J Cardiovasc Ultrasound.
2014 Jun;22(2):95-97. 10.4250/jcu.2014.22.2.95.
Efficacy of Inhaled Iloprost in Cor Pulmonale and Severe Pulmonary Hypertension Associated with Tuberculous Destroyed Lung
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Heart Center, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea. heart@gilhospital.com
- 2Gachon Cardiovascular Research Institute, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea.
- 3Division of Pulmonology, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea.
- 4Department of Pediatric Cardiology, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea.
- 5Division of Rheumatology, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2177470
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4250/jcu.2014.22.2.95
Abstract
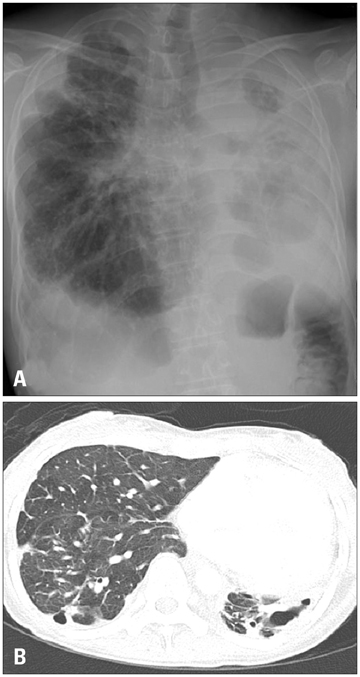
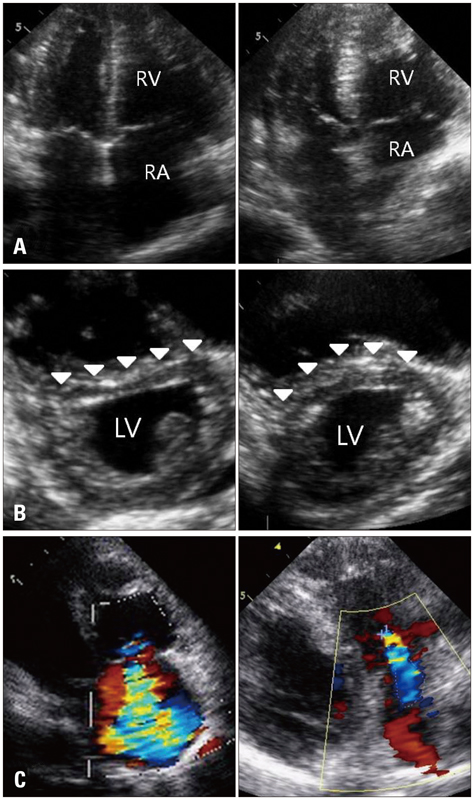
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is one of the causes of cor pulmonale. Cor pulmonale patients with pulmonary hypertension have a significant lower survival rate than patients without. However, there is no conclusive treatment options in cor pulmonale and pulmonary hypertension associated with COPD until now. We report a patient with cor pulmonale and pulmonary hypertension associated with severe form of COPD and tuberculous destroyed lung who achieved marked clinical, functional and echocardiographic hemodynamic improvements with inhaled iloprost for six months.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Oswald-Mammosser M, Weitzenblum E, Quoix E, Moser G, Chaouat A, Charpentier C, Kessler R. Prognostic factors in COPD patients receiving long-term oxygen therapy. Importance of pulmonary artery pressure. Chest. 1995; 107:1193–1198.
Article2. Hoeper MM, Schwarze M, Ehlerding S, Adler-Schuermeyer A, Spiekerkoetter E, Niedermeyer J, Hamm M, Fabel H. Long-term treatment of primary pulmonary hypertension with aerosolized iloprost, a prostacyclin analogue. N Engl J Med. 2000; 342:1866–1870.
Article3. Opitz CF, Wensel R, Winkler J, Halank M, Bruch L, Kleber FX, Höffken G, Anker SD, Negassa A, Felix SB, Hetzer R, Ewert R. Clinical efficacy and survival with first-line inhaled iloprost therapy in patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur Heart J. 2005; 26:1895–1902.
Article4. Boeck L, Tamm M, Grendelmeier P, Stolz D. Acute effects of aerosolized iloprost in COPD related pulmonary hypertension - a randomized controlled crossover trial. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e52248.
Article5. Hegewald MJ, Elliott CG. Sustained improvement with iloprost in a COPD patient with severe pulmonary hypertension. Chest. 2009; 135:536–537.
Article6. Barberà JA, Blanco I. Pulmonary hypertension in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: advances in pathophysiology and management. Drugs. 2009; 69:1153–1171.
Article7. Dernaika TA, Beavin M, Kinasewitz GT. Iloprost improves gas exchange and exercise tolerance in patients with pulmonary hypertension and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respiration. 2010; 79:377–382.
Article8. Wilkens H, Bauer M, Forestier N, König J, Eichler A, Schneider S, Schäfers HJ, Sybrecht GW. Influence of inhaled iloprost on transpulmonary gradient of big endothelin in patients with pulmonary hypertension. Circulation. 2003; 107:1509–1513.
Article9. Opitz CF, Wensel R, Bettmann M, Schaffarczyk R, Linscheid M, Hetzer R, Ewert R. Assessment of the vasodilator response in primary pulmonary hypertension. Comparing prostacyclin and iloprost administered by either infusion or inhalation. Eur Heart J. 2003; 24:356–365.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Therapeutic Effect of Inhaled Iloprost in Newborn Infants with Severe Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension Refractory to Inhaled Nitric Oxide
- A case of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn: Treatment with inhaled iloprost
- Echocardiographic Evaluation of Right Ventricular Diastolic Function in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension is Normalized Following Six Years of Inhaled Iloprost Treatment in a Patient with Systemic Sclerosis
- Use of Inhaled Iloprost in an Infant With Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Pulmonary Artery Hypertension