J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2013 Jul;54(1):19-24. 10.3340/jkns.2013.54.1.19.
Thromboembolic Events Associated with Electrolytic Detachment of Guglielmi Detachable Coils and Target Coils : Comparison with Use of Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. nsshin@gmail.com
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Korea.
- 4Department of Radiology, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2190852
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2013.54.1.19
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
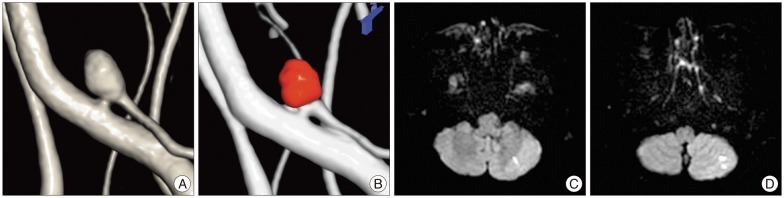
The purpose of this study was to retrospectively evaluate and compare the incidence of diffusion-weighted image (DWI) lesions between the Guglielmi detachable coil (GDC) and the Target coil for treating unruptured intracranial aneurysm.
METHODS
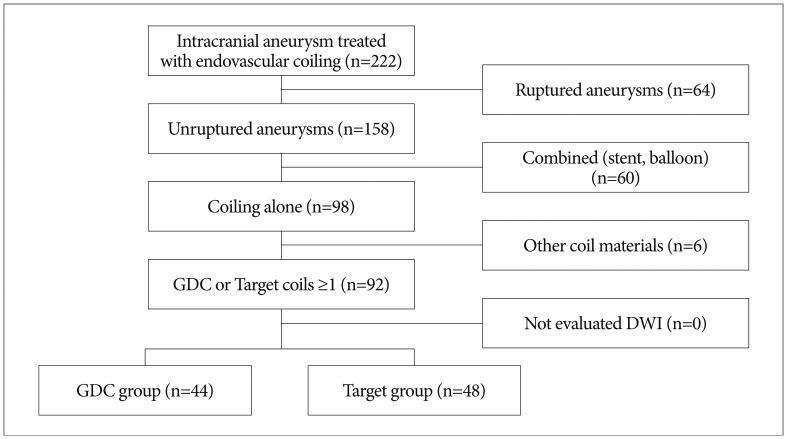
From 2010 to 2011, consecutive 222 patients with an intracranial aneurysm underwent coil embolization. Inclusion criterias were : 1) unruptured intracranial aneurysm, 2) one or more GDC or Target coils used with or without other coils, 3) DWI examination within 24 hours after coiling, and 4) coiling performed without a balloon or stent.
RESULTS
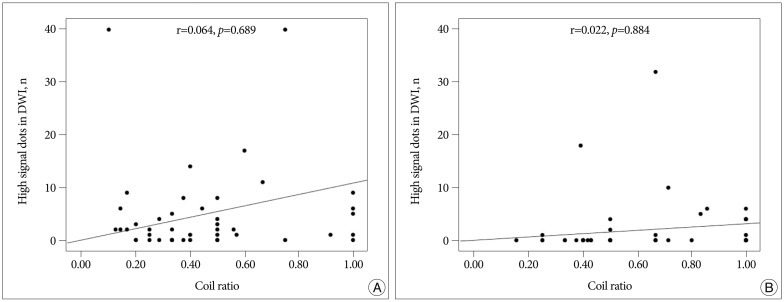
Ninety patients (92 cases) met the inclusion criteria. DWI lesions were detected in 55 (61.1%) of 90 patients. In the GDC group (n=44), DWI lesions were detected in 31 (70.5%). The average number of DWI lesions was 5.0+/-8.7 (mean+/-SD; range, 1-40) in aneurysm-related territory. In the Target coil group (n=48), DWI lesions were detected in 24 (50.0%). The number of DWI lesion was 2.1+/-5.4 (range, 1-32) in aneurysm-related territory. There was no significant correlation between a number of coils and DWI lesions. No significant differences were also observed in the number of DWI lesions in each group.
CONCLUSION
The GDC and Target coils, which have an electrolytic detachable system, showed no differences in the incidence of DWI lesion.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Albayram S, Selcuk H, Kara B, Bozdag E, Uzma O, Kocer N, et al. Thromboembolic events associated with balloon-assisted coil embolization: evaluation with diffusion-weighted MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004; 25:1768–1777. PMID: 15569744.2. Bendszus M, Koltzenburg M, Burger R, Warmuth-Metz M, Hofmann E, Solymosi L. Silent embolism in diagnostic cerebral angiography and neurointerventional procedures: a prospective study. Lancet. 1999; 354:1594–1597. PMID: 10560674.
Article3. Debrun GM, Aletich VA, Kehrli P, Misra M, Ausman JI, Charbel F. Selection of cerebral aneurysms for treatment using Guglielmi detachable coils: the preliminary University of Illinois at Chicago experience. Neurosurgery. 1998; 43:1281–1295. discussion 1296-1297. PMID: 9848841.
Article4. Han MH, Kwon OK, Yoon CJ, Kwon BJ, Cha SH, Chang KH. Gas generation and clot formation during electrolytic detachment of Guglielmi detachable coils: in vitro observations and animal experiment. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003; 24:539–544. PMID: 12637312.5. Hwang G, Park H, Bang JS, Jin SC, Kim BC, Oh CW, et al. Comparison of 2-year angiographic outcomes of stent- and nonstent-assisted coil embolization in unruptured aneurysms with an unfavorable configuration for coiling. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011; 32:1707–1710. PMID: 21852378.
Article6. Klötzsch C, Nahser HC, Henkes H, Kühne D, Berlit P. Detection of microemboli distal to cerebral aneurysms before and after therapeutic embolization. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998; 19:1315–1318. PMID: 9726475.7. Koebbe CJ, Veznedaroglu E, Jabbour P, Rosenwasser RH. Endovascular management of intracranial aneurysms: current experience and future advances. Neurosurgery. 2006; 59(5 Suppl 3):S93–S102. discussion S3-S13. PMID: 17053622.
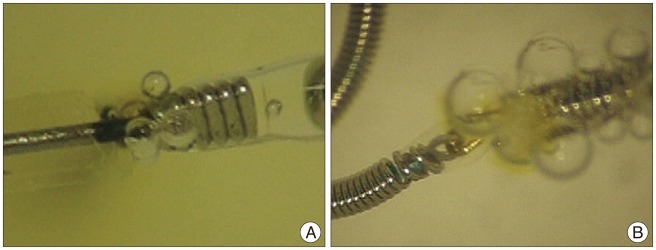
Article8. Lee DH, Hwang SM, Lim OK, Kim JK. In vitro observation of air bubbles during delivery of various detachable aneurysm embolization coils. Korean J Radiol. 2012; 13:412–416. PMID: 22778562.
Article9. Moret J, Cognard C, Weill A, Castaings L, Rey A. The "Remodelling Technique" in the Treatment of Wide Neck Intracranial Aneurysms. Angiographic Results and Clinical Follow-up in 56 Cases. Interv Neuroradiol. 1997; 3:21–35. PMID: 20678369.
Article10. Murayama Y, Nien YL, Duckwiler G, Gobin YP, Jahan R, Frazee J, et al. Guglielmi detachable coil embolization of cerebral aneurysms: 11 years' experience. J Neurosurg. 2003; 98:959–966. PMID: 12744354.
Article11. Murayama Y, Viñuela F, Duckwiler GR, Gobin YP, Guglielmi G. Embolization of incidental cerebral aneurysms by using the Guglielmi detachable coil system. J Neurosurg. 1999; 90:207–214. PMID: 9950490.
Article12. Nelson PK, Levy DI. Balloon-assisted coil embolization of wide-necked aneurysms of the internal carotid artery: medium-term angiographic and clinical follow-up in 22 patients. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001; 22:19–26. PMID: 11158882.13. Padolecchia R, Guglielmi G, Puglioli M, Castagna M, Nardini V, Collavoli PL, et al. Role of electrothrombosis in aneurysm treatment with Guglielmi detachable coils: an in vitro scanning electron microscopic study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001; 22:1757–1760. PMID: 11673174.14. Pelz DM, Lownie SP, Fox AJ. Thromboembolic events associated with the treatment of cerebral aneurysms with Guglielmi detachable coils. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998; 19:1541–1547. PMID: 9763391.15. Qureshi AI, Suri MF, Khan J, Kim SH, Fessler RD, Ringer AJ, et al. Endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms by using Guglielmi detachable coils in awake patients: safety and feasibility. J Neurosurg. 2001; 94:880–885. PMID: 11409514.
Article16. Rordorf G, Bellon RJ, Budzik RE Jr, Farkas J, Reinking GF, Pergolizzi RS, et al. Silent thromboembolic events associated with the treatment of unruptured cerebral aneurysms by use of Guglielmi detachable coils: prospective study applying diffusion-weighted imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001; 22:5–10. PMID: 11158880.17. Sakai H, Sakai N, Nakahara I, Shimozuru T, Higashi T, Takahashi JC, et al. Embolic Complications of Endovascular Surgery for Cerebrovascular Diseases. Evaluation with Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging. Interv Neuroradiol. 2000; 6 Suppl 1:223–226. PMID: 20667253.
Article18. Soeda A, Sakai N, Sakai H, Iihara K, Yamada N, Imakita S, et al. Thromboembolic events associated with Guglielmi detachable coil embolization of asymptomatic cerebral aneurysms: evaluation of 66 consecutive cases with use of diffusion-weighted MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003; 24:127–132. PMID: 12533341.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Persistent Trigeminal Artery Aneurysm Treated with Guglielmi Detachable Coils
- Direct Electrothrombosis of a Pseudoaneurysm after Obliteration of a Carotid Cavernous Fistula:Treatment with Guglielmi Detachable Coils: Case Report
- In Vitro Observation of Air Bubbles during Delivery of Various Detachable Aneurysm Embolization Coils
- Transarterial Embolization of a Carotid Cavernous Fistula with Guglielmi Detachable Coils: A Case Report
- Endovascular Coil Trapping of a Ruptured Dissecting Aneurysm of the Vertebral Artery Using Detachable Coils and Micro-Tornado(R) Coils