J Korean Acad Prosthodont.
2010 Oct;48(4):251-258. 10.4047/jkap.2010.48.4.251.
The influence of surface conditioning on the shear bond strength of self-adhesive resin cement to zirconia ceramics
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dentistry, Graduate School, Wonkwang University, Iksan, Korea. pro11@wku.ac.kr
- KMID: 2195540
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jkap.2010.48.4.251
Abstract
- PURPOSE
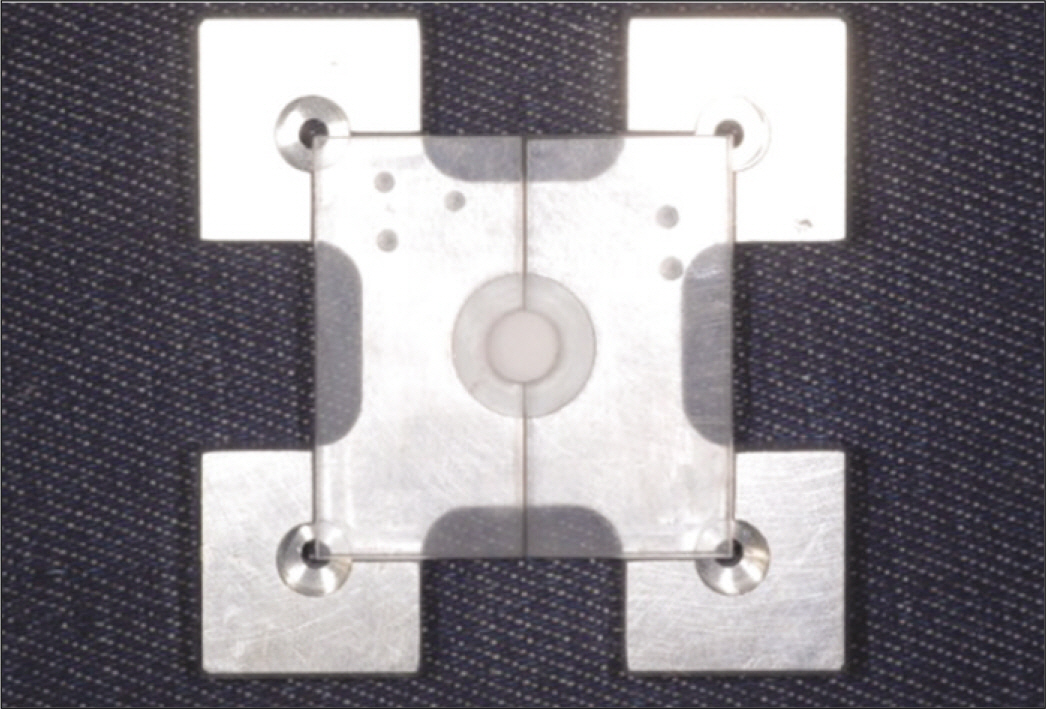
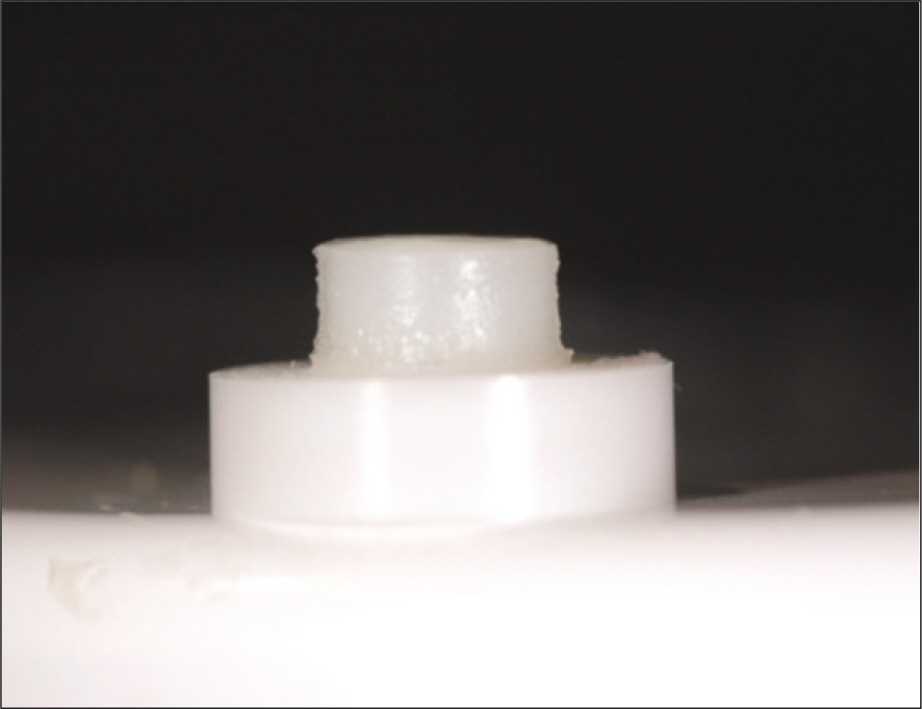
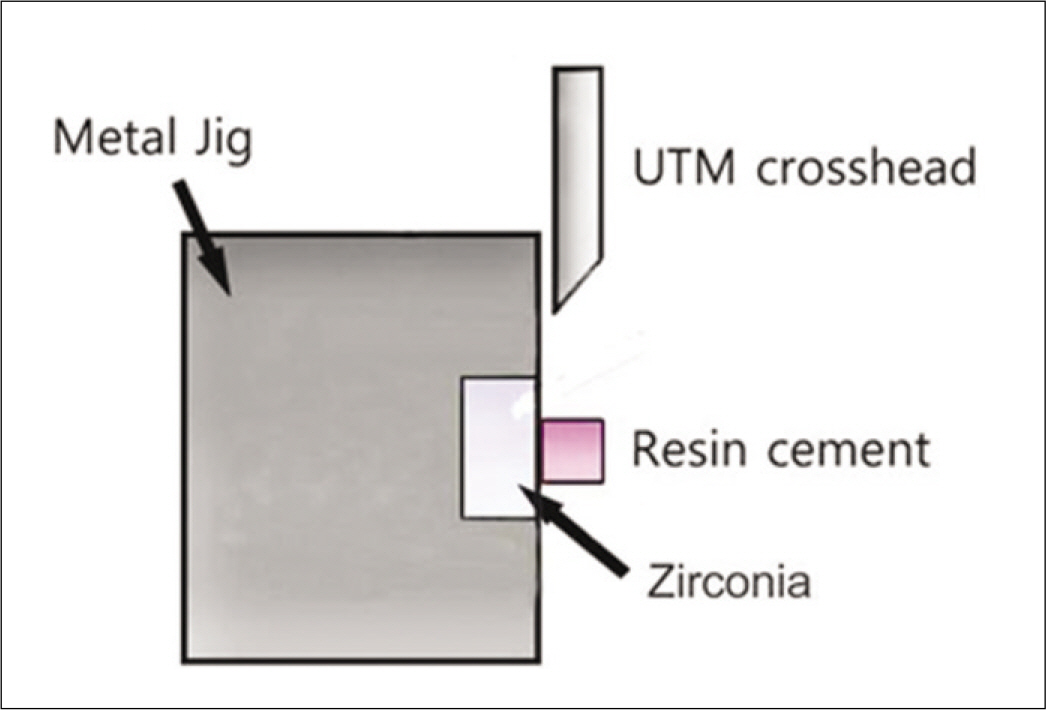
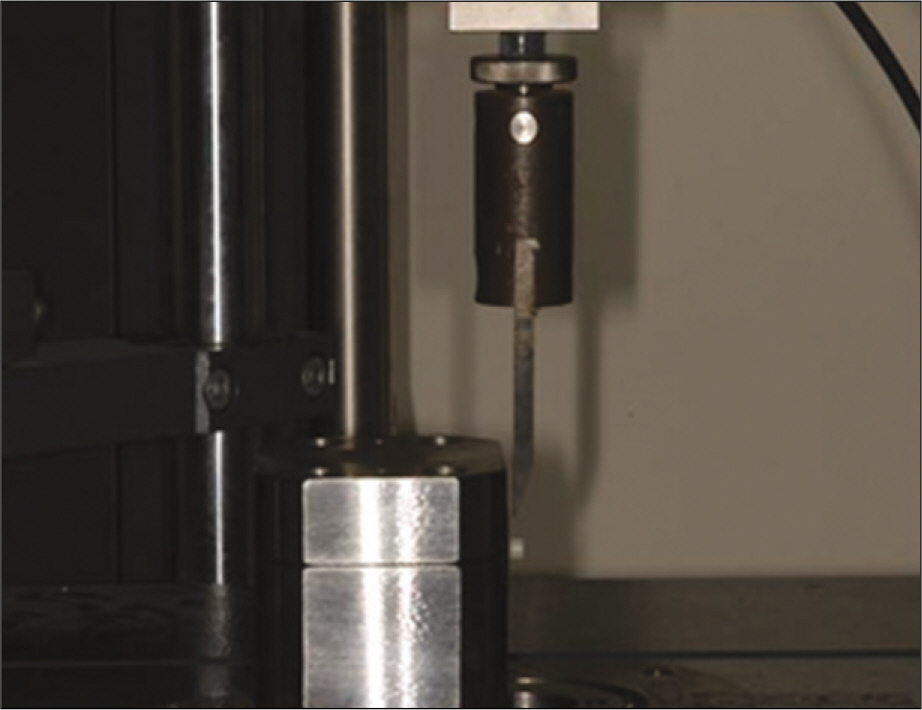
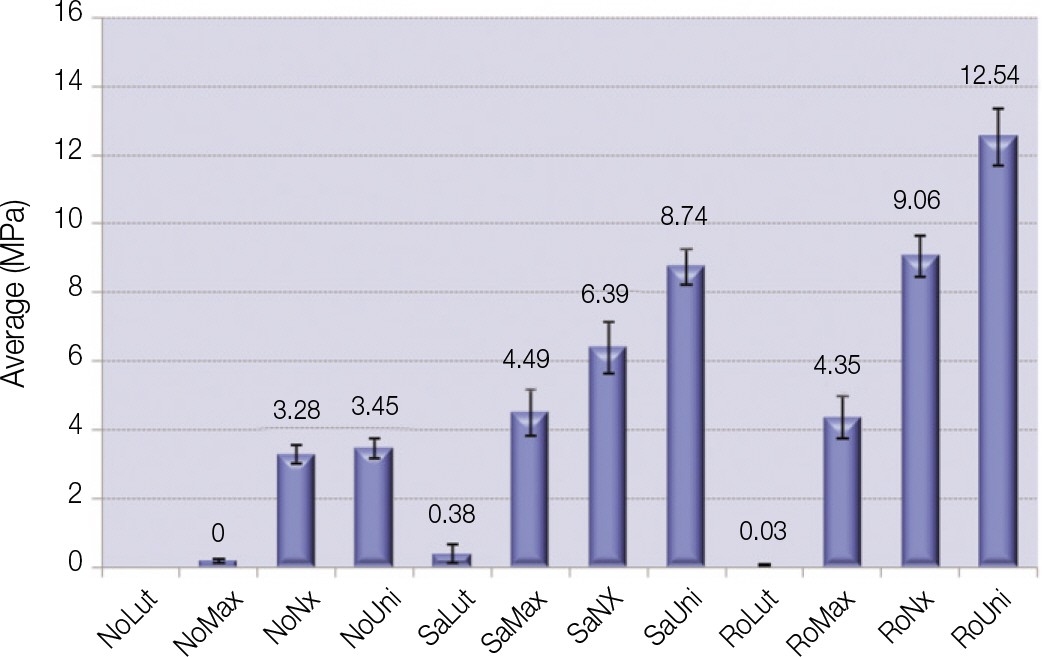
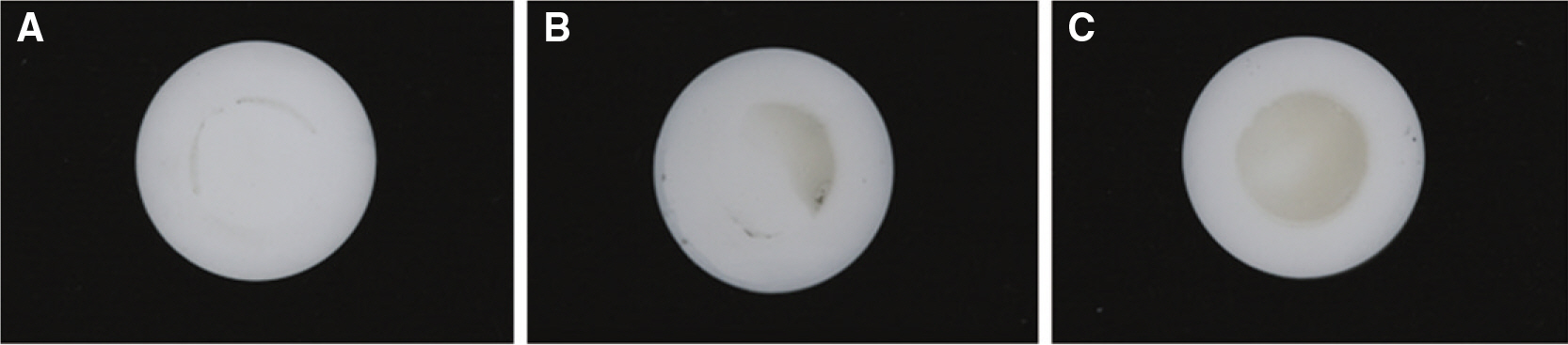
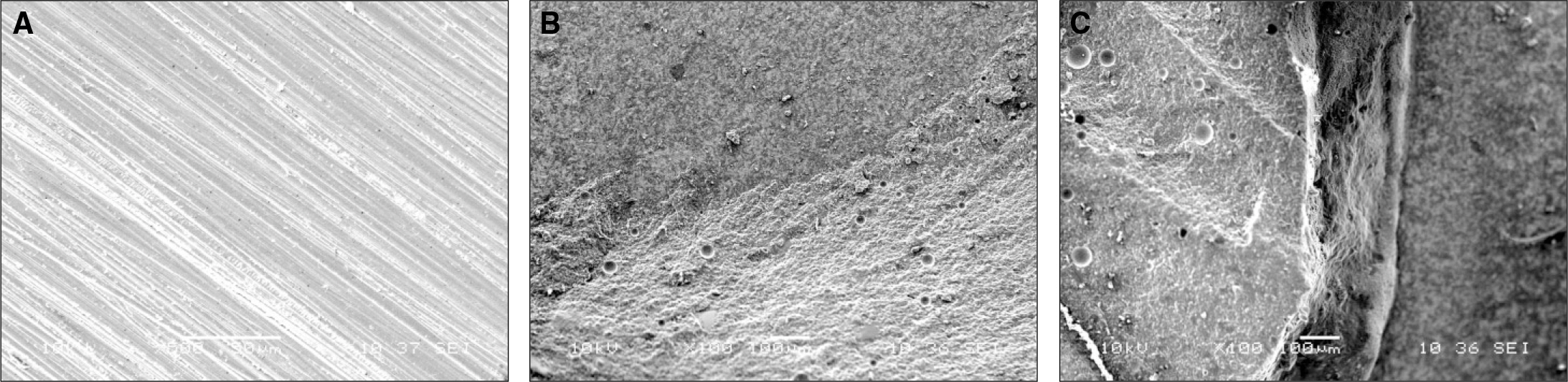
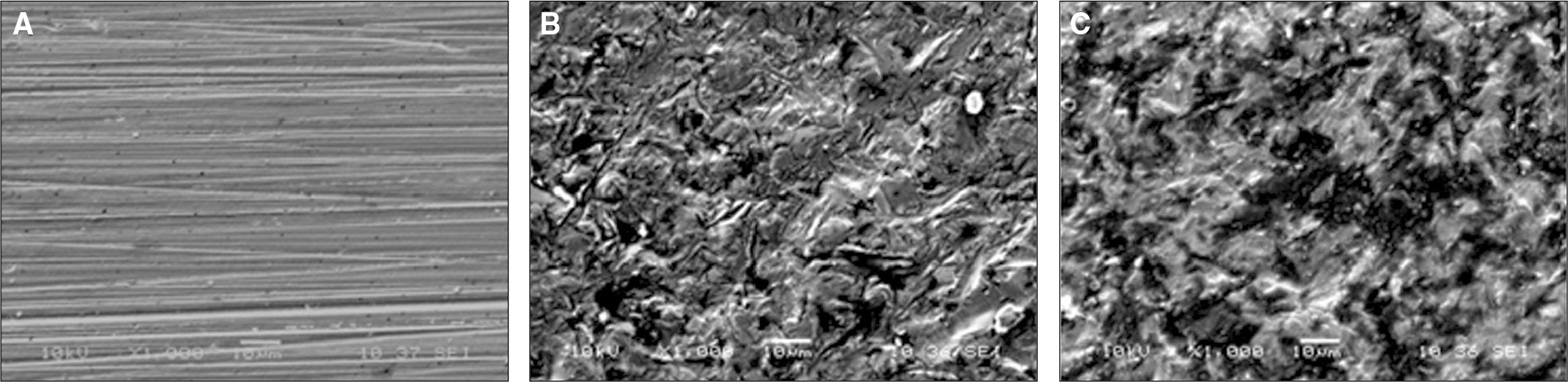
To evaluate the effect of surface conditioning on the shear bond strength of zirconium-oxide ceramic to 4 luting agents. MATERIAL AND METHODS: A total of 120 disk-shaped zirconium-oxide ceramic blocks (3Y-TZP, Kyoritsu, Japan) were treated as follows: (1) Sandblasting with 110 microm aluminum-oxide (Al2O3) particles; (2) tribochemical silica coating (Rocatec) using 110 microm Al2O3 particles modified by silica; (3) no treatment. Then zirconium-oxide ceramic blocks bonded with 4 luting cements (RelyX luting (3M ESPE), Maxcem (Kerr), Nexus3 (Kerr), Rely X Unicem (3M ESPE)). Each group was tested in shear bond strengths by UTM. A 1-way analysis of variance and 2-way analysis of variance was used to analyze the data (alpha = .05).
RESULTS
RelyX unicem in combination tribochemical silica-coating produced a highest bond strength (P < .05). Air abrasion group and Rocatec treatment groups resulted in significantly higher than no conditioning group (P < .05). RelyX Luting groups showed lower bond strength than other groups. There were significant differences among groups (P < .05).
CONCLUSION
Within the limitation of this study, RelyX Unicem cement provided the highest bond strength and Rocatec treatment enhanced the bond strength.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effect of universal primer on shear bond strength between resin cement and restorative materials
Nahong Kim, June-Sung Shim, Hong-Suk Moon, Keun-Woo Lee
J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2012;50(2):112-118. doi: 10.4047/jkap.2012.50.2.112.
Reference
-
1.Ozcan M., Vallittu PK. Effect of surface conditioning methods on the bond strength of luting cement to ceramics. Dent Mater. 2003. 19:725–31.2.Phark JH., Duarte S Jr., Blatz M., Sadan A. An in vitro evaluation of the long-term resin bond to a new densely sintered high-purity zirconium-oxide ceramic surface. J Prosthet Dent. 2009. 101:29–38.
Article3.Palacios RP., Johnson GH., Phillips KM., Raigrodski AJ. Retention of zirconium oxide ceramic crowns with three types of cement. J Prosthet Dent. 2006. 96:104–14.
Article4.Ozcan M., Nijhuis H., Valandro LF. Effect of various surface conditioning methods on the adhesion of dual-cure resin cement with MDP functional monomer to zirconia after thermal aging. Dent Mater J. 2008. 27:99–104.5.Manicone PF., Rossi Iommetti P., Raffaelli L. An overview of zirconia ceramics: basic properties and clinical applications. J Dent. 2007. 35:819–26.
Article6.Aboushelib MN., Matinlinna JP., Salameh Z., Ounsi H. Innovations in bonding to zirconia-based materials: Part I. Dent Mater. 2008. 24:1268–72.
Article7.Lu ¨thy H., Loeffel O., Hammerle CH. Effect of thermocycling on bond strength of luting cements to zirconia ceramic. Dent Mater. 2006. 22:195–200.8.Chaiyabutr Y., McGowan S., Phillips KM., Kois JC., Giordano RA. The effect of hydrofluoric acid surface treatment and bond strength of a zirconia veneering ceramic. J Prosthet Dent. 2008. 100:194–202.
Article9.Bindl A., Lu ¨thy H., Mo ¨rmann WH. Thin-wall ceramic CAD/CAM crown copings: strength and fracture pattern. J Oral Rehabil. 2006. 33:520–8.
Article10.Ernst CP., Cohnen U., Stender E., Willershausen B. In vitro retentive strength of zirconium oxide ceramic crowns using different luting agents. J Prosthet Dent. 2005. 93:551–8.
Article11.Blatz MB., Chiche G., Holst S., Sadan A. Influence of surface treatment and simulated aging on bond strengths of luting agents to zirconia. Quintessence Int. 2007. 38:745–53.12.Derand T., Molin M., Kvam K. Bond strength of composite luting cement to zirconia ceramic surfaces. Dent Mater. 2005. 21:1158–62.
Article13.Spohr AM., Borges GA., Ju′nior LH., Mota EG., Oshima HM. Surface modification of In-Ceram Zirconia ceramic by Nd: YAG laser, Rocatec system, or aluminum oxide sandblasting and its bond strength to a resin cement. Photomed Laser Surg. 2008. 26:203–8.14.Kern M., Wegner SM. Bonding to zirconia ceramic: adhesion methods and their durability. Dent Mater. 1998. 14:64–71.
Article15.De′rand P., De′rand T. Bond strength of luting cements to zirconium oxide ceramics. Int J Prosthodont. 2000. 13:131–5.16.de Oyagu ¨e RC., Monticelli F., Toledano M., Osorio E., Ferrari M., Osorio R. Influence of surface treatments and resin cement selection on bonding to densely-sintered zirconium-oxide ceramic. Dent Mater. 2009. 25:172–9.17.Kumbuloglu O., Lassila LV., User A., Vallittu PK. Bonding of resin composite luting cements to zirconium oxide by two air-particle abrasion methods. Oper Dent. 2006. 31:248–55.
Article18.Blatz MB., Phark JH., Ozer F., Mante FK., Saleh N., Bergler M., Sadan A. In vitro comparative bond strength of contemporary self-adhesive resin cements to zirconium oxide ceramic with and without air-particle abrasion. Clin Oral Investig. 2010. 14:187–92.
Article19.Kosmac T., Oblak C., Jevnikar P., Funduk N., Marion L. The effect of surface grinding and sandblasting on flexural strength and reliability of Y-TZP zirconia ceramic. Dent Mater. 1999. 15:426–33.20.Willer J., Rossbach A., Weber HP. Computer-assisted milling of dental restorations using a new CAD/CAM data acquisition system. J Prosthet Dent. 1998. 80:346–53.
Article21.Wolfart M., Lehmann F., Wolfart S., Kern M. Durability of the resin bond strength to zirconia ceramic after using different surface conditioning methods. Dent Mater. 2007. 23:45–50.
Article22.Blatz MB., Sadan A., Martin J., Lang B. In vitro evaluation of shear bond strengths of resin to densely-sintered high-purity zirconium-oxide ceramic after long-term storage and thermal cycling. J Prosthet Dent. 2004. 91:356–62.
Article23.Janda R., Roulet JF., Wulf M., Tiller HJ. A new adhesive technology for all-ceramics. Dent Mater. 2003. 19:567–73.
Article24.Blixt M., Adamczak E., Linde′n LA., Ode′n A., Arvidson K. Bonding to densely sintered alumina surfaces: effect of sandblasting and silica coating on shear bond strength of luting cements. Int J Prosthodont. 2000. 13:221–6.25.Radovic I., Monticelli F., Goracci C., Vulicevic ZR., Ferrari M. Self-adhesive resin cements: a literature review. J Adhes Dent. 2008. 10:251–8.26.Senyilmaz DP., Palin WM., Shortall AC., Burke FJ. The effect of surface preparation and luting agent on bond strength to a zirconium-based ceramic. Oper Dent. 2007. 32:623–30.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Bond strength of resin cement to CO2 and Er:YAG laser-treated zirconia ceramic
- Effect Of Dentin Desensitizers On Shear Bond Strength Of Resin Cements
- Effect of surface treatments of zirconia ceramic on the bond strength of resin cements
- Influence of nano-structured alumina coating treatment on shear bond strength between zirconia ceramic and resin cement
- The effect of surface treatment conditioning on shear bond strength between zirconia and dental resin cements