J Korean Fract Soc.
2011 Apr;24(2):191-194. 10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.2.191.
Flexor Pollicis Longus Tendon Rupture as a Complication of a Closed Distal Radius Fracture: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Institure for Skeletal Aging & Orthopedic Surgery, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea. seoem@hallym.or.kr
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kangwon National University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2183864
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.2.191
Abstract
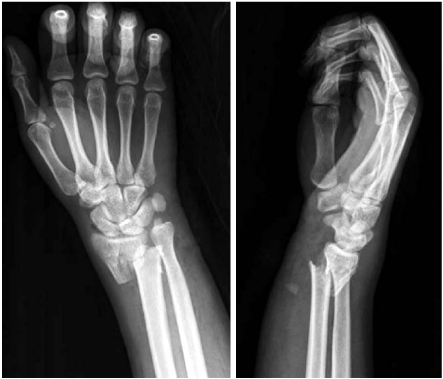
- There are few reported cases of flexor pollicis longus tendon (FPL) rupture complicating a closed distal radius fracture. We report a case of FPL tendon rupture complicating a closed distal radius fracture. A 24-year-old male presented with a severe right wrist pain. He had a closed distal radius fracture that was treated by closed manual reduction. Three days later, he complained forearm pain and limitation of thumb motion. The physical examination revealed loss of active interphalangeal joint flexion of thumb. He was taken to the operating room. Intraoperatively, the FPL was found to be discontinuous at the level of the radius fracture site. The FPL was repaired by a modified Kessler technique, and the fracture was repaired with a volar plate. Clinicians must be cautious in possibility of tendon injury complicating a closed distal radius fracture and assessing patients with distal radius fracture following closed reduction.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Choi JY, Jung HJ, Kim HK, Lee JK, Chang IS. T-Plate fixation for fractures of distal radius. J Korean Fract Soc. 2004. 17:350–358.
Article2. DiMatteo L, Wolf JM. Flexor carpi radialis tendon rupture as a complication of a closed distal radius fracture: a case report. J Hand Surg Am. 2007. 32:818–820.
Article3. Hallett JP, Motta GR. Tendon ruptures in the hand with particular reference to attrition ruptures in the carpal tunnel. Hand. 1982. 14:283–290.
Article4. Kato N, Nemoto K, Arino H, Ichikawa T, Fujikawa K. Ruptures of flexor tendons at the wrist as a complication of fracture of the distal radius. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg. 2002. 36:245–248.
Article5. McMaster PE. Late ruptures of extensor and flexor pollicis longus tendons following Colles' fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1932. 14:93–101.6. McMaster PE. Tendon and muscle ruptures Clinical and experimental studies in the causes and location of subcutaneous ruptures. J Bone Joint Surg. 1933. 15:705–722.7. Roberts JO, Regan PJ, Roberts AH. Rupture of flexor pollicis longus as a complication of Colles' fracture: a case report. J Hand Surg Br. 1990. 15:370–372.
Article8. Suppaphol S, Woratanarat P, Channoom T. Flexor tendon rupture after distal radius fracture Report of 2 cases. J Med Assoc Thai. 2007. 90:2695–2698.9. Thomsen S, Falstie-Jensen S. Rupture of the flexor pollicis longus tendon associated with an ununited fracture of the scaphoid. J Hand Surg Am. 1988. 13:220–222.
Article10. Yim SJ, Jeong YC, Yoon SR, Choi JG, Suh YS, Rah SK. Delayed rupture of the extensor pollicis longus due to fracture of the distal radius: a case report. J Korean Soc Fract. 1999. 12:162–165.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Rupture of the Extensor Pollicis Longus after Fracture of the Distal end of the Radius: Report of 3 cases
- Delayed Rupture of the Extensor Pollicis Longus due to Fracture of the distal radius: A Case Report
- Acute Rupture of Flexor Tendons as a Complication of Distal Radius Fracture
- Delayed Rupture of Flexor Pollicis Longus after Volar Plating for a Distal Radius Fracture
- Rupture of the Extensor Pollicis Longus Tendon at the Proximal Screw of Volar Plate Fixation for Distal Radius Fracture: A Case Report