J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2013 Feb;39(1):27-30. 10.5125/jkaoms.2013.39.1.27.
Angiographic embolization for hemorrhage control after dental implantation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School of Dentistry, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea. kwondk@knu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Diagnostic Radiology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2189559
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2013.39.1.27
Abstract
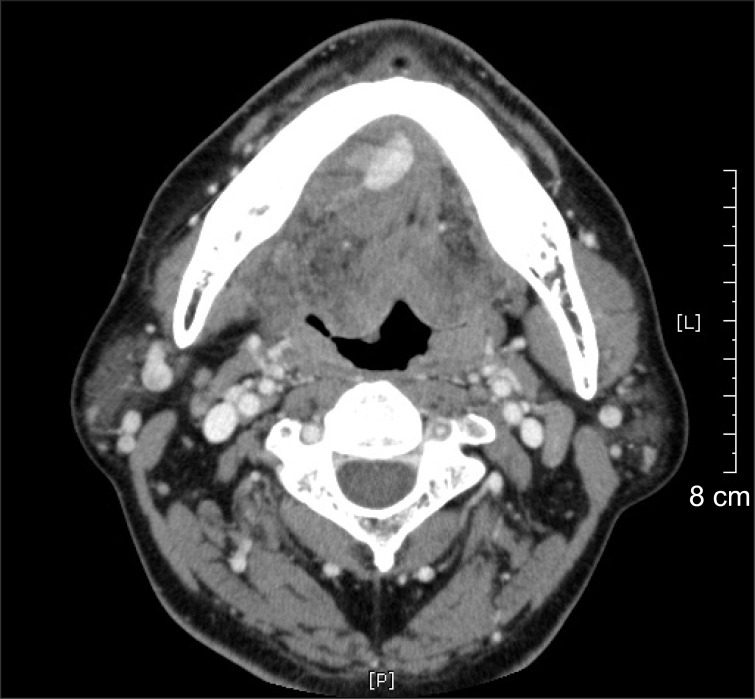
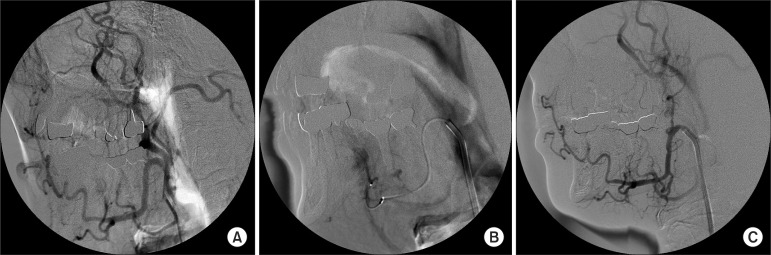
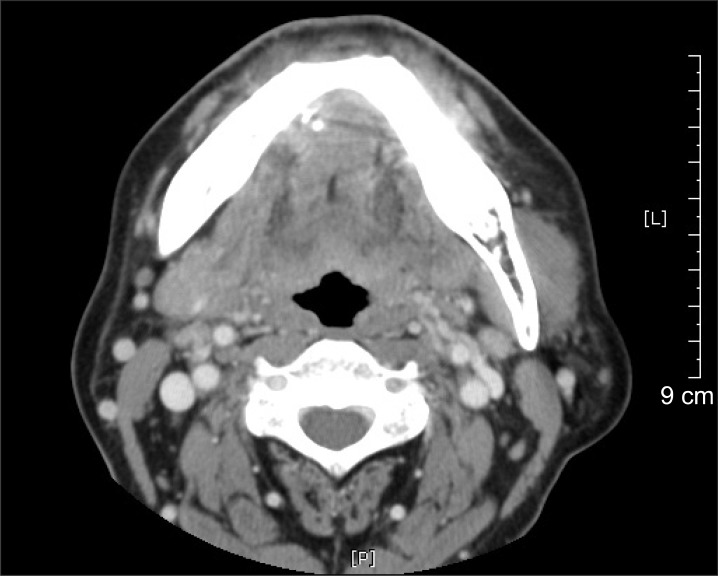
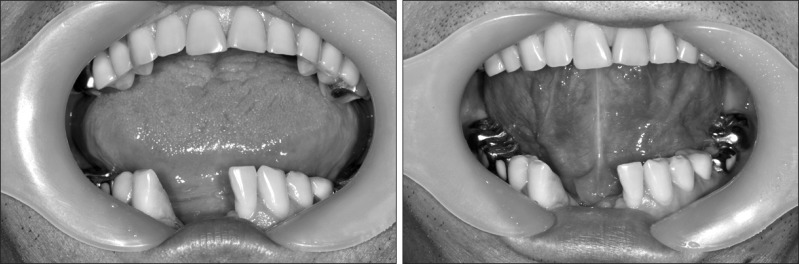
- Dental implantation in the mandibular anterior region is considered a safe and reliable surgical procedure. On the other hand, several articles have reported that inadvertent hemorrhage of the sublingual artery can result in life-threatening airway obstruction. Surgical ligation under intubation or tracheostomy is the most widely used approach for controlling mouth floor bleeding in this highly vascular region. Nonetheless, surgically exploring the bleeding focus is difficult because of anatomical distortion followed by widespread edema and swelling. Since swelling of the mouth floor advances quickly, timely management is essential for favorable postoperative outcome. This paper reports a case of immediate hemorrhage control with angiographic embolization to perform rapid hemostasis before the ongoing swelling causes airway obstruction. Less invasive, angiographic embolization can prevent neurovascular damage during a surgical exploration of injured vascular structures on the mouth floor.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Darriba MA, Mendonça-Caridad JJ. Profuse bleeding and life-threatening airway obstruction after placement of mandibular dental implants. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1997; 55:1328–1330. PMID: 9371130.
Article2. Kalpidis CD, Konstantinidis AB. Critical hemorrhage in the floor of the mouth during implant placement in the first mandibular premolar position: a case report. Implant Dent. 2005; 14:117–124. PMID: 15968182.
Article3. Dubois L, de Lange J, Baas E, Van Ingen J. Excessive bleeding in the floor of the mouth after endosseus implant placement: a report of two cases. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010; 39:412–415. PMID: 20079609.
Article4. Loukas M, Kinsella CR Jr, Kapos T, Tubbs RS, Ramachandra S. Anatomical variation in arterial supply of the mandible with special regard to implant placement. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008; 37:367–371. PMID: 18262766.
Article5. Bavitz JB, Harn SD, Homze EJ. Arterial supply to the floor of the mouth and lingual gingiva. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1994; 77:232–235. PMID: 8170652.
Article6. Goldstein BH. Acute dissecting hematoma: a complication of oral and maxillofacial surgery. J Oral Surg. 1981; 39:40–43. PMID: 6969794.7. Woo BM, Al-Bustani S, Ueeck BA. Floor of mouth haemorrhage and life-threatening airway obstruction during immediate implant placement in the anterior mandible. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006; 35:961–964. PMID: 16829038.
Article8. Niamtu J 3rd. Near-fatal airway obstruction after routine implant placement. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2001; 92:597–600. PMID: 11740473.
Article9. Bynoe RP, Kerwin AJ, Parker HH 3rd, Nottingham JM, Bell RM, Yost MJ, et al. Maxillofacial injuries and life-threatening hemorrhage: treatment with transcatheter arterial embolization. J Trauma. 2003; 55:74–79. PMID: 12855884.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Angiographic Embokization in the Control of Bleeding Related to Gynecologic Malignancy
- Analysis of failed arterial embolization for postpartum hemorrhage
- Angiographic embolization in the management of obstetrical hemorrhage
- Angiographic Embolization as a Treatment of Postoperative Bleeding
- A case of preoperative angiographic uterine artery embolization for the conservative treatment of cervical pregnancy