J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2012 Jan;51(1):51-53. 10.3340/jkns.2012.51.1.51.
Femoral Neuropathy due to Iliacus Muscle Hematoma in a Patient on Warfarin Therapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea. ktcho21@naver.com
- 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- 3Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Seoul National University Boramae Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2190473
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2012.51.1.51
Abstract
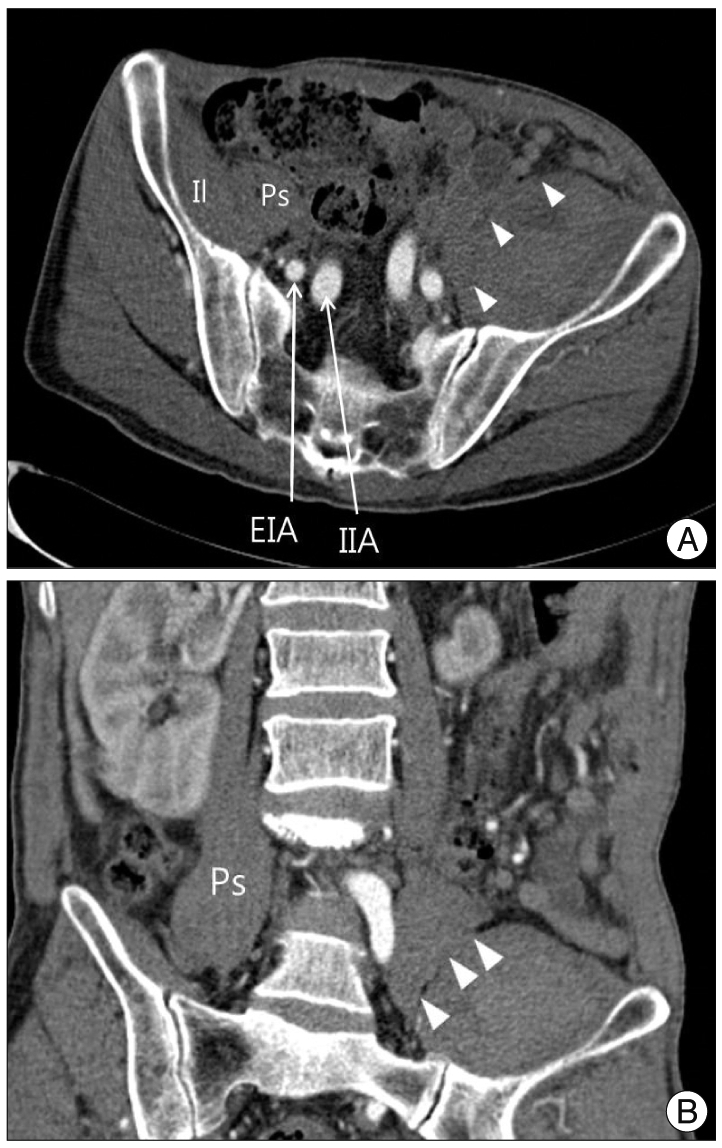
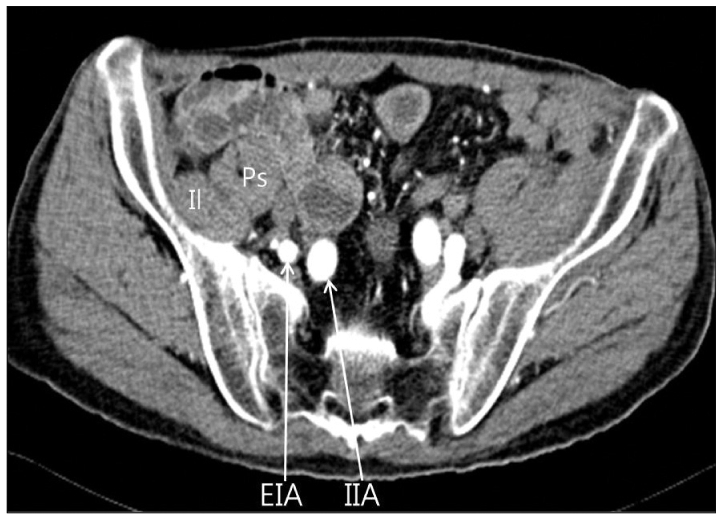
- Spontaneous hematomas of the iliacus muscle are rare lesions and these are seen in individuals receiving anticoagulation therapy or patients with blood dyscrasias such as hemophilia. It can cause femoral neuropathy and resultant pain and paralysis. Although there is no clear consensus for the treatment of femoral neuropathy from iliacus muscle hematomas, delays in the surgical evacuation of hematoma for decompression of the femoral nerve can lead to a prolonged or permanent disability. We report here on a rare case of a spontaneous iliacus muscle hematoma that caused femoral neuropathy in a patient who was taking warfarin for occlusive vascular disease and we discuss the treatment.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Non-operative Treatment of Femoral Neuropathy Caused by Iliacus Hematoma: A Case Report
Jong-Mun Jin, Soon Yong Kwon, Hyun-Jin Lee, Ju Yeob Lee
Hip Pelvis. 2014;26(1):50-54. doi: 10.5371/hp.2014.26.1.50.
Reference
-
1. Ashrani AA, Osip J, Christie B, Key NS. Iliopsoas haemorrhage in patients with bleeding disorders--experience from one centre. Haemophilia. 2003; 9:721–726. PMID: 14750939.
Article2. Balkan C, Kavakli K, Karapinar D. Iliopsoas haemorrhage in patients with haemophilia : results from one centre. Haemophilia. 2005; 11:463–467. PMID: 16128889.
Article3. Goodfellow J, Fearn CB, Matthews JM. Iliacus haematoma. A common complication of haemophilia. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1967; 49:748–756. PMID: 6073189.4. Guha SC, Poole MD. Stress fracture of the iliac bone with subfascial femoral neuropathy : unusual complications at a bone graft donor site : case report. Br J Plast Surg. 1983; 36:305–306. PMID: 6860856.
Article5. Guivarc'h M. [Hematoma of the iliac psoas muscle. 29 cases]. J Chir (Paris). 1997; 134:382–389. PMID: 9682753.6. Marquardt G, Barduzal Angles S, Leheta F, Seifert V. Spontaneous haematoma of the iliac psoas muscle : a case report and review of the literature. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2002; 122:109–111. PMID: 11880914.7. Merrick HW, Zeiss J, Woldenberg LS. Percutaneous decompression for femoral neuropathy secondary to heparin-induced retroperitoneal hematoma : case report and review of the literature. Am Surg. 1991; 57:706–711. PMID: 1660685.8. Nakamura Y, Mitsui H, Toh S, Hayashi Y. Femoral nerve palsy associated with iliacus hematoma following pseudoaneurysm after revision hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2008; 23:1240e1–e4. PMID: 18534465.
Article9. Nakao A, Sakagami K, Mitsuoka S, Uda M, Tanaka N. Retroperitoneal hematoma associated with femoral neuropathy : a complication under antiplatelets therapy. Acta Med Okayama. 2001; 55:363–366. PMID: 11779099.10. Nobel W, Marks SC Jr, Kubik S. The anatomical basis for femoral nerve palsy following iliacus hematoma. J Neurosurg. 1980; 52:533–540. PMID: 6445414.
Article11. Parmer SS, Carpenter JP, Fairman RM, Velazquez OC, Mitchell ME. Femoral neuropathy following retroperitoneal hemorrhage : case series and review of the literature. Ann Vasc Surg. 2006; 20:536–540. PMID: 16741653.
Article12. Pirouzmand F, Midha R. Subacute femoral compressive neuropathy from iliacus compartment hematoma. Can J Neurol Sci. 2001; 28:155–158. PMID: 11383942.
Article13. Qanadli SD, El Hajjam M, Mignon F, Bruckert F, Chagnon S, Lacombe P. Life-threatening spontaneous psoas haematoma treated by transcatheter arterial embolization. Eur Radiol. 1999; 9:1231–1234. PMID: 10415268.
Article14. Rochman AS, Vitarbo E, Levi AD. Femoral nerve palsy secondary to traumatic pseudoaneurysm and iliacus hematoma. J Neurosurg. 2005; 102:382–385. PMID: 15739570.
Article15. Wada Y, Yanagihara C, Nishimura Y. Bilateral iliopsoas hematomas complicating anticoagulant therapy. Intern Med. 2005; 44:641–643. PMID: 16020897.
Article16. Wicky S, Mayor B, Schnyder P. Clinical impact of imaging iliopsoas hematomas during anticoagulation. Emerg Radiol. 1995; 2:2–6.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Non-operative Treatment of Femoral Neuropathy Caused by Iliacus Hematoma: A Case Report
- Iliacus Hematoma with Femoral Neuropathy in Hemophilia: A Case report
- Femoral Neuropathy and Meralgia Paresthetica Secondary to an Iliacus Hematoma
- Femoral Neuropathy Secondary to Iliacus Hematoma: A Case Report
- Bilateral Femoral Neuropathy Secondary to Unilateral Retroperitoneal Hematoma