J Clin Neurol.
2011 Jun;7(2):53-59. 10.3988/jcn.2011.7.2.53.
Ischemic Stroke and Cancer: Stroke Severely Impacts Cancer Patients, While Cancer Increases the Number of Strokes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. nmboy@unitel.co.kr
- 2Department of Neurology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurology, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Neurology, Yeungnam University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 5Department of Neurology, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Neurology, Chung-Ang University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2178967
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2011.7.2.53
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Cancer and ischemic stroke are two of the most common causes of death among the elderly, and associations between them have been reported. However, the main pathomechanisms of stroke in cancer patients are not well known, and can only be established based on accurate knowledge of the characteristics of cancer-related strokes. We review herein recent studies concerning the clinical, laboratory, and radiological features of patients with cancer-related stroke. MAIN CONTENTS: This review covers the epidemiology, underlying mechanisms, and acute and preventive treatments for cancer-related stroke. First, the characteristics of stroke (clinical and radiological features) and systemic cancer (type and extent) in patients with cancer-specific stroke are discussed. Second, the role of laboratory tests in the early identification of patients with cancer-specific stroke is discussed. Specifically, serum D-dimer levels (as a marker of a hypercoagulable state) and embolic signals on transcranial Doppler (suggestive of embolic origin) may provide clues regarding changes in the levels of coagulopathy related to cancer and anticoagulation. Finally, strategies for stroke treatment in cancer patients are discussed, emphasizing the importance of preventive strategies (i.e., the use of anticoagulants) over acute revascularization therapy in cancer-related stroke.
CONCLUSION
Recent studies have revealed that the characteristics of cancer-related stroke are distinct from those of conventional stroke. Our understanding of the characteristics of cancer-related stroke is essential to the correct management of these patients. The studies presented in this review highlight the importance of a personalized approach in treating stroke patients with cancer.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Massive Extra-Ischemic Hemorrhage after Intravenous Thrombolysis in a Patient with Malignancy
Sung-Joo Park, Jung-Hwan Oh
J Neurocrit Care. 2017;10(2):140-142. doi: 10.18700/jnc.170028.Multiple embolic infarctions and intracranial hemorrhage in a patient with gestational trophoblastic disease
Kyong Young Kim, Seunguk Jung, Changhyo Yoon, Heejeong Jeong, Eun Bin Cho, Tae-Won Yang, Seung Joo Kim, Sean Hwang, Ki-Jong Park
J Neurocrit Care. 2020;13(2):123-127. doi: 10.18700/jnc.200012.
Reference
-
1. Graus F, Rogers LR, Posner JB. Cerebrovascular complications in patients with cancer. Medicine (Baltimore). 1985. 64:16–35.
Article2. Bick RL. Cancer-associated thrombosis. N Engl J Med. 2003. 349:109–111.
Article3. Rogers LR. Cerebrovascular complications in patients with cancer. Semin Neurol. 2004. 24:453–460.
Article4. Grisold W, Oberndorfer S, Struhal W. Stroke and cancer: a review. Acta Neurol Scand. 2009. 119:1–16.
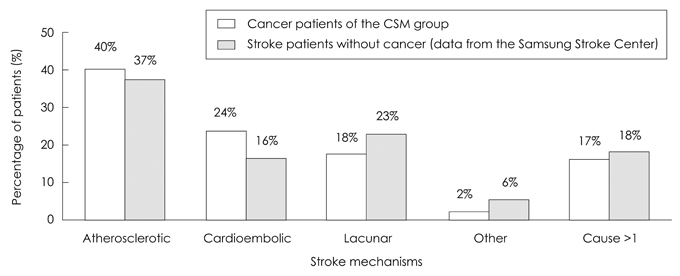
Article5. Kim SG, Hong JM, Kim HY, Lee J, Chung PW, Park KY, et al. Ischemic stroke in cancer patients with and without conventional mechanisms: a multicenter study in Korea. Stroke. 2010. 41:798–801.
Article6. Chaturvedi S, Ansell J, Recht L. Should cerebral ischemic events in cancer patients be considered a manifestation of hypercoagulability? Stroke. 1994. 25:1215–1218.
Article7. Zhang YY, Chan DK, Cordato D, Shen Q, Sheng AZ. Stroke risk factor, pattern and outcome in patients with cancer. Acta Neurol Scand. 2006. 114:378–383.
Article8. Zhang YY, Cordato D, Shen Q, Sheng AZ, Hung WT, Chan DK. Risk factor, pattern, etiology and outcome in ischemic stroke patients with cancer: a nested case-control study. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2007. 23:181–187.
Article9. Cestari DM, Weine DM, Panageas KS, Segal AZ, DeAngelis LM. Stroke in patients with cancer: incidence and etiology. Neurology. 2004. 62:2025–2030.
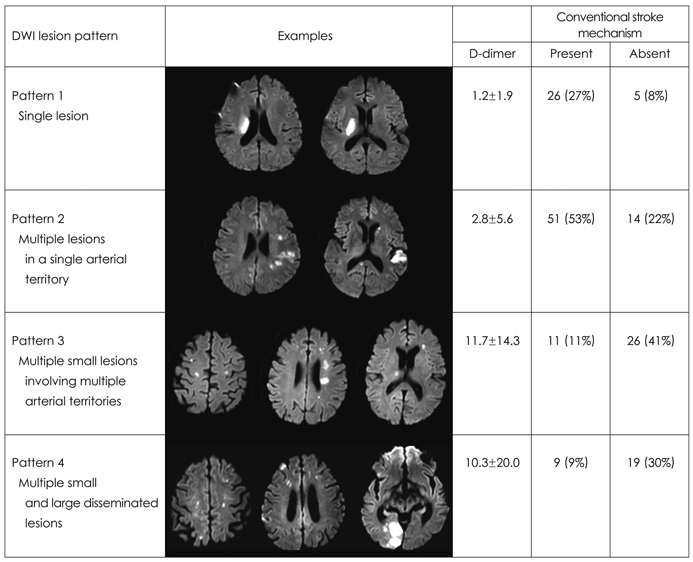
Article10. Baird AE, Lövblad KO, Schlaug G, Edelman RR, Warach S. Multiple acute stroke syndrome: marker of embolic disease? Neurology. 2000. 54:674–678.
Article11. Bang OY, Lee PH, Heo KG, Joo US, Yoon SR, Kim SY. Specific DWI lesion patterns predict prognosis after acute ischaemic stroke within the MCA territory. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2005. 76:1222–1228.
Article12. Kwon HM, Kang BS, Yoon BW. Stroke as the first manifestation of concealed cancer. J Neurol Sci. 2007. 258:80–83.
Article13. ten Wolde M, Kraaijenhagen RA, Prins MH, Büller HR. The clinical usefulness of D-dimer testing in cancer patients with suspected deep venous thrombosis. Arch Intern Med. 2002. 162:1880–1884.
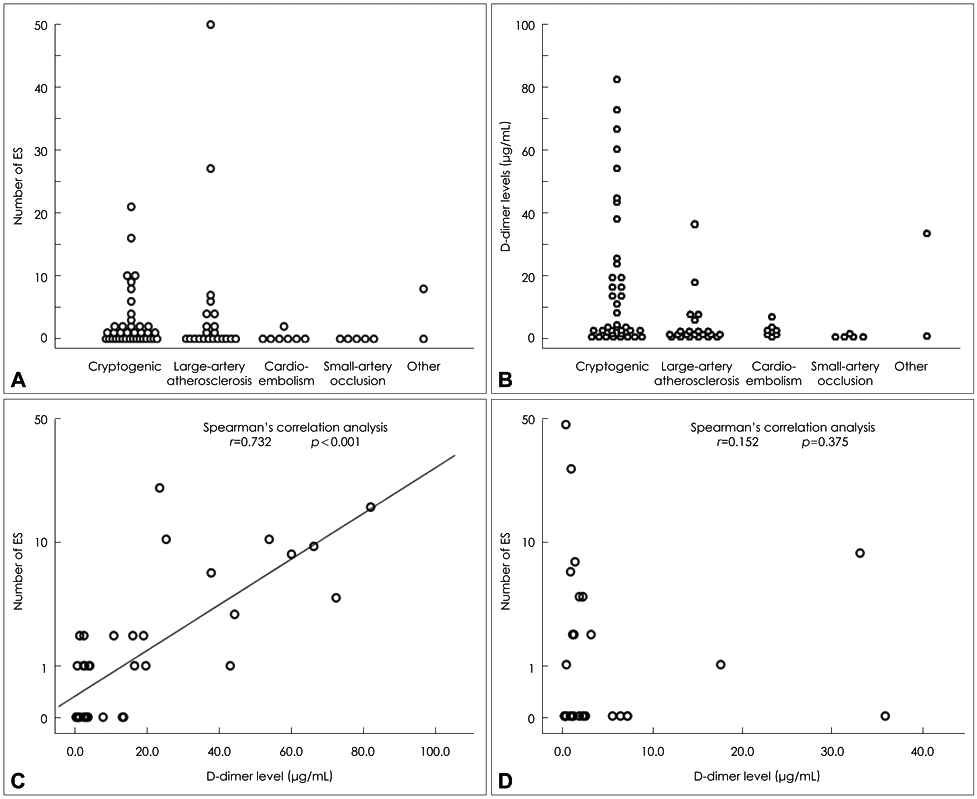
Article14. Seok JM, Kim SG, Kim JW, Chung CS, Kim GM, Lee KH, et al. Coagulopathy and embolic signal in cancer patients with ischemic stroke. Ann Neurol. 2010. 68:213–219.15. Dirix LY, Salgado R, Weytjens R, Colpaert C, Benoy I, Huget P, et al. Plasma fibrin D-dimer levels correlate with tumour volume, progression rate and survival in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2002. 86:389–395.
Article16. Buccheri G, Torchio P, Ferrigno D. Plasma levels of D-dimer in lung carcinoma: clinical and prognostic significance. Cancer. 2003. 97:3044–3052.17. Blackwell K, Hurwitz H, Liebérman G, Novotny W, Snyder S, Dewhirst M, et al. Circulating D-dimer levels are better predictors of overall survival and disease progression than carcinoembryonic antigen levels in patients with metastatic colorectal carcinoma. Cancer. 2004. 101:77–82.
Article18. Poppert H, Sadikovic S, Sander K, Wolf O, Sander D. Embolic signals in unselected stroke patients: prevalence and diagnostic benefit. Stroke. 2006. 37:2039–2043.19. Singhal AB, Topcuoglu MA, Buonanno FS. Acute ischemic stroke patterns in infective and nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis: a diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging study. Stroke. 2002. 33:1267–1273.
Article20. Rickles FR, Patierno S, Fernandez PM. Tissue factor, thrombin, and cancer. Chest. 2003. 124:58S–68S.
Article21. Li SH, Chen WH, Tang Y, Rau KM, Chen YY, Huang TL, et al. Incidence of ischemic stroke post-chemotherapy: a retrospective review of 10,963 patients. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2006. 108:150–156.
Article22. Ratajczak J, Wysoczynski M, Hayek F, Janowska-Wieczorek A, Ratajczak MZ. Membrane-derived microvesicles: important and underappreciated mediators of cell-to-cell communication. Leukemia. 2006. 20:1487–1495.
Article23. Mostefai HA, Andriantsitohaina R, Martínez MC. Plasma membrane microparticles in angiogenesis: role in ischemic diseases and in cancer. Physiol Res. 2008. 57:311–320.
Article24. Yu JL, May L, Lhotak V, Shahrzad S, Shirasawa S, Weitz JI, et al. Oncogenic events regulate tissue factor expression in colorectal cancer cells: implications for tumor progression and angiogenesis. Blood. 2005. 105:1734–1741.
Article25. Hron G, Kollars M, Weber H, Sagaster V, Quehenberger P, Eichinger S, et al. Tissue factor-positive microparticles: cellular origin and association with coagulation activation in patients with colorectal cancer. Thromb Haemost. 2007. 97:119–123.
Article26. Yu JL, Rak JW. Shedding of tissue factor (TF)-containing microparticles rather than alternatively spliced TF is the main source of TF activity released from human cancer cells. J Thromb Haemost. 2004. 2:2065–2067.
Article27. Bang OY. Multimodal MRI for ischemic stroke: from acute therapy to preventive strategies. J Clin Neurol. 2009. 5:107–119.
Article28. Albers GW, Thijs VN, Wechsler L, Kemp S, Schlaug G, Skalabrin E, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging profiles predict clinical response to early reperfusion: the diffusion and perfusion imaging evaluation for understanding stroke evolution (DEFUSE) study. Ann Neurol. 2006. 60:508–517.
Article29. Varki A. Trousseau's syndrome: multiple definitions and multiple mechanisms. Blood. 2007. 110:1723–1729.
Article30. Sousou T, Khorana AA. New insights into cancer-associated thrombosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2009. 29:316–320.
Article31. Carrier M, Lee AY. Prophylactic and therapeutic anticoagulation for thrombosis: major issues in oncology. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 2009. 6:74–84.
Article32. Lee AY, Levine MN, Baker RI, Bowden C, Kakkar AK, Prins M, et al. Low-molecular-weight heparin versus a coumarin for the prevention of recurrent venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003. 349:146–153.
Article33. Agnelli G, Gussoni G, Bianchini C, Verso M, Mandalá M, Cavanna L, et al. Nadroparin for the prevention of thromboembolic events in ambulatory patients with metastatic or locally advanced solid cancer receiving chemotherapy: a randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Lancet Oncol. 2009. 10:943–949.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Risk Factors and Biomarkers of Ischemic Stroke in Cancer Patients
- Cancer-Related Stroke: An Emerging Subtype of Ischemic Stroke with Unique Pathomechanisms
- Acute Ischemic Stroke in a Patient with Metastatic Gastric Cancer after Ramucirumab Chemotherapy
- Causes and Types of Childhood Strokes
- Epidemiology and Characteristics of Recurrent Stroke: The Occurrence Type of Restroke is Similar as Previous Stroke