Free Hand Pedicle Screw Placement in the Thoracic Spine without Any Radiographic Guidance : Technical Note, a Cadaveric Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Spine Center, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Wooridul Spine Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Neurosurgery, College of Medicine, Inha University, Incheon, Korea.
- 5Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Spine Service, Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons, New York, NY, USA. scrhim@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2190479
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2012.51.1.66
Abstract
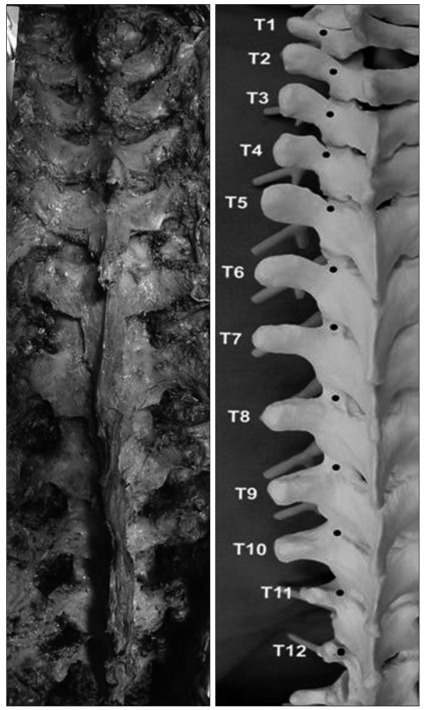
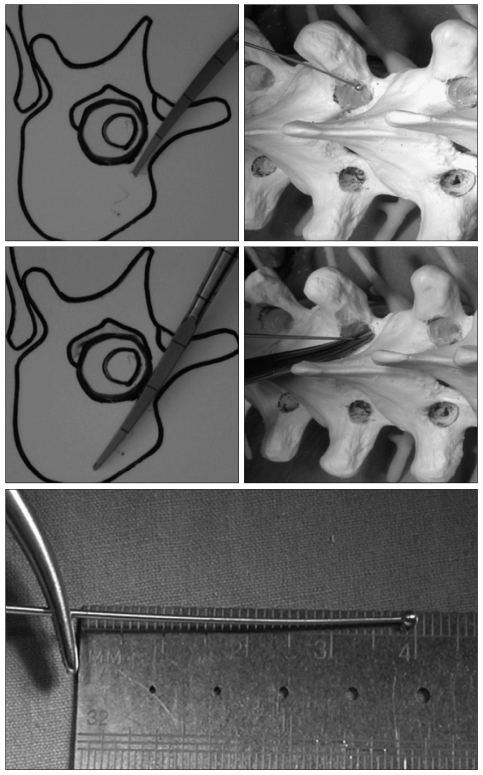
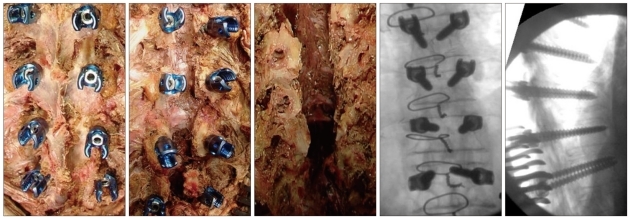
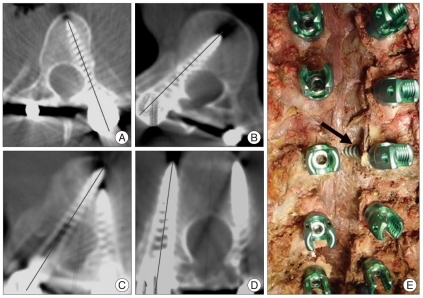
- Thoracic pedicle screw fixation techniques are still controversial for thoracic deformities because of possible complications including neurologic deficit. Methods to aid the surgeon in appropriate screw placement have included the use of intraoperative fluoroscopy and/or radiography as well as image-guided techniques. We describe our technique for free hand pedicle screw placement in the thoracic spine without any radiographic guidance and present the results of pedicle screw placement analyzed by computed tomographic scan in two human cadavers. This free hand technique of thoracic pedicle screw placement performed in a step-wise, consistent, and compulsive manner is an accurate, reliable, and safe method of insertion to treat a variety of spinal disorders, including spinal deformity.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Surgical Impacts of Metastatic Non-small Cell Lung Cancer to the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine
Jong-myung Jung, Seung-Jae Hyun, Ki-Jeong Kim
J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(7):e52. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e52.Surgical Outcomes According to Dekyphosis in Patients with Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament in the Thoracic Spine
Soo Yeon Kim, Seung-Jae Hyun, Ki-Jeong Kim, Tae-Ahn Jahng
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2020;63(1):89-98. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2018.0177.Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Treatment by a Korean Neurosurgeon: The Changing Role for Neurosurgeons
Seung-Jae Hyun, Woong-Beom Kim, Young-Seop Park, Ki-Jeong Kim, Tae-Ahn Jahng, Yongjung J. Kim
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2015;58(1):50-53. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2015.58.1.50.Pedicle Screw Placement in the Thoracolumbar Spine Using a Novel, Simple, Safe, and Effective Guide-Pin : A Computerized Tomography Analysis
Seung-Jae Hyun, Yongjung J. Kim, Seung-Chul Rhim, Gene Cheh, Samuel K. Cho
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2015;58(1):9-13. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2015.58.1.9.
Reference
-
1. Amiot LP, Lang K, Putzier M, Zippel H, Labelle H. Comparative results between conventional and computer-assisted pedicle screw installation in the thoracic, lumbar, and sacral spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000; 25:606–614. PMID: 10749638.
Article2. Brown CA, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Geideman WM, Hasan SA, Blanke K. Complications of pediatric thoracolumbar and lumbar pedicle screws. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998; 23:1566–1571. PMID: 9682313.
Article3. Cotrel Y, Dubousset J, Guillaumat M. New universal instrumentation in spinal surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988; 227:10–23. PMID: 3338200.
Article4. Esses SI, Sachs BL, Dreyzin V. Complications associated with the technique of pedicle screw fixation. A selected survey of ABS members. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993; 18:2231–2238. discussion 2238-2239. PMID: 8278838.
Article5. Kim KD, Johnson JP, Babbitz JD. Image-guided thoracic pedicle screw placement : a technical study in cadavers and preliminary clinical experience. Neurosurg Focus. 2001; 10:E2. PMID: 16749749.6. Kim YJ, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Cho YS, Riew KD. Free hand pedicle screw placement in the thoracic spine : is it safe? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004; 29:333–342. discussion 342. PMID: 14752359.7. Kim YJ, Lenke LG, Cheh G, Riew KD. Evaluation of pedicle screw placement in the deformed spine using intraoperative plain radiographs : a comparison with computerized tomography. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30:2084–2088. PMID: 16166900.
Article8. Kuntz C 4th, Maher PC, Levine NB, Kurokawa R. Prospective evaluation of thoracic pedicle screw placement using fluoroscopic imaging. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2004; 17:206–214. PMID: 15167336.
Article9. Li G, Lv G, Passias P, Kozanek M, Metkar US, Liu Z, et al. Complications associated with thoracic pedicle screws in spinal deformity. Eur Spine J. 2010; 19:1576–1584. PMID: 20237943.
Article10. Liljenqvist UR, Halm HF, Link TM. Pedicle screw instrumentation of the thoracic spine in idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997; 22:2239–2245. PMID: 9346144.
Article11. Liljenqvist UR, Link TM, Halm HF. Morphometric analysis of thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000; 25:1247–1253. PMID: 10806501.
Article12. Lonstein JE, Denis F, Perra JH, Pinto MR, Smith MD, Winter RB. Complications associated with pedicle screws. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999; 81:1519–1528. PMID: 10565643.
Article13. Rajasekaran S, Vidyadhara S, Ramesh P, Shetty AP. Randomized clinical study to compare the accuracy of navigated and non-navigated thoracic pedicle screws in deformity correction surgeries. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007; 32:E56–E64. PMID: 17224800.
Article14. Sarlak AY, Tosun B, Atmaca H, Sarisoy HT, Buluç L. Evaluation of thoracic pedicle screw placement in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 2009; 18:1892–1897. PMID: 19526376.
Article15. Suk SI, Kim WJ, Lee SM, Kim JH, Chung ER. Thoracic pedicle screw fixation in spinal deformities : are they really safe? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001; 26:2049–2057. PMID: 11547207.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Technical Report of Free Hand Pedicle Screw Placement using the Entry Points with Junction of Proximal Edge of Transverse Process and Lamina in Lumbar Spine: Analysis of 2601 Consecutive Screws
- Thoracic Extrapedicular (Transverse Process) Screws Fixation : Technical Note
- Accuracy of Free Hand Pedicle Screw Installation in the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine by a Young Surgeon: An Analysis of the First Consecutive 306 Screws Using Computed Tomography
- A Study on Accuracy and Safety of Thoracic Pedicle Screw Fixation
- Freehand S2 Alar-Iliac Screw Placement Using K-Wire and Cannulated Screw: Technical Case Series