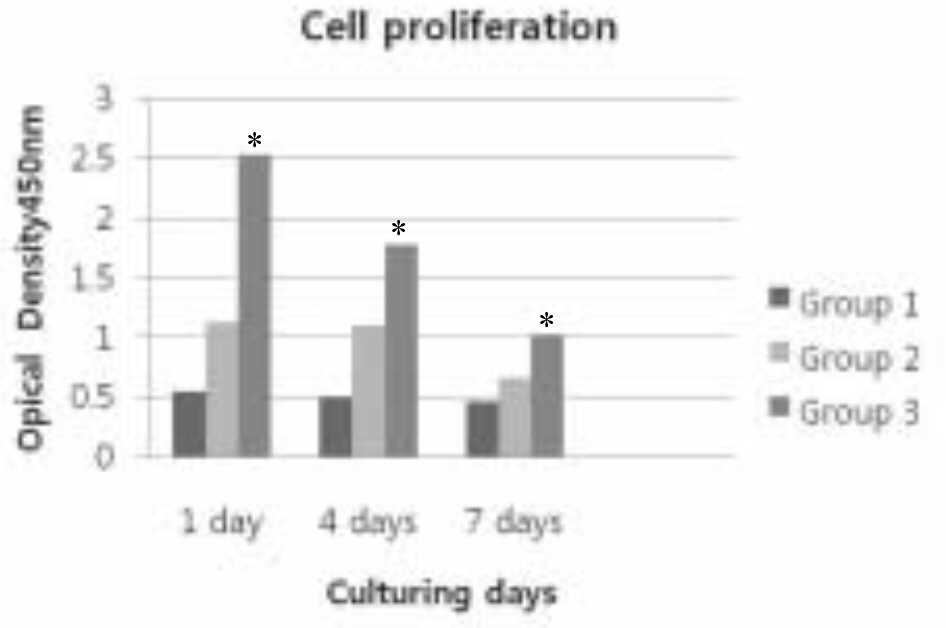
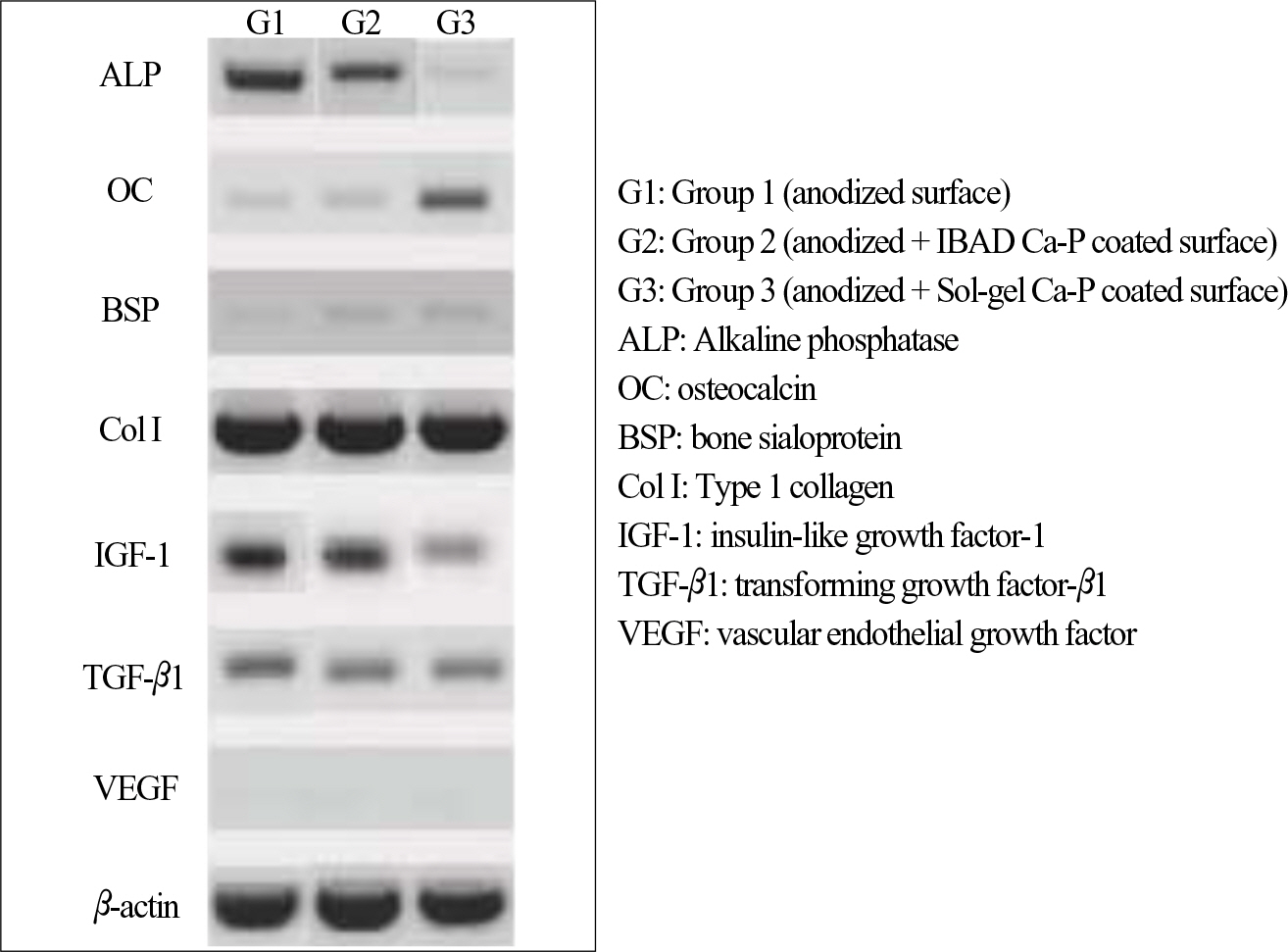
The Ra value of Ca-P coated surface by IBAD method was significantly higher than Ca-P coated surface by Sol-gel process (P<.05). The level of cell proliferation and ALP activity was higher in Ca-P coated surface by IBAD method (P<.05). The expression of ALP showed higher level expression in Ca-P coated surface by IBAD method. Cells grown on Ca-P coated surface by IBAD method were uniformly distributed and developed a very close layer.
CONCLUSION
These experiments showed better performances of Ca-P coated surface by IBAD method with respect to Ca-P coated surface by Sol-gel process. Ca-P coated surface by IBAD method appear to give rise more mature osteoblast characteristics and might result in increased bone growth and bone-implant contact.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Bra � nemark PI. Osseointegration and its experimental background. J Prosthet Dent. 1983. 50:399–410.2.Albrektsson T., Wennerberg A. Oral implant surfaces: Part 1-review focusing on topographic and chemical properties of different surfaces and in vivo responses to them. Int J Prosthodont. 2004. 17:536–43.3.Wong M., Eulenberger J., Schenk R., Hunziker E. Effect of surface topology on the osseointegration of implant materials in trabecular bone. J Biomed Mater Res. 1995. 29:1567–75.
Article4.Albrektsson T., Wennerberg A. Oral implant surfaces: Part 2-review focusing on clinical knowledge of different surfaces. Int J Prosthodont. 2004. 17:544–64.5.Osborn JF., Newesly H. Dynamic aspects of the implant-bone-interface. In: Heimke G (ed). Dental Implants. Materials and Systems. Munich: Hanser;1980. p. 111–23.6.Hench LL. Bioceramics: material characteristics versus in vivo behavior. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988. 523:54–71.7.Kim HM., Takadama H., Miyaji F., Kokubo T., Nishiguchi S., Nakamura T. Formation of bioactive functionally graded structure on Ti-6Al-4V alloy by chemical surface treatment. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2000. 11:555–9.8.Caulier H., van der Waerden JP., Paquay YC., Wolke JG., Kalk W., Naert I., Jansen JA. Effect of calcium phosphate (Ca-P) coatings on trabecular bone response: a histological study. J Biomed Mater Res. 1995. 29:1061–9.
Article9.Caulier H., Vercaigne S., Naert I., van der Waerden JP., Wolke JG., Kalk W., Jansen JA. The effect of Ca-P plasma-sprayed coatings on the initial bone healing of oral implants: an experimental study in the goat. J Biomed Mater Res. 1997. 34:121–8.
Article10.Caulier H., van der Waerden JP., Wolke JG., Kalk W., Naert I., Jansen JA. A histological and histomorphometrical evaluation of the application of screw-designed calciumphosphate (Ca-P)-coated implants in the cancellous maxillary bone of the goat. J Biomed Mater Res. 1997. 35:19–30.
Article11.Caulier H., Hayakawa T., Naert I., Van Der Waerden JP., Wolke JG., Jansen JA. An animal study on the bone behaviour of Ca-P-coated implants: influence of implant location. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 1997. 8:531–6.12.Cook SD., Thomas KA., Dalton JE., Volkman TK., Whitecloud TS 3rd., Kay JF. Hydroxylapatite coating of porous implants improves boneing rowth and interface attachment strength. J Biomed Mater Res. 1992. 26:989–1001.13.Tong W., Yang Z., Zhang X., Yang A., Feng J., Cao Y., Chen J. Studies on diffusion maximum in x-ray diffraction patterns of plasma-sprayed hydroxyapatite coatings. J Biomed Mater Res. 1998. 40:407–13.
Article14.Garci、a F., Arias JL., Mayor B., Pou J., Rehman I., Knowles J., Best S., Leo ´ n B., Pe ´ rez-Amor M., Bonfield W. Effect of heat treatment on pulsed laser deposited amorphous calcium phosphate coatings. J Biomed Mater Res. 1998. 43:69–76.15.Choi JM., Kim HE., Lee IS. Ion-beam-assisted deposition (IBAD) of hydroxyapatite coating layer on Ti-based metal substrate. Biomaterials. 2000. 21:469–73.
Article16.Li P., de Groot K. Better bioactive ceramics through sol-gel process. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol. 1994. 2:797–801.
Article17.Hamad K., Kon M., Hanawa T., Yokoyama K., Miyamoto Y., Asaoka K. Hydrothermal modification of titanium surface in calcium solutions. Biomaterials. 2002. 23:2265–72.
Article18.Ma J., Wang C., Peng KW. Electrophoretic deposition of porous hydroxyapatite scaffold. Biomaterials. 2003. 24:3505–10.
Article19.Milella E., Cosentino F., Licciulli A., Massaro C. Preparation and characterisation of titania/hydroxyapatite composite coatings obtained by sol-gel process. Biomaterials. 2001. 22:1425–31.
Article20.Kasemo B., Lausmaa J. Aspect of surface physics on titanium implants. Swed Dent J. 1983. 28:19–36.21.Hulbert SC. Bioactive ceramic-bone interface. In: Yamamuro T, Hench L, Wilson J (eds). Handbook of Bioactive Ceramics. Vol I. Boca Raton. FL: CRC. 1990. 32:409–17.22.LeGeros RZ. Properties of osteoconductive biomaterials: calcium phosphates. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002. 395:81–98.
Article23.Jung YC., Han CH., Lee IS., Kim HE. Effects of ion beam-assisted deposition of hydroxyapatite on the osseointegration of endosseous implants in rabbit tibiae. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2001. 16:809–18.24.Park YS., Yi KY., Lee IS., Han CH., Jung YC. The effects of ion beam-assisted deposition of hydroxyapatite on the grit-blasted surface of endosseous implants in rabbit tibiae. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2005. 20:31–8.25.Haddow DB., Kothari S., James PF., Short RD., Hatton PV., van Noort R. Synthetic implant surfaces. 1. The formation and characterization of sol-gel titania films. Biomaterials. 1996. 17:501–7.26.Milella E., Cosentino F., Licciulli A., Massaro C. Preparation and characterization of titania/hydroxyapatite composite coatings obtained by sol-gel process. Biomaterials. 2001. 22:1425–31.27.Ramires PA., Wennerberg A., Johansson CB., Cosentino F., Tundo S., Milella E. Biological behavior of sol-gel coated dental implants. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2003. 14:539–45.28.Listgarten MA., Buser D., Steinemann SG., Donath K., Lang NP., Weber HP. Light and transmission electron microscopy of the intact interfaces between non-submerged titanium-coated epoxy resin implants and bone or gingiva. J Dent Res. 1992. 71:364–71.
Article29.Rodriguez R., Kim K., Ong JL. In vitro osteoblast response to anodized titanium and anodized titanium followed by hydrothermal treatment. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2003. 65:352–8.30.Sul YT., Johansson CB., Jeong Y., Albrektsson T. The electrochemical oxide growth behaviour on titanium in acid and alkaline electrolytes. Med Eng Phys. 2001. 23:329–46.
Article31.Sul YT., Johansson CB., Petronis S., Krozer A., Jeong Y., Wennerberg A., Albrektsson T. Characteristics of the surface oxides on turned and electrochemically oxidized pure titanium implants up to dielectric breakdown: the oxide thickness, micropore configurations, surface roughness, crystal structure and chemical composition. Biomaterials. 2002. 23:491–501.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The effect of implant surface treated by anodizing on proliferation of the rat osteoblast
- A study on osteoblast-like cell responses to surface-modified titanium
- Bone response of two different surface titanium subperiosteal implants: anodized surface, ibad ha coating surface
- Surface characteristics and bioactivity of an anodized titanium surface
- Cell response to a newly developed Ti-10Ta-10Nb alloy and its sputtered nanoscale coating