J Clin Neurol.
2014 Jul;10(3):222-228. 10.3988/jcn.2014.10.3.222.
Distribution of Cerebral Microbleeds Determines Their Association with Impaired Kidney Function
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jhheo@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Neurology, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurology, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea.
- 4Department of Biostatistics, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2179449
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2014.10.3.222
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
Cerebral microbleeds (CMBs) are associated with various pathologies of the cerebral small vessels according to their distribution (i.e., cerebral amyloid angiopathy or hypertensive angiopathy). We investigated the association between CMB location and kidney function in acute ischemic stroke patients.
METHODS
We enrolled 1669 consecutive patients with acute ischemic stroke who underwent gradient-recalled echo brain magnetic resonance imaging. Kidney function was determined using the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). CMBs were classified into strictly lobar, strictly nonlobar (i.e., only deep or infratentorial), and a combination of both lobar and nonlobar. Multinomial logistic regression analyses were used to determine the factors associated with the existence of CMBs according to their location.
RESULTS
The patients were aged 66+/-12 years (mean+/-standard deviation), and 61.9% (1033/1669) of them were male. CMBs were found in 27.0% (452/1669) of the patients. The stroke subtypes of small-artery occlusion and cardioembolism occurred more frequently in those with strictly nonlobar CMBs (10.8%) and strictly lobar CMBs (48.8%), respectively. The mean eGFR was lower in the strictly nonlobar CMBs group (72+/-28 mL/min/1.73 m2) and the both lobar and nonlobar CMBs group (72+/-25 mL/min/1.73 m2) than in the no-CMBs group (86+/-29 mL/min/1.73 m2). Multivariate multinomial logistic regression revealed that eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2 was independently related to strictly nonlobar CMBs (odds ratio=2.63, p=0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
Impaired kidney function is associated with strictly nonlobar CMBs. Our findings indicate that the distribution of CMBs should be considered when evaluating their relationships or prognoses.
MeSH Terms
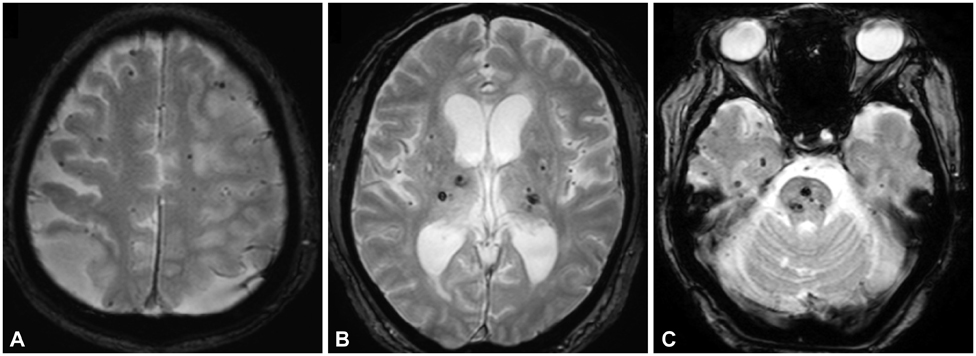
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
The Effect of Pulsatility Index on Infarct Volume in Acute Lacunar Stroke
Yoon Kim, Hanbin Lee, Se-A An, Byeongsoo Yim, Jonguk Kim, Ok Joon Kim, Won Chan Kim, Hyun Sook Kim, Seung Hun Oh, Jinkwon Kim
Yonsei Med J. 2016;57(4):950-955. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.4.950.Characteristics for Ischemic Stroke in 18–30 Years Old Patients, Multicenter Stroke Registry Study
Yoonkyung Chang, Tae-Jin Song, Young-Jae Kim, Ji Hoe Heo, Kyung-Yul Lee, Young Eun Kim, Min Uk Jang, Soo-Jin Cho, Suk Yun Kang
Ewha Med J. 2017;40(3):128-135. doi: 10.12771/emj.2017.40.3.128.
Reference
-
1. Greenberg SM, Vernooij MW, Cordonnier C, Viswanathan A, Al-Shahi Salman R, Warach S, et al. Cerebral microbleeds: a guide to detection and interpretation. Lancet Neurol. 2009; 8:165–174.
Article2. Fazekas F, Kleinert R, Roob G, Kleinert G, Kapeller P, Schmidt R, et al. Histopathologic analysis of foci of signal loss on gradient-echo T2*-weighted MR images in patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: evidence of microangiopathy-related microbleeds. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999; 20:637–642.3. Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med. 2004; 351:1296–1305.
Article4. Nakayama M, Metoki H, Terawaki H, Ohkubo T, Kikuya M, Sato T, et al. Kidney dysfunction as a risk factor for first symptomatic stroke events in a general Japanese population--the Ohasama study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2007; 22:1910–1915.
Article5. O'Rourke MF, Safar ME. Relationship between aortic stiffening and microvascular disease in brain and kidney: cause and logic of therapy. Hypertension. 2005; 46:200–204.6. Khatri M, Wright CB, Nickolas TL, Yoshita M, Paik MC, Kranwinkel G, et al. Chronic kidney disease is associated with white matter hyperintensity volume: the Northern Manhattan Study (NOMAS). Stroke. 2007; 38:3121–3126.
Article7. Ryu WS, Lee SH, Kim CK, Kim BJ, Yoon BW. The relation between chronic kidney disease and cerebral microbleeds: difference between patients with and without diabetes. Int J Stroke. 2012; 7:551–557.
Article8. Cho AH, Lee SB, Han SJ, Shon YM, Yang DW, Kim BS. Impaired kidney function and cerebral microbleeds in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Neurology. 2009; 73:1645–1648.
Article9. Shima H, Ishimura E, Naganuma T, Yamazaki T, Kobayashi I, Shidara K, et al. Cerebral microbleeds in predialysis patients with chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010; 25:1554–1559.
Article10. Lee BI, Nam HS, Heo JH, Kim DI. Yonsei Stroke Team. Yonsei Stroke Registry. Analysis of 1,000 patients with acute cerebral infarctions. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2001; 12:145–151.11. Levey AS, Bosch JP, Lewis JB, Greene T, Rogers N, Roth D. Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study Group. A more accurate method to estimate glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine: a new prediction equation. Ann Intern Med. 1999; 130:461–470.
Article12. Adams HP Jr, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, Biller J, Love BB, Gordon DL, et al. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke. 1993; 24:35–41.
Article13. Song TJ, Kim J, Lee HS, Nam CM, Nam HS, Heo JH, et al. The frequency of cerebral microbleeds increases with CHADS(2) scores in stroke patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. Eur J Neurol. 2013; 20:502–508.
Article14. Vernooij MW, van der Lugt A, Ikram MA, Wielopolski PA, Niessen WJ, Hofman A, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of cerebral microbleeds: the Rotterdam Scan Study. Neurology. 2008; 70:1208–1214.
Article15. Knudsen KA, Rosand J, Karluk D, Greenberg SM. Clinical diagnosis of cerebral amyloid angiopathy: validation of the Boston criteria. Neurology. 2001; 56:537–539.
Article16. Fazekas F, Chawluk JB, Alavi A, Hurtig HI, Zimmerman RA. MR signal abnormalites at 1.5 T in Alzheimer's dementia and normal aging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1987; 149:351–356.17. Biffi A, Greenberg SM. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy: a systematic review. J Clin Neurol. 2011; 7:1–9.
Article18. Park JH, Seo SW, Kim C, Kim GH, Noh HJ, Kim ST, et al. Pathogenesis of cerebral microbleeds: In vivo imaging of amyloid and subcortical ischemic small vessel disease in 226 individuals with cognitive impairment. Ann Neurol. 2013; 73:584–593.
Article19. Smith EE. Leukoaraiosis and stroke. Stroke. 2010; 41:10 Suppl. S139–S143.
Article20. Takahashi W, Tsukamoto Y, Takizawa S, Kawada S, Takagi S. Relationship between chronic kidney disease and white matter hyperintensities on magnetic resonance imaging. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2012; 21:18–23.
Article21. Iadecola C, Pelligrino DA, Moskowitz MA, Lassen NA. Nitric oxide synthase inhibition and cerebrovascular regulation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1994; 14:175–192.
Article22. Ito S, Nagasawa T, Abe M, Mori T. Strain vessel hypothesis: a viewpoint for linkage of albuminuria and cerebro-cardiovascular risk. Hypertens Res. 2009; 32:115–121.
Article23. Endemann DH, Schiffrin EL. Endothelial dysfunction. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004; 15:1983–1992.
Article24. Annuk M, Zilmer M, Lind L, Linde T, Fellström B. Oxidative stress and endothelial function in chronic renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001; 12:2747–2752.
Article25. Markus HS, Hunt B, Palmer K, Enzinger C, Schmidt H, Schmidt R. Markers of endothelial and hemostatic activation and progression of cerebral white matter hyperintensities: longitudinal results of the Austrian Stroke Prevention Study. Stroke. 2005; 36:1410–1414.
Article26. Román GC, Erkinjuntti T, Wallin A, Pantoni L, Chui HC. Subcortical ischaemic vascular dementia. Lancet Neurol. 2002; 1:426–436.
Article27. Conijn MM, Hoogduin JM, van der Graaf Y, Hendrikse J, Luijten PR, Geerlings MI. Microbleeds, lacunar infarcts, white matter lesions and cerebrovascular reactivity -- a 7 T study. Neuroimage. 2012; 59:950–956.
Article28. Ovbiagele B, Liebeskind DS, Pineda S, Saver JL. Strong independent correlation of proteinuria with cerebral microbleeds in patients with stroke and transient ischemic attack. Arch Neurol. 2010; 67:45–50.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Characteristics of Cerebral Microbleeds
- Relationship Between Cerebral Microbleeds and Aspirin Use Regarding White Matter Hyperintensity Volume
- Distribution Analysis of Cerebral Microbleeds in Alzheimer's Disease and Cerebral Infarction with Susceptibility Weighted MR Imaging
- Cerebral Microbleed Induced Seizure Misdiagnosed with Transient Ischemic Attack
- Cerebral Small Vessel Disease and Chronic Kidney Disease