J Clin Neurol.
2015 Jan;11(1):104-105. 10.3988/jcn.2015.11.1.104.
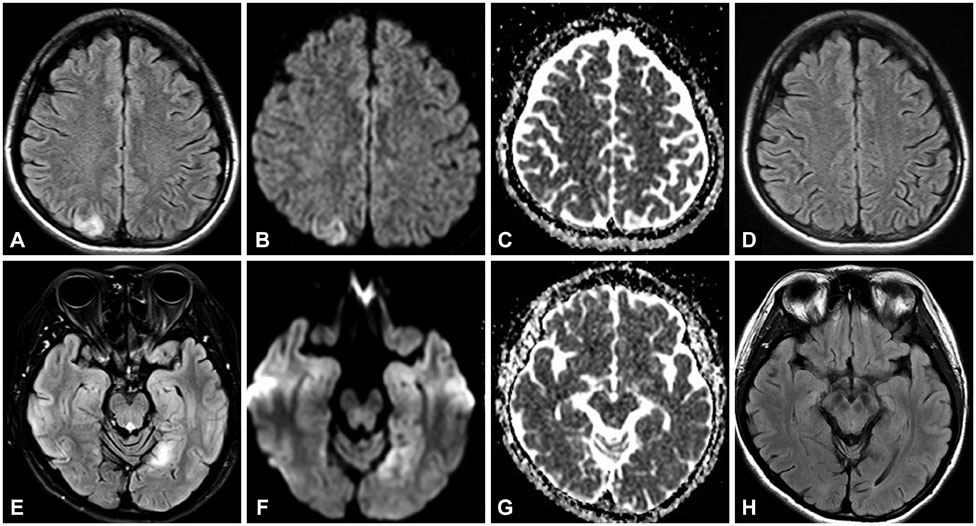
Mitochondrial Encephalopathy, Lactic Acidosis, and Stroke-Like Episode Syndrome Presenting with Prolonged Visual Aura
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. drdongwkim@gmail.com
- KMID: 2179582
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2015.11.1.104
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bindoff LA, Engelsen BA. Mitochondrial diseases and epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2012; 53:Suppl 4. 92–97.
Article2. Zeviani M, Di Donato S. Mitochondrial disorders. Brain. 2004; 127(Pt 10):2153–2172.
Article3. Loder E, Cardona L. Evaluation for secondary causes of headache: the role of blood and urine testing. Headache. 2011; 51:338–345.
Article4. Tzoulis C, Bindoff LA. Serial diffusion imaging in a case of mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes. Stroke. 2009; 40:e15–e17.
Article5. Renard D, Taieb G. Neurological picture. Cortical susceptibility-weighted imaging hypointensity after stroke-like episode in MELAS. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2014; 85:1055–1056.
Article6. Sproule DM, Kaufmann P. Mitochondrial encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and strokelike episodes: basic concepts, clinical phenotype, and therapeutic management of MELAS syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008; 1142:133–158.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome in a Patient With Mitochondrial Encephalopathy, Lactic Acidosis and Stroke-Like Episodes Syndrome
- Status Epilepticus as the Initial Manifestation of Mitochondrial Myopathy, Encephalopathy, Lactic Acidosis, and Stroke-Like Episodes Syndrome
- Vascular Hyperemia and Crossed Cerebellar Diaschisis in MELAS Patient Presented as Stroke-Like Episode and Seizure
- A Case of MELAS Syndrome Diagnosed in a Woman in Her 50s
- A Case of Myopathy, Encephalopathy, Lactic Acidosis and Stroke-Like Episodes (MEALS) Syndrome with Intracardiac Thrombus