J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2007 Oct;42(5):659-664. 10.4055/jkoa.2007.42.5.659.
Arthroscopic Internal Fixation of Displaced Tibial EminenceFracture Using Cannulated Screw
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea. ktkim@dau.ac.kr
- KMID: 2186474
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2007.42.5.659
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: This study examined the outcome of arthroscopic internal fixation for types II and III tibial eminence fractures in children using a cannulated screw.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
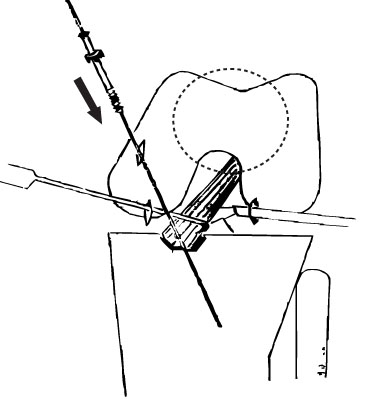
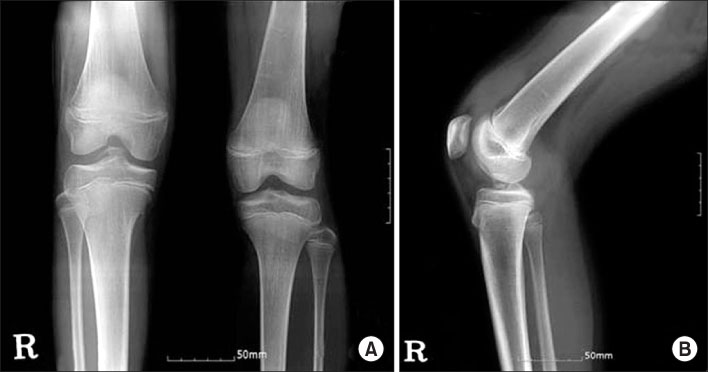
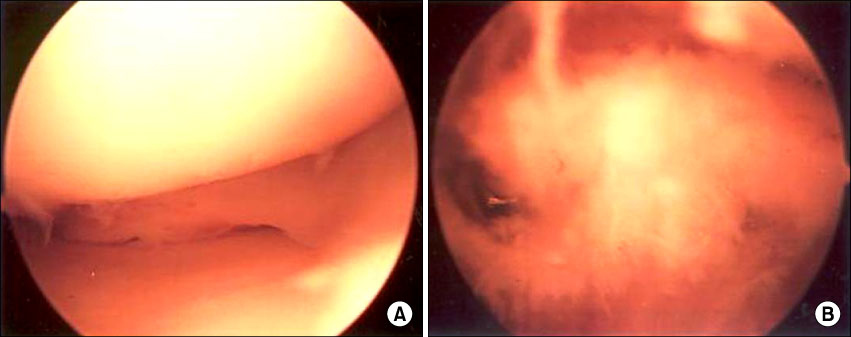
A series of 10 cases of displaced fractures of tibial eminence of the tibia that were treated with an arthroscopic cannulated screw fixation from February, 1997 to October, 2005 were examined. Four patients had a type II and six patients had a type III tibial eminence fracture according to the Meyer and McKeever's classification. All the patients were reviewed radiographically and clinically for bone union, instability and the range of motion after an average follow-up of 22.4 months (range, 12 to 81 months).
RESULTS
There were no cases of nonunion. The clinical examination showed that, all the patients with types II and III lesions had a negative Lachman test, and a full range of motion with the exception of one patient with a type III fracture. The average Lysholm functional score was 96.3 (mim 92.6-max 99.0) for all types II and III lesions.
CONCLUSION
Arthroscopic internal fixation with a cannulated screw for types II and III avulsion fractures of the tibial eminence in children can provide a satisfactory outcome through firm fixation of the fragment and an early start of the range of motion.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ahn JH, Cho JH. Arthroscopic reduction and pull-out suture for the tibial eminence of the tibia. J Korean Arthroscopy. 1994. 6:184–189.2. Andersen JW, Mejdahl S. Bilateral fracture of the tibial spine. Acta Orthop Belg. 1993. 59:394–397.3. Ando T, Nishihara K. Arthroscopic internal fixation of fractures of the intercondylar eminence of the tibia. Arthroscopy. 1996. 12:616–622.
Article4. Bakalim G, Wilppula E. Closed treatment of fracture of the tibial spines. Injury. 1974. 5:210–212.
Article5. Baxter MP, Wiley JJ. Fractures of the tibial spine in children. An evaluation of knee stability. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1988. 70:228–230.
Article6. Berg EE. Comminuted tibial eminence anterior cruciate ligament avulsion fractures: failure of arthroscopic treatment. Arthroscopy. 1993. 9:446–450.
Article7. Canale ST. Fractures and dislocations in children. Campbell's operative orthopaedics. 1998. 9th ed. Missouri: Mosby;407–2421.8. Clanton TO, DeLee JC, Sanders B, Neidre A. Knee ligament injuries in children. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979. 61:1195–1201.
Article9. van Loon T, Marti RK. A fracture of the intercondylar eminence of the tibia treated by arthroscopic fixation. Arthroscopy. 1991. 7:385–388.
Article10. McLennan JG. The role of arthroscopic surgery in the treatment of fractures of the intercondylar eminence of the tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1982. 64:477–480.
Article11. Meyers MH, McKeever FM. Fracture of the intercondylar eminence of the tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1959. 41:209–220.
Article12. Meyers MH, McKeever FM. Fracture of the intercondylar eminence of the tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1970. 52:1677–1684.
Article13. Molander ML, Wallin G, Wikstad I. Fracture of the intercondylar eminence of the tibia: a review of 35 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1981. 63:89–91.
Article14. Ohkoshi Y, Yasuda K, Ohno K. Arthroscopic surgery of the tibial eminence fracture. Arthroscopy. 1990. 9:131–137.15. Rockwood CA Jr, Wilkins KE, Beaty JH. Fractures in children. 1996. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven;1290–1300.16. Zaricznyj B. Avulsion fracture of the tibial eminence: treatment by open reduction and pinning. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977. 59:1111–1114.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Arthroscopy Assisted Percutaneous Reduction and Screw Fixation of a Displaced Intra-articular Glenoid Fracture: A Case Report
- Arthroscopy Assisted 2 Cannulated Screw Fixation for Transverse Glenoid Fracture: A Case Report
- Treatment of Tibial Plateau Fractures by Cannulated screw Fixation
- Arthroscopic Internal Fixation of Displaced Intercondylar Eminence Frecture Using Cannulated Screw - Three Cases Report -
- Arthroscopic Treatment of Displaced tibial Intercondylar Eminence Fractures: A Comparison of K-wires vs. Screw Fixation