J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2016 Feb;42(1):55-59. 10.5125/jkaoms.2016.42.1.55.
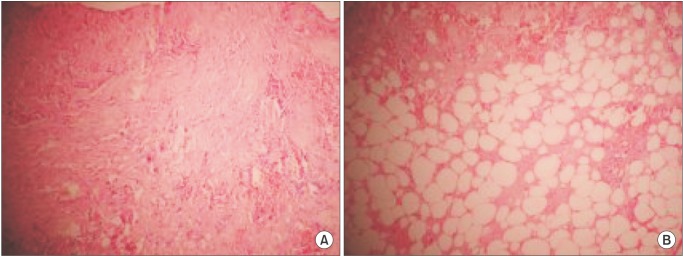
Myositis ossificans of the platysma mimicking a malignancy: a case report with review of the literature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Army Dental Centre, Military Hospital, Lagos, Nigeria. taiwo_adebayo@yahoo.com
- 2Department of Pathology, 44 Nigeria Army Reference Hospital, Kaduna, Nigeria.
- 3Department of Dental Surgery, Ahmadu Bello University, Shika-Zaria, Nigeria.
- KMID: 2189418
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2016.42.1.55
Abstract
- The two main forms of myositis ossificans are congenital and acquired. Either form is rare in the head and neck region. The acquired form is often due to trauma, with bullying as a fairly common cause. This report of myositis ossificans of the platysma in an 11-year-old female patient emphasizes the need for a high index of suspicion in unexplainable facial swellings in children and the benefit of modern investigative modalities in their management.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fletcher E, Moss MS. Myositis ossificans progressiva. Ann Rheum Dis. 1965; 24:267–272. PMID: 14297341.
Article2. Bar Oz B, Boneh A. Myositis ossificans progressiva: a 10-year follow-up on a patient treated with etidronate disodium. Acta Paediatr. 1994; 83:1332–1334. PMID: 7734885.
Article3. Lungu SG. Myositis ossificans: two case presentations. Med J Zambia. 2011; 38:25–31.4. Kruse AL, Dannemann C, Grätz KW. Bilateral myositis ossificans of the masseter muscle after chemoradiotherapy and critical illness neuropathy: report of a rare entity and review of literature. Head Neck Oncol. 2009; 1:30. PMID: 19674466.
Article5. Man SC, Schnell CN, Fufezan O, Mihut G. Myositis ossificans traumatica of the neck: a pediatric case. Maedica (Buchar). 2011; 6:128–131. PMID: 22205895.6. Bridges AJ, Hsu KC, Singh A, Churchill R, Miles J. Fibrodysplasia (myositis) ossificans progressiva. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1994; 24:155–164. PMID: 7899873.
Article7. Micheli A, Trapani S, Brizzi I, Campanacci D, Resti M, de Martino M. Myositis ossificans circumscripta: a paediatric case and review of the literature. Eur J Pediatr. 2009; 168:523–529. PMID: 19130083.
Article8. Shugar MA, Weber AL, Mulvaney TJ. Myositis ossificans following radical neck dissection. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1981; 90:169–171. PMID: 7224517.
Article9. Patel S, Richards A, Trehan R, Railton GT. Post-traumatic myositis ossificans of the sternocleidomastoid following fracture of the clavicle: a case report. Cases J. 2008; 1:413. PMID: 19102776.
Article10. Schajowicz F. Tumours and tumour-like lesions of bone. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer;1994.11. Nuovo MA, Norman A, Chumas J, Ackerman LV. Myositis ossificans with atypical clinical, radiographic, or pathologic findings: a review of 23 cases. Skeletal Radiol. 1992; 21:87–101. PMID: 1566115.
Article12. Booth DW, Westers BM. The management of athletes with myositis ossificans traumatica. Can J Sport Sci. 1989; 14:10–16. PMID: 2647253.13. Kransdorf MJ, Meis JM, Jelinek JS. Myositis ossificans: MR appearance with radiologic-pathologic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1991; 157:1243–1248. PMID: 1950874.
Article14. Sodl JF, Bassora R, Huffman GR, Keenan MA. Traumatic myositis ossificans as a result of college fraternity hazing. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008; 466:225–230. PMID: 18196398.
Article15. Hanna SL, Magill HL, Brooks MT, Burton EM, Boulden TF, Seidel FG. Cases of the day. Pediatric. Myositis ossificans circumscripta. Radiographics. 1990; 10:945–949. PMID: 2217980.
Article16. Wang XL, Malghem J, Parizel PM, Gielen JL, Vanhoenacker F, De Schepper AM. Pictorial essay. Myositis ossificans circumscripta. JBR-BTR. 2003; 86:278–285. PMID: 14651084.17. Resnick D, Niwayama G. Soft tissues. In : Resnick D, editor. Diagnosis of bone and joint disorders. Philadelphia, PA: WB Saunders;1995. p. 4491–4622.18. Tyler P, Saifuddin A. The imaging of myositis ossificans. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2010; 14:201–216. PMID: 20486028.
Article19. Yu Chuah T, Loh TP, Loi HY, Lee KH. Myositis ossificans. West J Emerg Med. 2011; 12:371. PMID: 22224121.20. Turan S, Topcu B, Gökçe İ, Güran T, Atay Z, Omar A, et al. Serum alkaline phosphatase levels in healthy children and evaluation of alkaline phosphatase z-scores in different types of rickets. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2011; 3:7–11. PMID: 21448327.
Article21. Hanquinet S, Ngo L, Anooshiravani M, Garcia J, Bugmann P. Magnetic resonance imaging helps in the early diagnosis of myositis ossificans in children. Pediatr Surg Int. 1999; 15:287–289. PMID: 10370048.
Article22. Russo R, Hughes M, Manolios N. Biopsy diagnosis of early myositis ossificans without radiologic evidence of calcification: success of early surgical resection. J Clin Rheumatol. 2010; 16:385–387. PMID: 21085015.23. Torrance DA, Degraauw C. Treatment of post-traumatic myositis ossificans of the anterior thigh with extracorporeal shock wave therapy. J Can Chiropr Assoc. 2011; 55:240–246. PMID: 22131560.