J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2012 Oct;52(4):334-338. 10.3340/jkns.2012.52.4.334.
Multiple Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Multiple Metachronous Brain Metastases Associated with Lung Cancer : Survival Time
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Research Institute of Clinical Medicine, Chonbuk National University Hospital-Chonbuk National University School of Medicine, Jeonju, Korea. kohejns@jbnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2190649
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2012.52.4.334
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
We compared the survival time between patients with multiple gamma knife radiosurgery (GKRS) and patients with a single GKRS plus whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT), in patients with multiple metachronous brain metastases from lung cancer.
METHODS
From May 2006 to July 2010, we analyzed 31 patients out of 112 patients who showed multiple metachronous brain metastases. 20 out of 31 patients underwent multiple GKRS (group A) and 11 patients underwent a single GKRS plus WBRT (group B). We compared the survival time between group A and B. Kaplan-Meier method and Cox proportional hazards were used to analyze relationship between survival and 1) the number of lesions in each patient, 2) the average volume of lesions in each patient, 3) the number of repeated GKRS, and 4) the interval of development of new lesions, respectively.
RESULTS
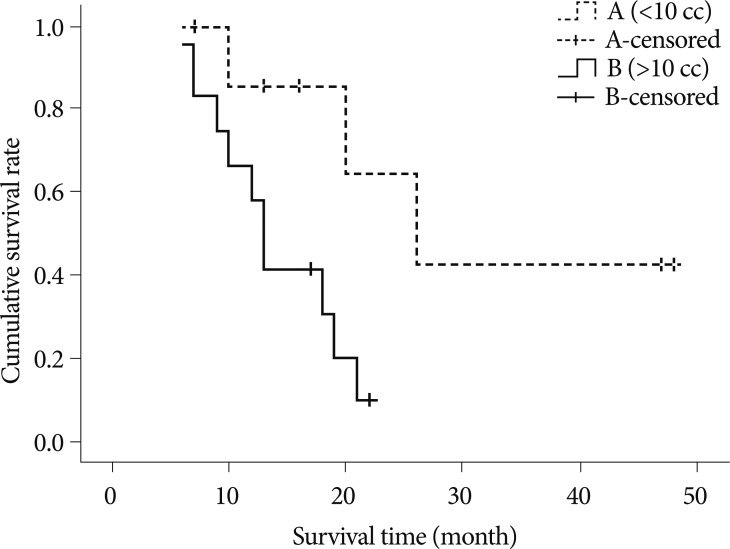
Median survival time was 18 months (range 6-50 months) in group A and 6 months (range 3-18 months) in group B. Only the average volume of individual lesion (over 10 cc) was negatively related with survival time according to Kaplan-Meier method. Cox-proportional hazard ratio of each variable was 1.1559 for the number of lesions, 1.0005 for the average volume of lesions, 0.0894 for the numbers of repeated GKRS, and 0.5970 for the interval of development of new lesions.
CONCLUSION
This study showed extended survival time in group A compared with group B. Our result supports that multiple GKRS is of value in extending the survival time in patients with multiple metachronous brain metastases, and that the number of the lesions and the frequency of development of new lesions are not an obstacle in treating patients with GKRS.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effects of an Epithelial Growth Factor Receptor-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Add-on in Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases Originating from Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Hyun Jung Kim, Woo Sung Kim, Do Hoon Kwon, Young Hyun Cho, Chang-Min Choi
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2015;58(3):205-210. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2015.58.3.205.
Reference
-
1. Aoyama H, Shirato H, Tago M, Nakagawa K, Toyoda T, Hatano K, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases : a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2006; 295:2483–2491. PMID: 16757720.
Article2. Aoyama H, Tago M, Kato N, Toyoda T, Kenjyo M, Hirota S, et al. Neurocognitive function of patients with brain metastasis who received either whole brain radiotherapy plus stereotactic radiosurgery or radiosurgery alone. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007; 68:1388–1395. PMID: 17674975.
Article3. Auchter RM, Lamond JP, Alexander E, Buatti JM, Chappell R, Friedman WA, et al. A multiinstitutional outcome and prognostic factor analysis of radiosurgery for resectable single brain metastasis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1996; 35:27–35. PMID: 8641923.
Article4. Bahl A, Kumar M, Sharma DN, Jothy Basu KS, Jaura MS, Rath GK, et al. Reirradiation for progressive brain metastases. J Cancer Res Ther. 2009; 5:161–164. PMID: 19841556.
Article5. Bhatnagar AK, Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD. Stereotactic radiosurgery for four or more intracranial metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006; 64:898–903. PMID: 16338097.
Article6. Chang WS, Kim HY, Chang JW, Park YG, Chang JH. Analysis of radiosurgical results in patients with brain metastases according to the number of brain lesions : is stereotactic radiosurgery effective for multiple brain metastases? J Neurosurg. 2010; 113:73–78. PMID: 21121789.
Article7. Combs SE, Schulz-Ertner D, Thilmann C, Edler L, Debus J. Treatment of cerebral metastases from breast cancer with stereotactic radiosurgery. Strahlenther Onkol. 2004; 180:590–596. PMID: 15378190.
Article8. Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD, Coffey RJ, Goodman ML, Shaw EG, et al. A multi-institutional experience with stereotactic radiosurgery for solitary brain metastasis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1994; 28:797–802. PMID: 8138431.
Article9. Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD, Somaza S, Kondziolka D. Radiosurgery : its role in brain metastasis management. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 1996; 7:497–504. PMID: 8823777.10. Hoffman R, Sneed PK, McDermott MW, Chang S, Lamborn KR, Park E, et al. Radiosurgery for brain metastases from primary lung carcinoma. Cancer J. 2001; 7:121–131. PMID: 11324765.11. Jawahar A, Willis BK, Smith DR, Ampil F, Datta R, Nanda A. Gamma knife radiosurgery for brain metastases : do patients benefit from adjuvant external-beam radiotherapy? An 18-month comparative analysis. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2002; 79:262–271. PMID: 12890985.
Article12. Joseph J, Adler JR, Cox RS, Hancock SL. Linear accelerator-based stereotaxic radiosurgery for brain metastases : the influence of number of lesions on survival. J Clin Oncol. 1996; 14:1085–1092. PMID: 8648361.
Article13. Karlsson B, Hanssens P, Wolff R, Söderman M, Lindquist C, Beute G. Thirty years’ experience with Gamma Knife surgery for metastases to the brain. J Neurosurg. 2009; 111:449–457. PMID: 19199505.
Article14. Muacevic A, Wowra B, Siefert A, Tonn JC, Steiger HJ, Kreth FW. Microsurgery plus whole brain irradiation versus Gamma Knife surgery alone for treatment of single metastases to the brain : a randomized controlled multicentre phase III trial. J Neurooncol. 2008; 87:299–307. PMID: 18157648.
Article15. Noël G, Proudhom MA, Valery CA, Cornu P, Boisserie G, Hasboun D, et al. Radiosurgery for re-irradiation of brain metastasis : results in 54 patients. Radiother Oncol. 2001; 60:61–67. PMID: 11410305.
Article16. Patchell RA, Tibbs PA, Regine WF, Dempsey RJ, Mohiuddin M, Kryscio RJ, et al. Postoperative radiotherapy in the treatment of single metastases to the brain : a randomized trial. JAMA. 1998; 280:1485–1489. PMID: 9809728.17. Sneed PK, Lamborn KR, Forstner JM, McDermott MW, Chang S, Park E, et al. Radiosurgery for brain metastases : is whole brain radiotherapy necessary? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999; 43:549–558. PMID: 10078636.
Article18. Sneed PK, Suh JH, Goetsch SJ, Sanghavi SN, Chappell R, Buatti JM, et al. A multi-institutional review of radiosurgery alone vs. radiosurgery with whole brain radiotherapy as the initial management of brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002; 53:519–526. PMID: 12062592.
Article19. Varlotto JM, Flickinger JC, Niranjan A, Bhatnagar A, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD. The impact of whole-brain radiation therapy on the long-term control and morbidity of patients surviving more than one year after gamma knife radiosurgery for brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005; 62:1125–1132. PMID: 15990018.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Analysis of Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases
- A Case of Brain Metastases from Advanced Ovarian Cancer
- Therapeutic Effect of Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Multiple Brain Metastases
- Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Single & Multiple brain Metastasis
- Clinical Application of 7.0 T Magnetic Resonance Images in Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for a Patient with Brain Metastases