J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2013 Sep;54(3):243-245. 10.3340/jkns.2013.54.3.243.
Rotational Vertebral Artery Compression : Bow Hunter's Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, School of Medicine, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea. 1coo3004@naver.com
- KMID: 2190906
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2013.54.3.243
Abstract
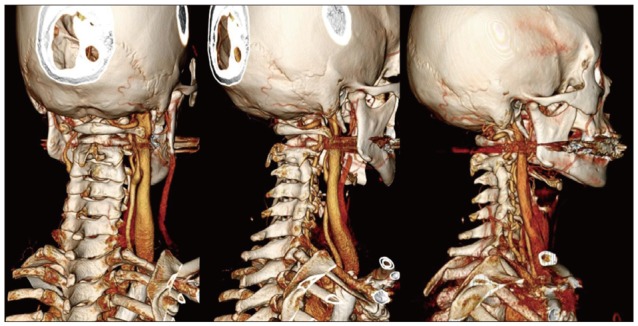
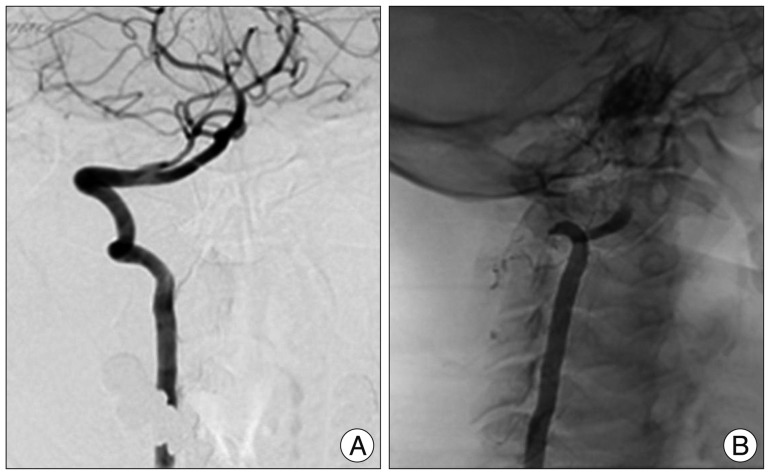
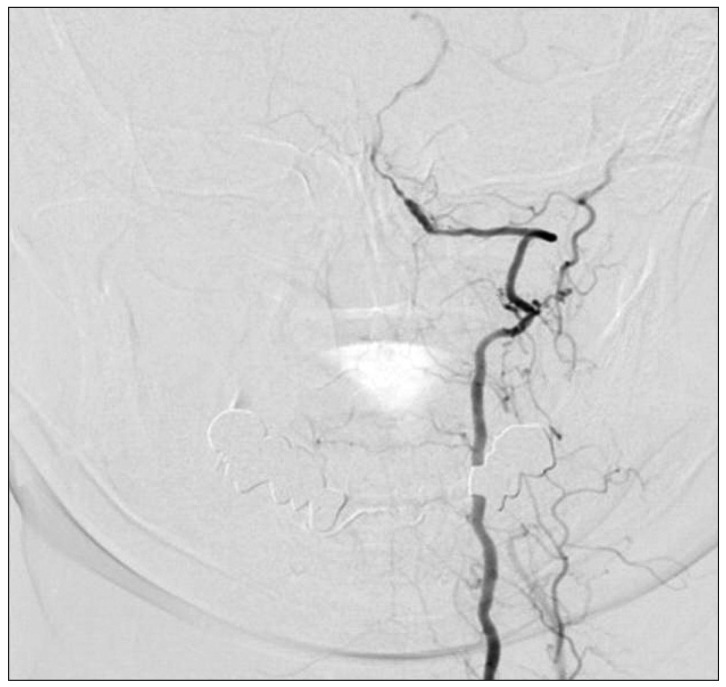
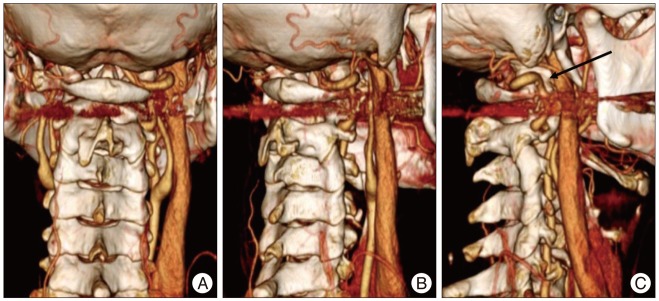
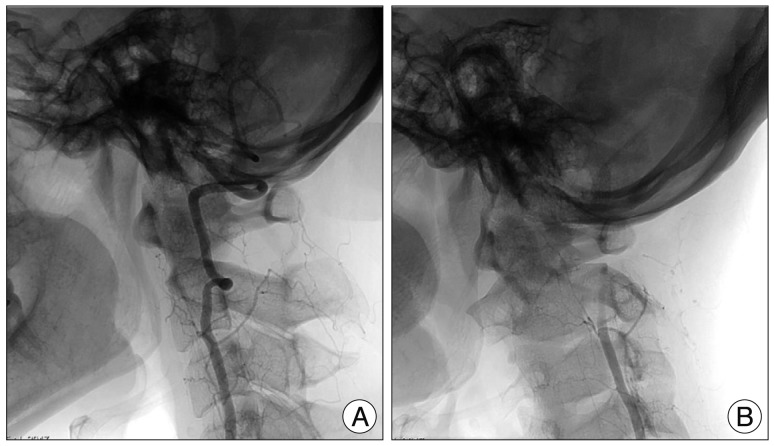
- Bow hunter's syndrome (BHS) is rare cause of vertebrobasilar insufficiency that arises from mechanical compression of the vertebral artery by head rotation. There is no standardized diagnostic regimen or treatment of BHS. Recently, we experienced 2 cases resisted continues medication and treated by surgical approach. In both cases, there were no complications after surgery and there were improvements in clinical symptoms. Thus, we describe our cases with surgical decompression with a review of the relevant medical literature.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Case of Rotational Vertebral Artery Syndrome after Vertebral Artery Dissection
Song Jae Lee, Ha Young Byun, Seung Hwan Lee, Jae Ho Chung
Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2020;63(5):228-232. doi: 10.3342/kjorl-hns.2019.00633.
Reference
-
1. Cornelius JF, George B, N'Dri Oka D, Spiriev T, Steiger HJ, Hanggi D. Bow-hunter's syndrome caused by dynamic vertebral artery stenosis at the cranio-cervical junction--a management algorithm based on a systematic review and a clinical series. Neurosurg Rev. 2012; 35:127–135. discussion 135. PMID: 21789571.
Article2. Diaz FG, Ausman JI, Shrontz C, Pearce J, Gehring R, Mehta B, et al. Surgical correction of lesions affecting the second portion of the vertebral artery. Neurosurgery. 1986; 19:93–100. PMID: 3748345.
Article3. Grossmann RI, Davis KR. Positional occlusion of the vertebral artery : a rare cause of embolic stroke. Neuroradiology. 1982; 23:227–230. PMID: 7121817.
Article4. Horowitz M, Jovin T, Balzar J, Welch W, Kassam A. Bow hunter's syndrome in the setting of contralateral vertebral artery stenosis : evaluation and treatment options. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002; 27:E495–E498. PMID: 12461405.5. Kuether TA, Nesbit GM, Clark WM, Barnwell SL. Rotational vertebral artery occlusion : A mechanism of vertebrobasilar insufficiency. Neurosurgery. 1997; 41:427–432. discussion 432-423. PMID: 9257311.6. Lu DC, Gupta N, Mummaneni PV. Minimally invasive decompression of a suboccipital osseous prominence causing rotational vertebral artery occlusion. Case report. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2009; 4:191–195. PMID: 19772401.
Article7. Matsuyama T, Morimoto T, Sakaki T. Comparison of c1-2 posterior fusion and decompression of the vertebral artery in the treatment of bow hunter's stroke. J Neurosurg. 1997; 86:619–623. PMID: 9120624.
Article8. Shimizu T, Waga S, Kojima T, Niwa S. Decompression of the vertebral artery for bow-hunter's stroke. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1988; 69:127–131. PMID: 3379466.10. Strupp M, Planck JH, Arbusow V, Steiger HJ, Bruckmann H, Brandt T. Rotational vertebral artery occlusion syndrome with vertigo due to "labyrinthine excitation". Neurology. 2000; 54:1376–1379. PMID: 10746615.
Article11. Tominaga T, Takahashi T, Shimizu H, Yoshimoto T. Rotational vertebral artery occlusion from occipital bone anomaly : a rare cause of embolic stroke. Case report. J Neurosurg. 2002; 97:1456–1459. PMID: 12507149.
Article12. Wakayama K, Murakami M, Suzuki M, Ono S, Shimizu N. Ischemic symptoms induced by occlusion of the unilateral vertebral artery with head rotation together with contralateral vertebral artery dissection--case report. J Neurol Sci. 2005; 236:87–90. PMID: 15979646.
Article13. Wang S, Wang C, Liu Y, Yan M, Zhou H. Anomalous vertebral artery in craniovertebral junction with occipitalization of the atlas. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009; 34:2838–2842. PMID: 20010391.
Article14. Yang PJ, Latack JT, Gabrielsen TO, Knake JE, Gebarski SS, Chandler WF. Rotational vertebral artery occlusion at c1-c2. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1985; 6:96–100. PMID: 3918425.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Rotational Vertebral Artery Syndrome (Bow Hunter’s Syndrome): A Rare Differential Diagnosis in Patients With Syncope
- A Case of Rotational Vertebral Artery Syndrome after Vertebral Artery Dissection
- Bow Hunter's Syndrome Caused by Bilateral Dynamic Occlusion of the Subaxial Vertebral Arteries during Neck Extension
- Bow Hunter's Stroke Caused by a Severe Facet Hypertrophy of C1-2
- Cervicogenic Vertigo Treated by C1 Transverse Foramen Decompression : A Case Report