J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2010 Dec;45(6):419-425. 10.4055/jkoa.2010.45.6.419.
Recent Trend in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Hanyang University Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases, Seoul, Korea. dhyoo@hanyang.ac.kr
- KMID: 2185488
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2010.45.6.419
Abstract
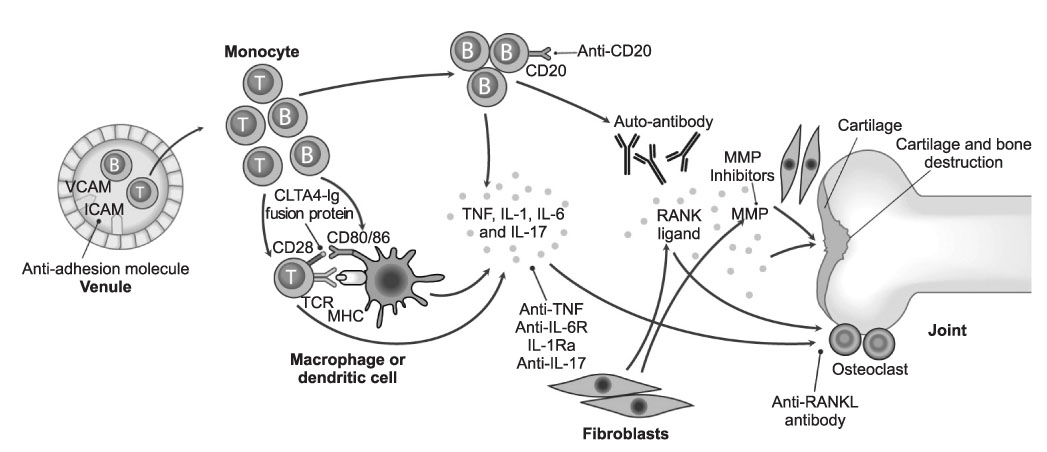
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic and destructive inflammatory disease resulting in disability. During the past 10 years, developments in medical science have improved RA treatment significantly, but have not proven curative. The most important developments over the past 10 years are the followings: 1) an emergence of new therapeutic agent against a specific single molecule or target, including biologic and chemical agents, 2) development and clinical usage of various outcome measures to detect disease activity more accurately and 3) introduction of new strategies in the treatment such as early and aggressive combination trials, depending on the disease activity. Over the course of these activities, we have been able to control clinical symptoms and signs more effectively, and slow the destruction of the joint, and finally improve the quality of life in RA patients. Here, we discuss the recent development of RA treatment and a perspective on future development.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. O'Dell JR. Therapeutic strategies for rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2004. 350:2591–2602.2. Plenge RM. Recent progress in rheumatoid arthritis genetics: one step towards improved patient care. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2009. 21:262–271.
Article3. Senolt L, Vencovský J, Pavelka K, Ospelt C, Gay S. Prospective new biological therapies for rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun Rev. 2009. 9:102–107.4. Donahue KE, Gartlehner G, Jonas DE, et al. Systematic review: comparative effectiveness and harms of disease-modifying medications for rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Intern Med. 2008. 148:124–134.
Article5. American College of Rheumatology Subcommittee on Rheumatoid Arthritis Guidelines. Guidelines for the management of rheumatoid arthritis: 2002 Update. Arthritis Rheum. 2002. 46:328–346.6. Aletaha D, Landewe R, Karonitsch T, et al. Reporting disease activity in clinical trials of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: EULAR/ACR collaborative recommendations. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008. 67:1360–1364.
Article7. Sharp JT, Strand V, Leung H, Hurley F, Loew-Friedrich I. Leflunomide Rheumatoid Arthritis Investigators Group. Treatment with leflunomide slows radiographic progression of rheumatoid arthritis: results from three randomized controlled trials of leflunomide in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000. 43:495–505.
Article8. Saag KG, Teng GG, Patkar NM, et al. American College of Rheumatology. American College of Rheumatology 2008 recommendations for the use of nonbiologic and biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. 59:762–784.9. Emery P, Keystone E, Tony HP, et al. IL-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab improves treatment outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-tumour necrosis factor biologicals: results from a 24-week multicentre randomised placebo-controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008. 67:1516–1523.
Article10. Emery P, Breedveld FC, Hall S, et al. Comparison of methotrexate monotherapy with a combination of methotrexate and etanercept in active, early, moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis (COMET): a randomised, double-blind, parallel treatment trial. Lancet. 2008. 372:375–382.
Article11. Kremer JM, Bloom BJ, Breedveld FC, et al. The safety and efficacy of a JAK inhibitor in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: Results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled phase IIa trial of three dosage levels of CP-690,550 versus placebo. Arthritis Rheum. 2009. 60:1895–1905.
Article12. Cohen S, Fleischmann R. Kinase inhibitors: a new approach to rheumatoid arthritis treatment. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2010. 22:330–335.
Article13. Ritchie DM, Boyle JA, McInnes JM, et al. Clinical studies with an articular index for the assessment of joint tenderness in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Q J Med. 1968. 37:393–406.14. Pincus T, Segurado OG. Most visits of most patients with rheumatoid arthritis to most rheumatologists do not include a formal quantitative joint count. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006. 65:820–822.
Article15. Felson DT, Anderson JJ, Boers M, et al. American college of rheumatology. Preliminary definition of improvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995. 38:727–735.
Article16. Fransen J, van Riel PL. The disease activity score and the EULAR response criteria. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2009. 35:745–757.
Article17. Aletaha D, Smolen JS. The simplified disease activity index and clinical disease activity index to monitor patients in standard clinical care. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2009. 35:759–772.
Article18. Yazici Y, Sokka T, Pincus T. Radiographic measures to assess patients with rheumatoid arthritis: advantages and limitations. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2009. 35:723–729.
Article19. Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Bijlsma JW, et al. T2T Expert Committee. Treating rheumatoid arthritis to target: recommendations of an international task force. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010. 69:631–637.20. Fransen J, Moens HB, Speyer I, van Riel PL. Effectiveness of systematic monitoring of rheumatoid arthritis disease activity in daily practice: a multicentre, cluster randomised controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005. 64:1294–1298.
Article21. Lard LR, Visser H, Speyer I, et al. Early versus delayed treatment in patients with recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis: comparison of two cohorts who received different treatment strategies. Am J Med. 2001. 111:446–451.
Article22. van Tuyl LH, Lems WF, Voskuyl AE, et al. Tight control and intensified COBRA combination treatment in early rheumatoid arthritis: 90% remission in a pilot trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008. 67:1574–1577.
Article23. Grigor C, Capell H, Stirling A, et al. Effect of a treatment strategy of tight control for rheumatoid arthritis (the TICORA study): a single-blind randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2004. 364:263–269.
Article24. Goekoop-Ruiterman YP, de Vries-Bouwstra JK, Allaart CF, et al. Comparison of treatment strategies in early rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2007. 146:406–415.25. Nell VP, Machold KP, Eberl G, Stamm TA, Uffmann M, Smolen JS. Benefit of very early referral and very early therapy with disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2004. 43:906–914.
Article26. Mierau M, Schoels M, Gonda G, Fuchs J, Aletaha D, Smolen JS. Assessing remission in clinical practice. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007. 46:975–979.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Medical Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis
- Clinical significance of rheumatoid factor in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
- Surgical Treatment for Hand and Wrist Problems in Rheumatoid Arthritis
- New Diagnostic and Classification Criteria of Chronic Pain Diseases: Rheumatoid Arthritis, Fibromyalgia and Spondylarthritis