J Korean Acad Prosthodont.
2015 Apr;53(2):157-166. 10.4047/jkap.2015.53.2.157.
Immediate restorations in a fully edentulous patient utilizing digital system: A case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, Wonju College of Medicine, Yonsei University, Wonju, Republic of Korea. smj3@yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Wonju College of Medicine, Yonsei University, Wonju, Republic of Korea.
- KMID: 2195399
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jkap.2015.53.2.157
Abstract
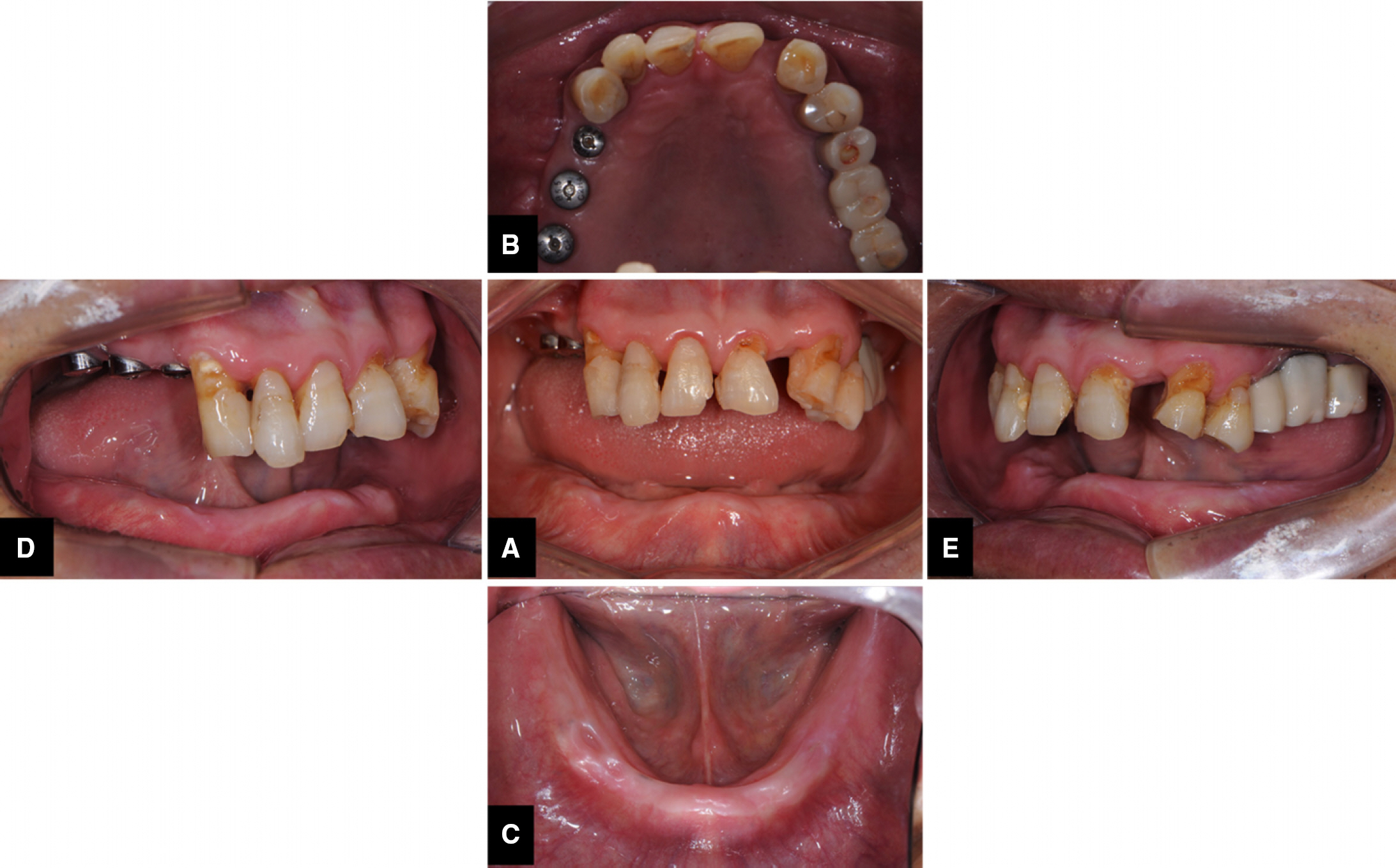
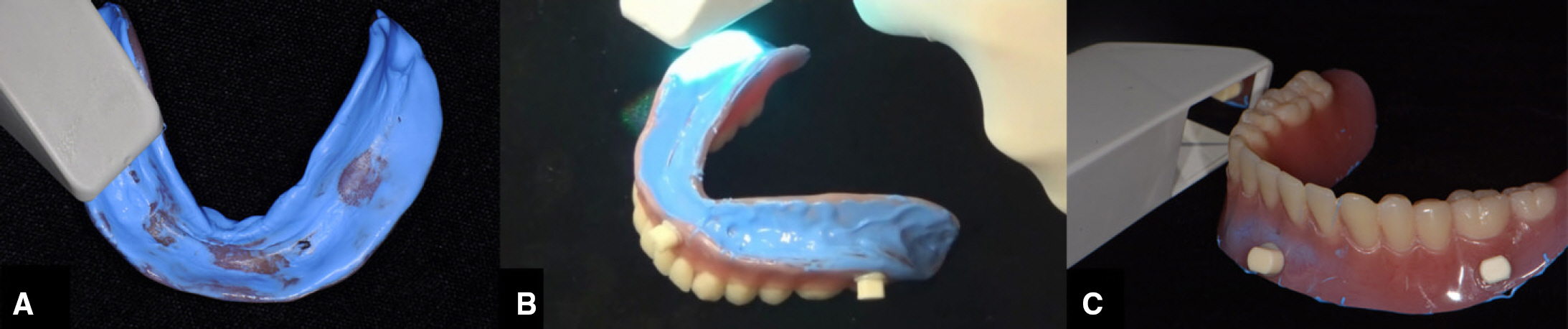
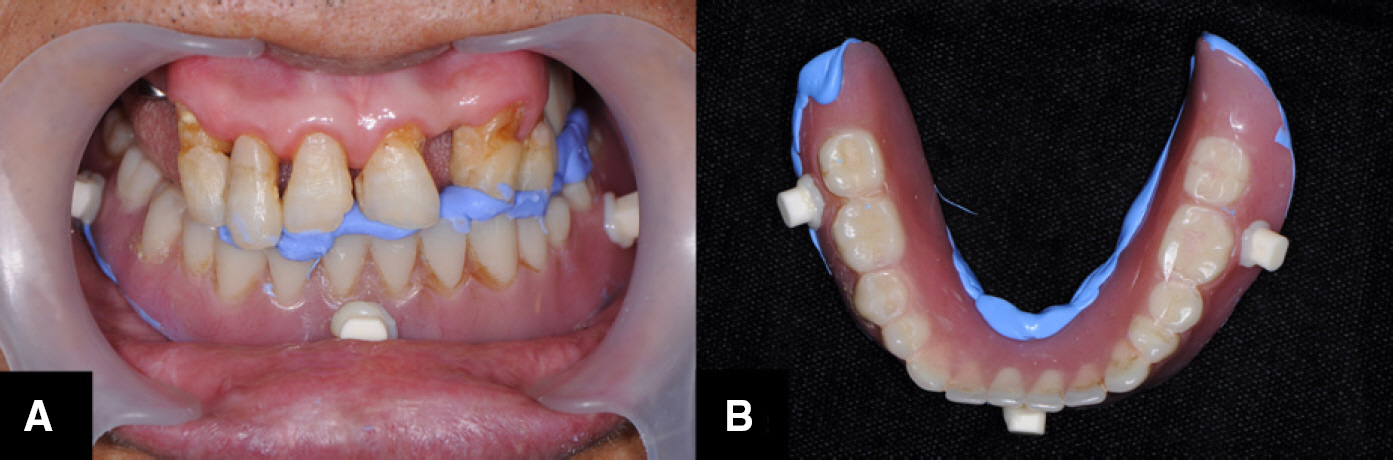
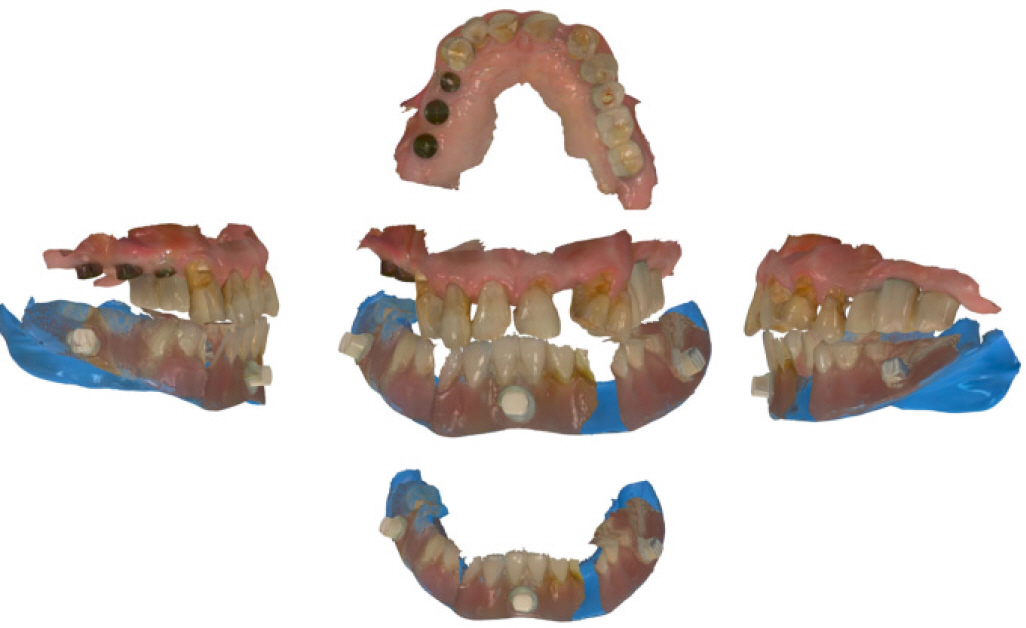
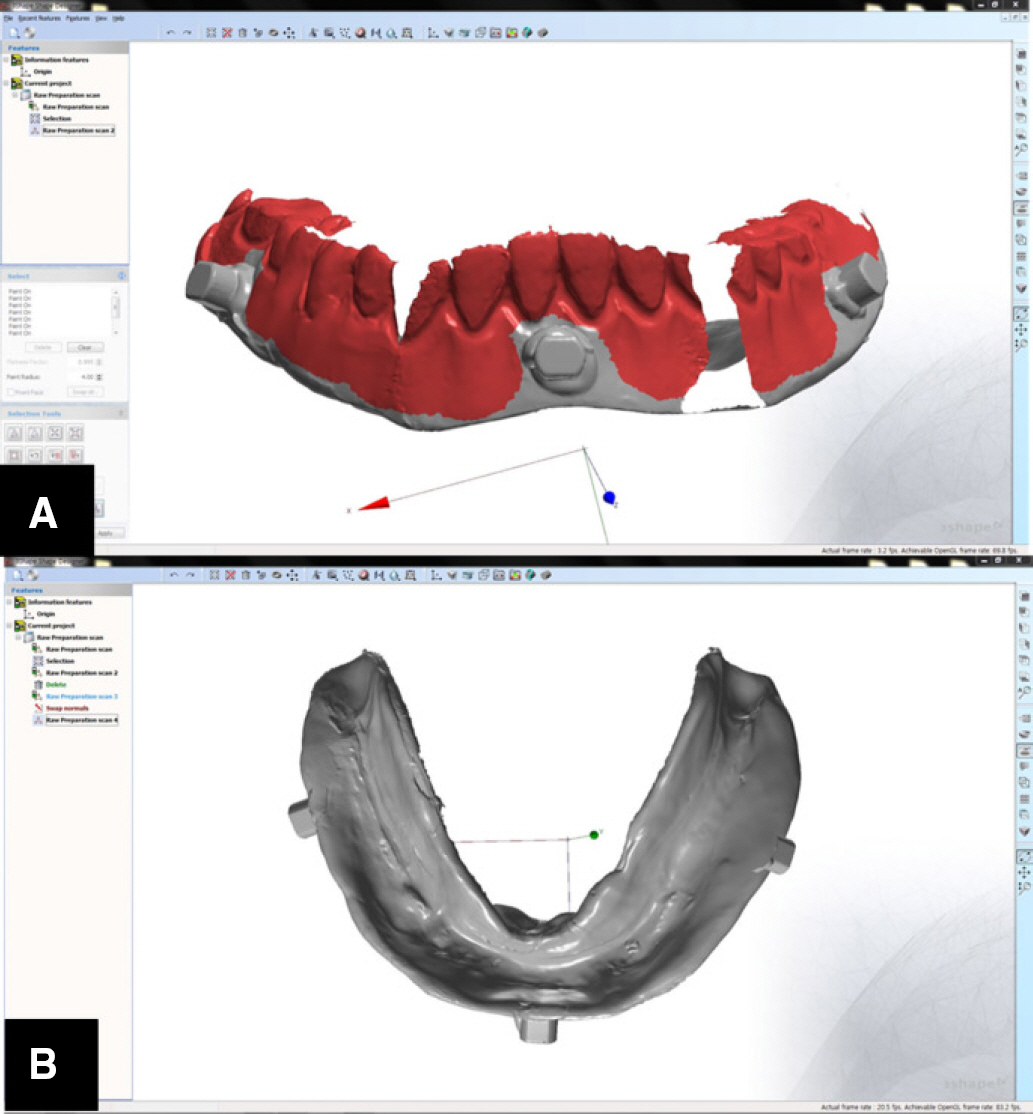
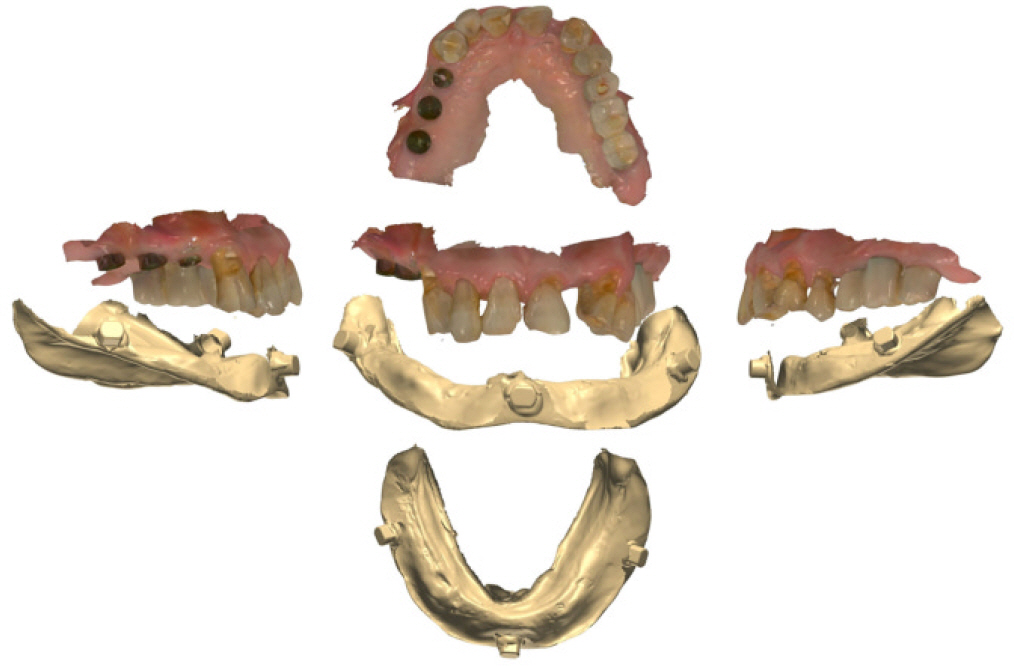
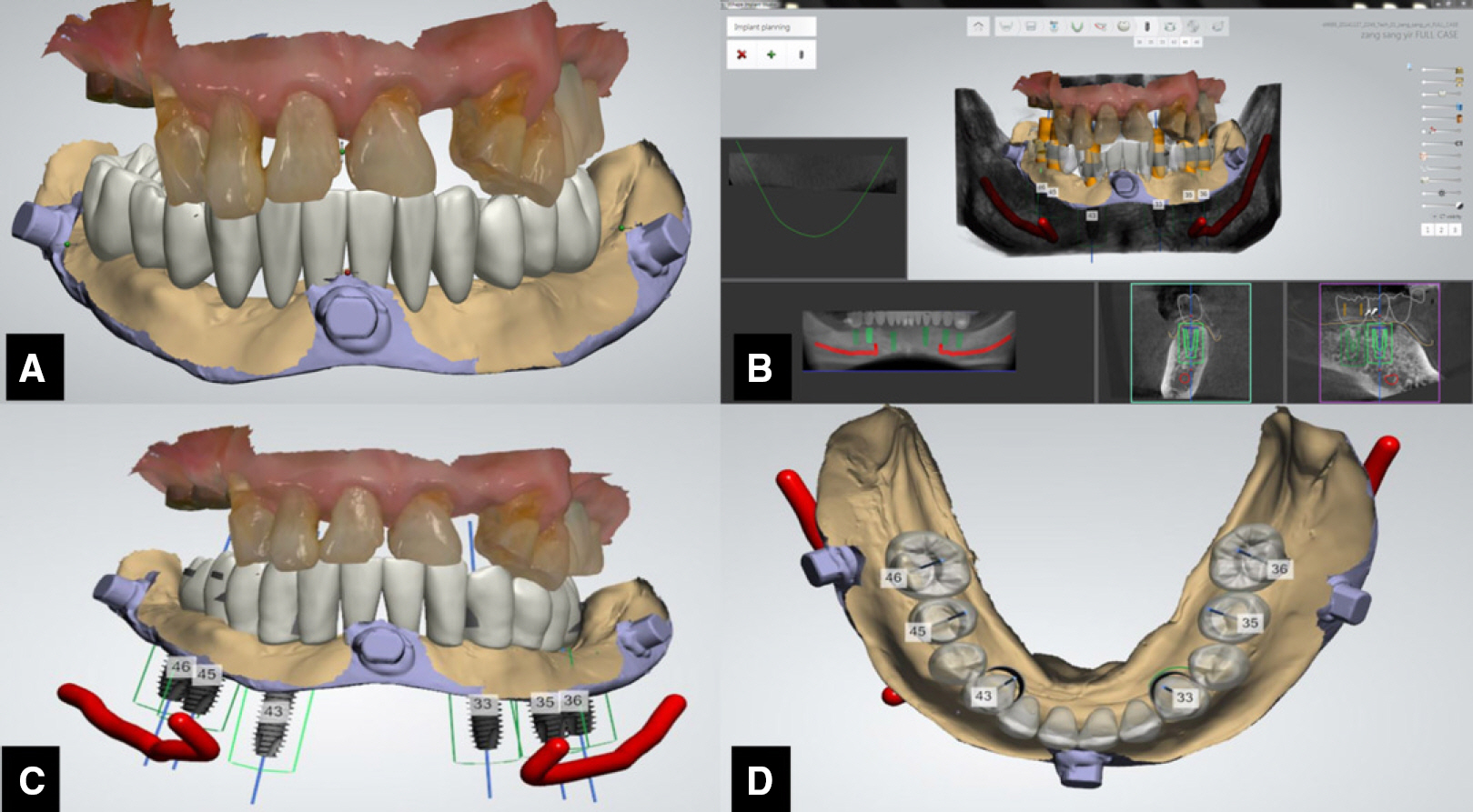
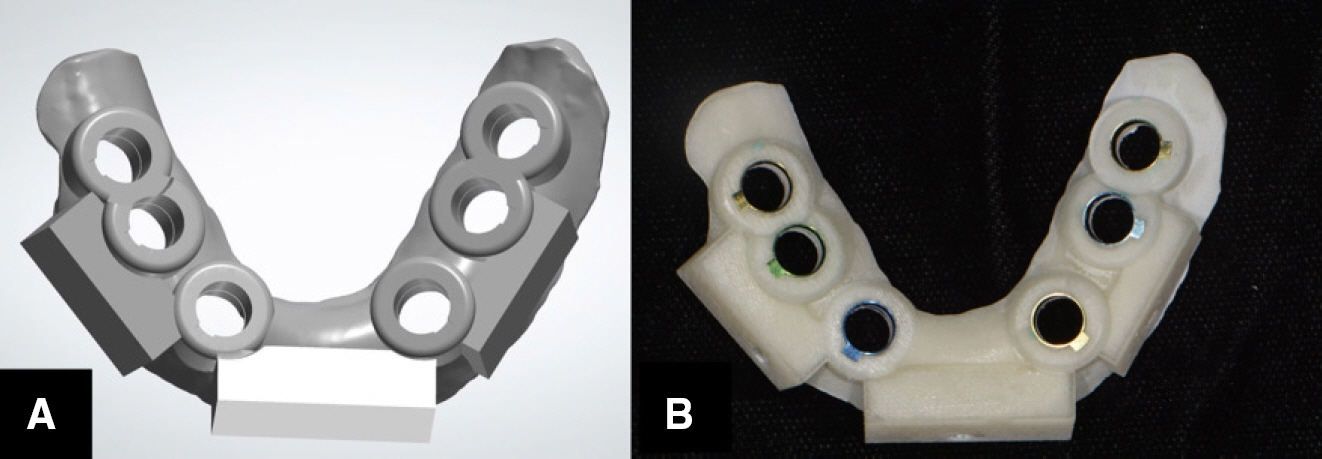
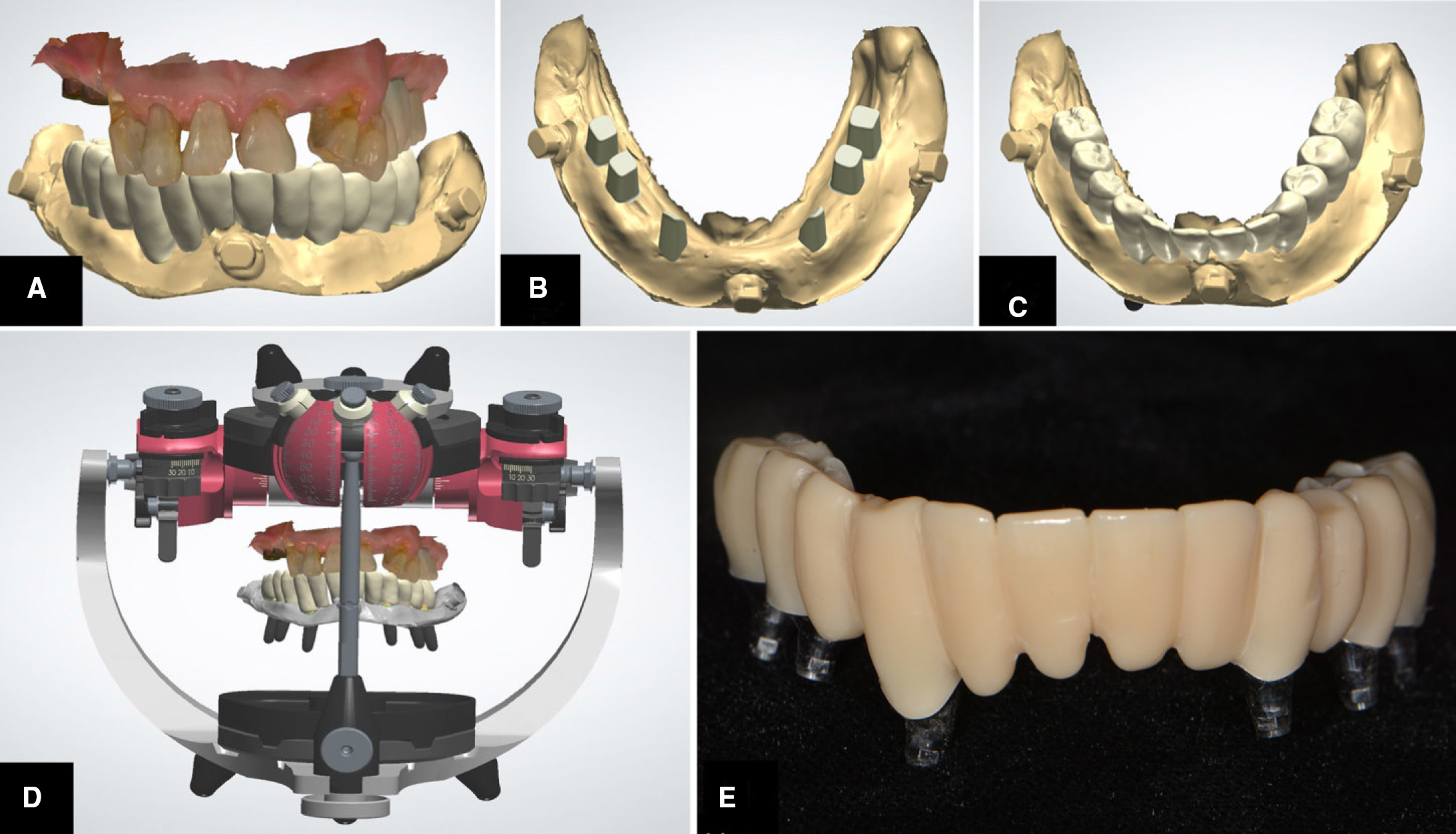
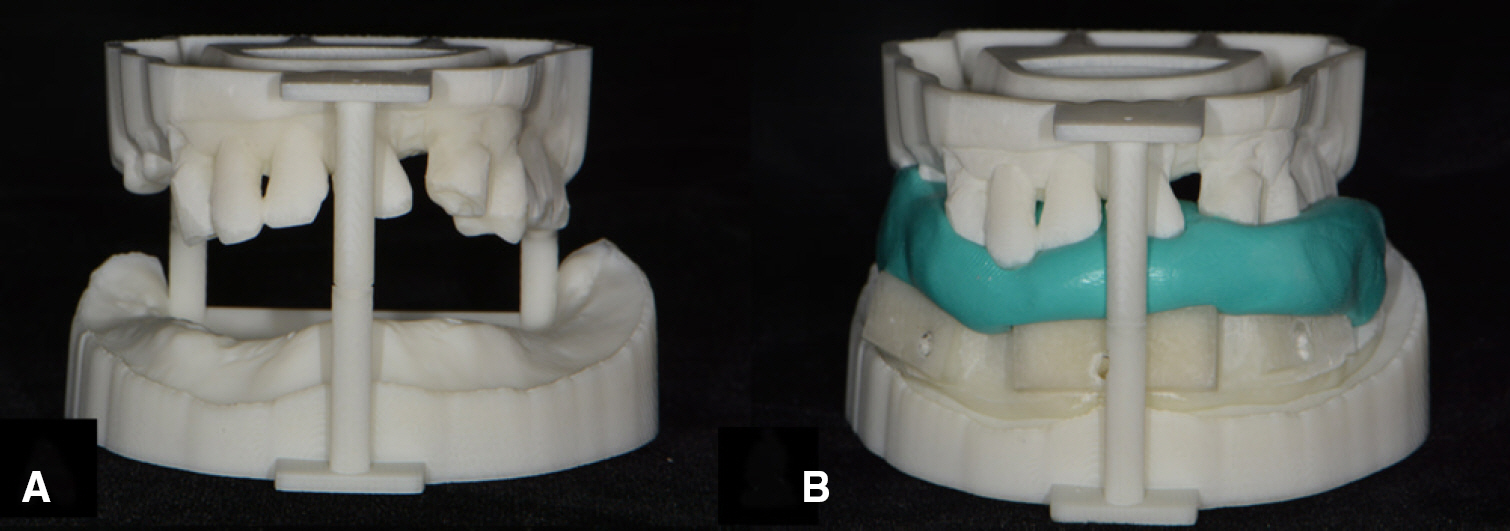
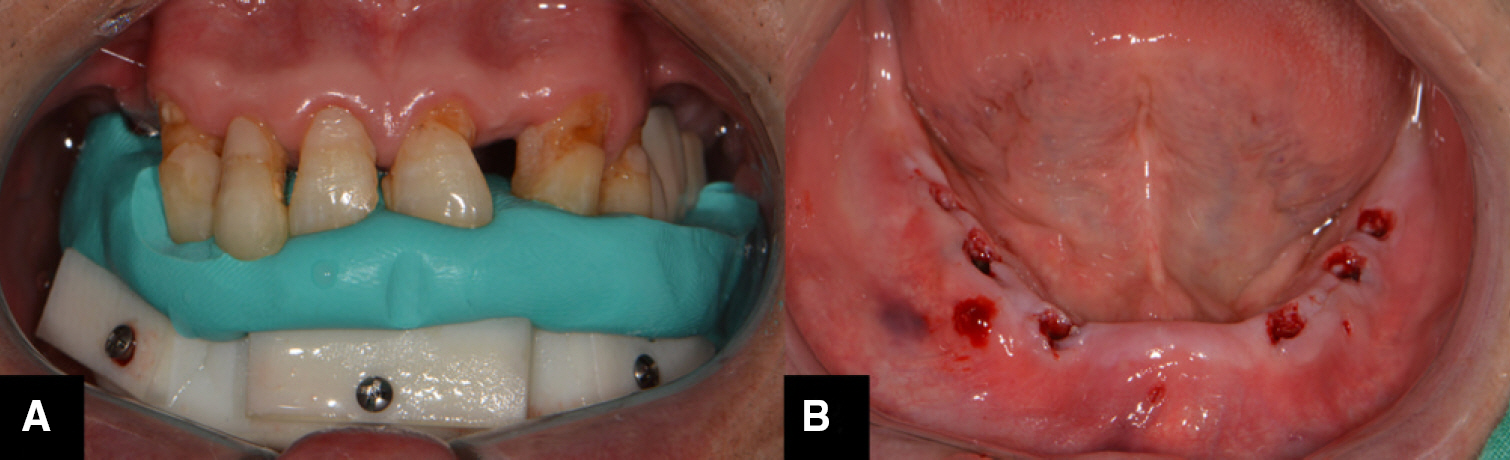
- This article describes how to use CBCT and an intraoral scanner in a fully edentulous case that enables the clinician to place implants with flapless guided surgery and to engage prefabricated, customized implant abutments at the time of implant surgery, with only 1 clinical consultation before implant surgery. The patient's existing denture is used to simulate the teeth, the soft tissue and the vertical dimension of occlusion, and jaw relationship in the fully edentulous jaw. It provides clinicians with a fast workflow and improves clinical efficiency.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Derhalli M. The digitalizing of implant dentistry: a clinical evaluation of 15 patients. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 2013; 34:192–6.2. Di Giacomo GA, Cury PR, de Araujo NS, Sendyk WR, Sendyk CL. Clinical application of stereolithographic surgical guides for implant placement: preliminary results. J Periodontol. 2005; 76:503–7.3. Ruppin J, Popovic A, Strauss M, Spü ntrup E, Steiner A, Stoll C. Evaluation of the accuracy of three different computer-aided surgery systems in dental implantology: optical tracking vs. stereolithographic splint systems. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2008; 19:709–16.
Article4. Van Assche N, van Steenberghe D, Guerrero ME, Hirsch E, Schutyser F, Quirynen M, Jacobs R. Accuracy of implant placement based on pre-surgical planning of three-dimensional cone-beam images: a pilot study. J Clin Periodontol. 2007; 34:816–21.
Article5. van Steenberghe D, Naert I, Andersson M, Brajnovic I, Van Cleynenbreugel J, Suetens P. A custom template and definitive prosthesis allowing immediate implant loading in the maxilla: a clinical report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2002; 17:663–70.6. Hermann S, Carsten T, Stephan I, Gü nter B, Robert S, Hans-Florian Z. Rapid Prototyping models for surgical planning with hard and soft tissue representation. Int Congress Series. 2004; 1268:567–72.7. Ganz SD. Use of stereolithographic models as diagnostic and restorative aids for predictable immediate loading of implants. Pract Proced Aesthet Dent. 2003; 15:763–71.8. Hajeer MY, Millett DT, Ayoub AF, Siebert JP. Applications of 3D imaging in orthodontics: part II. J Orthod. 2004; 31:154–62.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Digital intraoral impression for immediate provisional restoration of maxillary single implant: A case report
- Fixed prosthesis restoration in edentulous patient fully implanted without considering definitive prosthesis: A case report
- Maxillary complete denture and mandibular implantsupported fixed prosthesis restoration utilizing digital workflow
- Full mouth rehabilitation of an edentulous patient using maxillary complete denture and mandibular implant supported fixed prostheses: a case report
- All-on-6 implant fixed prosthesis restoration with fulldigital system on edentulous patient: A case report