J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2013 Jun;53(6):342-348. 10.3340/jkns.2013.53.6.342.
Reappraisal of Anatomic Outcome Scales of Coiled Intracranial Aneurysms in the Prediction of Recanalization
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Hallym University Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiology, Kwandong University Myongji Hospital, Kwandong University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea. bjkwon74@gmail.com
- 3Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2190821
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2013.53.6.342
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
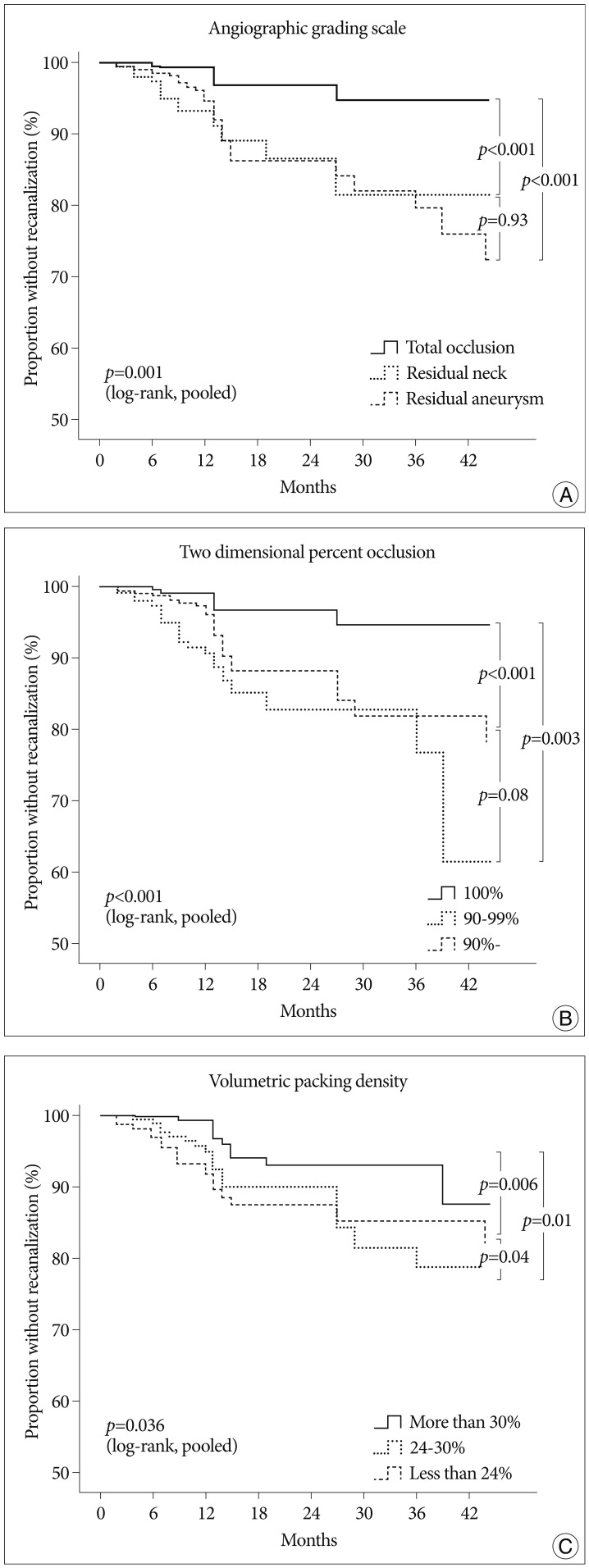
Several scales are currently used to assess occlusion rates of coiled cerebral aneurysms. This study compared these scales as predictors of recanalization.
METHODS
Clinical data of 827 patients harboring 901 aneurysms treated by coiling were retrospectively reviewed. Occlusion rates were assessed using angiographic grading scale (AGS), two-dimensional percent occlusion (2DPO), and volumetric packing density (vPD). Every scale had 3 categories. Followed patients were dichotomized into either presence or absence of recanalization. Kaplan-Meier analysis was conducted, and Cox proportional hazards analysis was performed to identify surviving probabilities of recanalization. Lastly, the predictive accuracies of three different scales were measured via Harrell's C index.
RESULTS
The cumulative risk of recanalization was 7% at 12-month, 10% at 24-month, and 13% at 36-month of postembolization, and significantly higher for the second and third categories of every scale (p<0.001). Multivariate-adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) of the second and third categories as compared with the first category of AGS (HR : 3.95 and 4.15, p=0.004 and 0.001) and 2DPO (HR : 4.87 and 3.12, p<0.001 and 0.01) were similar. For vPD, there was no association between occlusion rates and recanalization. The validated and optimism-adjusted C-indices were 0.50 [confidence (CI) : -1.09-2.09], 0.47 (CI : -1.10-2.09) and 0.44 (CI : -1.10-2.08) for AGS, 2DPO, and vPD, respectively.
CONCLUSION
Total occlusion should be reasonably tried in coiling to maximize the benefit of the treatment. AGS may be the best to predict recanalization, whereas vPD should not be used alone.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cognard C, Weill A, Castaings L, Rey A, Moret J. Intracranial berry aneurysms : angiographic and clinical results after endovascular treatment. Radiology. 1998; 206:499–510. PMID: 9457205.
Article2. Gallas S, Pasco A, Cottier JP, Gabrillargues J, Drouineau J, Cognard C, et al. A multicenter study of 705 ruptured intracranial aneurysms treated with Guglielmi detachable coils. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005; 26:1723–1731. PMID: 16091521.3. Harrell FE Jr, Lee KL, Mark DB. Multivariable prognostic models : issues in developing models, evaluating assumptions and adequacy, and measuring and reducing errors. Stat Med. 1996; 15:361–387. PMID: 8668867.
Article4. Hayakawa M, Murayama Y, Duckwiler GR, Gobin YP, Guglielmi G, Viñuela F. Natural history of the neck remnant of a cerebral aneurysm treated with the Guglielmi detachable coil system. J Neurosurg. 2000; 93:561–568. PMID: 11014533.
Article5. Johnston SC, Dowd CF, Higashida RT, Lawton MT, Duckwiler GR, Gress DR. CARAT Investigators. Predictors of rehemorrhage after treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysms : the Cerebral Aneurysm Rerupture After Treatment (CARAT) study. Stroke. 2008; 39:120–125. PMID: 18048860.
Article6. Kai Y, Hamada J, Morioka M, Yano S, Kuratsu J. Evaluation of the stability of small ruptured aneurysms with a small neck after embolization with Guglielmi detachable coils : correlation between coil packing ratio and coil compaction. Neurosurgery. 2005; 56:785–792. discussion 682-683. PMID: 15792517.
Article7. Kawanabe Y, Sadato A, Taki W, Hashimoto N. Endovascular occlusion of intracranial aneurysms with Guglielmi detachable coils : correlation between coil packing density and coil compaction. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2001; 143:451–455. PMID: 11482694.
Article8. Kwon BJ, Chang HW, Youn SW, Kim JE, Han MH. Intracranial aneurysm perforation during endosaccular coiling : impact on clinical outcome, initial occlusion, and recanalization rates. Neurosurgery. 2008; 63:676–682. discussion 682-683. PMID: 18981878.9. Mason AM, Cawley CM, Barrow DL. Surgical management of intracranial aneurysms in the endovascular era : review article. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2009; 45:133–142. PMID: 19352474.
Article10. Molyneux A, Kerr R, Stratton I, Sandercock P, Clarke M, Shrimpton J, et al. International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT) of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular coiling in 2143 patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms : a randomised trial. Lancet. 2002; 360:1267–1274. PMID: 12414200.
Article11. Molyneux AJ, Kerr RS, Birks J, Ramzi N, Yarnold J, Sneade M, et al. Risk of recurrent subarachnoid haemorrhage, death, or dependence and standardised mortality ratios after clipping or coiling of an intracranial aneurysm in the International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT) : long-term follow-up. Lancet Neurol. 2009; 8:427–433. PMID: 19329361.
Article12. Murayama Y, Nien YL, Duckwiler G, Gobin YP, Jahan R, Frazee J, et al. Guglielmi detachable coil embolization of cerebral aneurysms : 11 years' experience. J Neurosurg. 2003; 98:959–966. PMID: 12744354.
Article13. Niimi Y, Song J, Madrid M, Berenstein A. Endosaccular treatment of intracranial aneurysms using matrix coils : early experience and mid-term follow-up. Stroke. 2006; 37:1028–1032. PMID: 16514098.
Article14. Piotin M, Daghman B, Mounayer C, Spelle L, Moret J. Ellipsoid approximation versus 3D rotational angiography in the volumetric assessment of intracranial aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006; 27:839–842. PMID: 16611775.15. Piotin M, Spelle L, Mounayer C, Salles-Rezende MT, Giansante-Abud D, Vanzin-Santos R, et al. Intracranial aneurysms : treatment with bare platinum coils--aneurysm packing, complex coils, and angiographic recurrence. Radiology. 2007; 243:500–508. PMID: 17293572.
Article16. Raymond J, Guilbert F, Weill A, Georganos SA, Juravsky L, Lambert A, et al. Long-term angiographic recurrences after selective endovascular treatment of aneurysms with detachable coils. Stroke. 2003; 34:1398–1403. PMID: 12775880.
Article17. Roy D, Milot G, Raymond J. Endovascular treatment of unruptured aneurysms. Stroke. 2001; 32:1998–2004. PMID: 11546888.
Article18. Slob MJ, Sluzewski M, van Rooij WJ, Roks G, Rinkel GJ. Additional coiling of previously coiled cerebral aneurysms : clinical and angiographic results. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004; 25:1373–1376. PMID: 15466335.19. Sluzewski M, van Rooij WJ, Rinkel GJ, Wijnalda D. Endovascular treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysms with detachable coils : long-term clinical and serial angiographic results. Radiology. 2003; 227:720–724. PMID: 12773678.
Article20. Sluzewski M, van Rooij WJ, Beute GN, Nijssen PC. Late rebleeding of ruptured intracranial aneurysms treated with detachable coils. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005; 26:2542–2549. PMID: 16286399.21. Sluzewski M, van Rooij WJ, Slob MJ, Bescós JO, Slump CH, Wijnalda D. Relation between aneurysm volume, packing, and compaction in 145 cerebral aneurysms treated with coils. Radiology. 2004; 231:653–658. PMID: 15118115.
Article22. Tamatani S, Ito Y, Abe H, Koike T, Takeuchi S, Tanaka R. Evaluation of the stability of aneurysms after embolization using detachable coils : correlation between stability of aneurysms and embolized volume of aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002; 23:762–767. PMID: 12006273.23. Tateshima S, Murayama Y, Gobin YP, Duckwiler GR, Guglielmi G, Viñuela F. Endovascular treatment of basilar tip aneurysms using Guglielmi detachable coils : anatomic and clinical outcomes in 73 patients from a single institution. Neurosurgery. 2000; 47:1332–1339. discussion 1339-1342. PMID: 11126904.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hemodynamic Characteristics Regarding Recanalization of Completely Coiled Aneurysms: Computational Fluid Dynamic Analysis Using Virtual Models Comparison
- Endovascular Treatment of Intracranial Aneurysms Using Polymer Polyglycolic-Lactic Acid Coated Coils
- Time-of-Flight Magnetic Resonance Angiography for Follow-Up of Coil Embolization with Enterprise Stent for Intracranial Aneurysm: Usefulness of Source Images
- The Merits of Endovascular Coil Surgery for Patients with Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms
- Delayed Subarachnoid Hemorrhage from an Embolized Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysm with Minor Recanalization: A Case Report